|
fenobucarb
Insecticide
IRAC 1A; carbamate
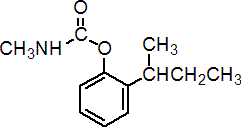
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenobucarb (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO); BPMC (JMAF, Thailand)
IUPAC name 2-sec-butylphenyl methylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name 2-(1-methylpropyl)phenyl methylcarbamate
CAS RN [3766-81-2] EEC no. 223-188-8 Development codes Bayer 41 367c Official codes OMS 313
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is >97%. Mol. wt. 207.3 M.f. C12H17NO2 Form Colourless solid; (tech., colourless to yellow-brown liquid or solid). M.p. 31-32 ºC; (tech., 26.5-31 ºC) B.p. 112-113 ºC/0.02 mmHg V.p. 13 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 2.79 Henry 6.4 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.035 at 30 ºC Solubility In water 420 mg/l (20 ºC), 610 mg/l (30 ºC). In acetone, benzene, chloroform, xylene, toluene >1 (all in kg/kg, room temperature). Stability Stable under normal storage conditions. Stable to light. Hydrolysed by acids and alkalis; (20 ºC) DT50 >28 d (buffer at pH 2), 16.9 d (pH 9), 2.06 d (pH 10). F.p. 142 °C (closed system)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by R. L. Metcalf et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1962, 55, 889). Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd, by Kumiai Chemical Industry Co., Ltd and Mitsubishi Chemical Industries (now Mitsubishi Chemical Corp., who sold their agrochemical business to Nihon Nohyaku Co., Ltd in 2002) jointly, and by Bayer AG (who no longer manufacture or market it); registered in Japan and first marketed in 1968. Manufacturers Hunan Linxiang; Jin Hung; Kuo Ching; Sinon; Sumitomo; Sundat; Taiwan Tainan Giant
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact action. Uses Control of leafhoppers, planthoppers, thrips, and weevils on rice, tea, sugar cane, wheat, cucurbits, aubergines, and capsicums. Control of bollworms and aphids on cotton, at 0.5-1.0 kg/ha; control of leafhoppers, at 0.6-1.2 kg/ha. Formulation types DP; EC; UL. Selected products: 'Osbac' (Sumitomo); 'Merlin' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Vibasa' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Bassa' (Nihon Nohyaku, Kumiai); 'Baycarb' (Bayer CropScience); 'Bipex' (Excel) mixtures: 'Kasu-rab-sumibassa' (+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate+ phthalide+ fenitrothion) (Hokko); 'Mitecidin' (+ polynactins) (Eiko Kasei); 'Vibaba' (+ diazinon) (Vipesco); 'Vibam' (+ dimethoate) (Vipesco); 'Viphensa' (+ phenthoate) (Vipesco)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by u.v. spectrometry of a derivative or by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 86). Details available from Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 623, female rats 657 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 10 250 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.366 mg tech./l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 4.1 mg/kg b.w. daily (100 mg/kg diet). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 323 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks >5500, bobwhite quail 5417 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 16 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) 0.32 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals 2-(2-Hydroxy-1-methylpropyl)-phenyl N-methylcarbamate is a metabolite. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants As for animals. Soil/Environment Soil Kom 125 (Utsunomia soil, 5.2% o.m.), 661 (Niigata soil, 1.8% o.m.); DT50 6-30 d and 6-14 d under paddy and upland conditions, respectively.
|