|
fenoxanil
Fungicide
FRAC 16.2, I2; MBI: dehydratase
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenoxanil (BSI, pa ISO)
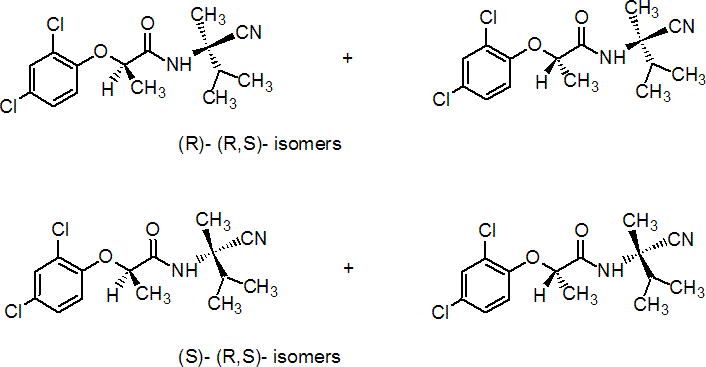
IUPAC name a mixture of 85% (R)-N-[(RS)-1-cyano-1,2-dimethylpropyl]-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propionamide and 15% (S)-N-[(RS)-1-cyano-1,2-dimethylpropyl]-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propionamide
Chemical Abstracts name N-(1-cyano-1,2-dimethylpropyl)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propanamide
CAS RN [115852-48-7] Development codes AC 382042; CL 382042; AC 901216 (all Cyanamid); WL 378309 (Shell); NNF-9425 (Nihon Nohyaku); BAS 546 F (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition A mixture of (R,R) and (R,S) diastereoisomers as major components, and (S,R and S,S) diastereoisomers as minor components. Mol. wt. 329.2 M.f. C15H18Cl2N2O2 Form Off-white, odourless solid. M.p. 69.0-72.5 °C V.p. 0.21?.021 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 3.53?.02 (25 °C) S.g./density 1.22 (20 °C) Solubility In water 30.7?.3 ´ 10-3 g/l (20 °C). Soluble in most organic solvents. Stability Essentially stable within the relevant pH range. F.p. 420 °C (OPPTS 830.6315)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered by Shell GmbH and acquired by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG). Reported by E. Sieverding et al., (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1998, 2, 359). Developed jointly by BASF and Nihon Nohyaku Co., Ltd. Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Melanin biosynthesis inhibitor. Inhibits dehydratase enzymes which dehydrate scytalone to trihydroxynaphthalene and vermelone to dihydroxynaphthalene. Mode of action Systemic, protective fungicide with residual effects. Uses Controls rice blast by foliar or into-water application, at 120-150 g/ha and 2.4-2.7 kg/ha respectively. Formulation types DL; GR; SC. Selected products: 'Achi-Bu' (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Achieve DL' (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Byochonguk' (BASF); 'Helmet' (BASF); 'Stopper' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Achieve Moncut F' (+ flutolanil) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Achieve Moncut Trebon' (+ flutolanil+ etofenprox) (Nihon Nohyaku)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by chiral hplc (Cyanamid method No. M-3446). Residues in rice grain and straw, by glc with NPD detection (Nihon Nohyaku unpublished report DE-49-97-0021); in soil, by hplc (Nihon Nohyaku unpublished report LSRC-R97-148A).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats >5000, female rats 4211, male and female mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats >5.18 mg/l. NOEL NOAEL (1 y) for dogs 1 mg/kg; (2 y) for male rats 0.698 mg/kg, female rats 0.857 mg/kg, non-carcinogenic; (18 month) for male mice 6.98 mg/kg, female mice 6.648 mg/kg, (hepatocellular carcinoma at 500 ppm dose group); (2 generation) for male rats 1.124 mg/kg, female rats 1.74 mg/kg, (no effect on reproduction); teratology for rats 50 mg/kg (parent), 250 mg/kg (foetus), for rabbits 10 mg/kg (parent), 200 mg/kg (foetus). ADI 0.0069 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-mutagenic in Ames, DNA repair, chromosome aberration and mouse micronucleus tests. Non-teratogenic.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds NOEL for quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) 5.90, asian pond loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) 12.3 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 6.0 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >7.0 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for Minaminuma shrimp (Neocaridina denticulate) 7.9, crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) >100, Numa frog tadpoles (Rana limnocharis) 8.54 mg/l; LC50 (120 h) for Shijimi clam (Corbicula learna) 8.16, Japanese littleneck (Tapes philippinarum) 1.78 mg/l. Worms LC50 (14 d) 71 mg/kg of soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, orally administered fenoxanil is readily adsorbed, distributed, and extensively metabolised through hydroxylation, hydrolysis and, following conjugation, excreted into faeces and urine. Plants In rice, the primary residue recovered from grain, hull and straw is parent compound. Fenoxanil that is metabolised is transformed by hydration of the amide moiety, hydroxylation of the isopropyl moiety and phenyl ring, and amide hydrolysis. The metabolite produced through hydroxylation of the phenyl ring is partially further metabolised through glucose conjugation. Soil/Environment In the laboratory, DT50 in clay loam and sandy clay loam soils 117 and 84 d respy. In field studies, soil DT50 4 d to <1 d. Koc 454-697; Kd 370. Hydrolytically stable at all pH values, and <50 °C. Aqueous photolysis DT50 41 d in natural water.
|