|
fenhexamid
Fungicide
FRAC 17, G3; hydroxyanilide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenhexamid (BSI, pa ISO)
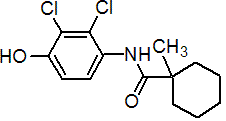
IUPAC name 2',3'-dichloro-4'-hydroxy-1-methylcyclohexanecarboxanilide
Chemical Abstracts name N-(2,3-dichloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylcyclohexanecarboxamide
CAS RN [126833-17-8] Development codes KBR 2738 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition >95% pure. Mol. wt. 302.2 M.f. C14H17Cl2NO2 Form White powder. M.p. 153 °C B.p. 320 °C (extrapolated) V.p. 4 ´ 10-4 mPa (20 °C, extrapolated) KOW logP = 3.51 (pH 7, 20 °C) Henry 5 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (pH 7, 20 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.34 (20 °C) Solubility In water 20 mg/l (pH 5-7, 20 °C). In dichloromethane 31, isopropanol 91, acetonitrile 15, toluene 5.7, n-hexane <0.1 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis for 30 d at pH 5, 7, 9 (25 °C).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered by Bayer AG in 1989. Reported by H-J. Rosslenbroich et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1998, 2, 327). First marketed in 1998. Patents EP 339418 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Biochemical target is sterol biosynthesis (SBI class III), acting on 3-keto-reductase during C4-demethylation, displaying a low to moderate risk for resistance development. Inhibits germ tube elongation and mycelium growth. Mode of action Foliar fungicide with protectant action; not translocated. Uses For control of Botrytis cinerea, Monilia spp. and related pathogens in grapes, berries, stone fruit, citrus, vegetables and ornamentals, at 500-1000 g/ha. Formulation types SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Decree' (in co-operation with Bayer) (Arvesta); 'Elevate' (in co-operation with Bayer) (Arvesta); 'Password' (Nihon Bayer); 'Teldor' (Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Talat' (+ tolylfluanid) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Dyemazine' (+ iminoctadine tris(albesilate)) (Japan) (Bayer CropScience); 'Justeet' (+ fludioxonil) (Japan) (Bayer CropScience); 'Young-gune' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, Korea) (Kyung Nong)
ANALYSIS
Method for determination in plant material by lc described by F. Nuesslein, Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. Bayer, 1999, 52, 2.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5057 mg/m3 air (dust) NOEL (24 mo) for rats 500, mice 800 mg/kg diet; (12 mo) for dogs 500 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.183 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-teratogenic, non-carcinogenic, non-mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard duck >5000 ppm of feed. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.34, bluegill sunfish 3.42 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >18.8 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 8.81 mg/l. ErC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus >26.1 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. NOEC (28 d) for Chironomus riparius 100 mg/l; EC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 2.3 mg/l. Bees LC50 (oral and contact) >200 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (2 w) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg dry soil. Other beneficial spp. Not toxic to predatory mites (Typhlodromus pyri), rove beetles (Aleochara bilineata), ladybirds (Coccinella septempunctata) and parasitoids (Aphidius rhopalosiphi), at 2 kg/ha. No adverse effect on microbial mineralisation.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
All data indicate that there is no danger to the consumer from fenhexamid residues. Animals In rats, rapidly absorbed and eliminated without accumulation within 48 h. The major elimination followed the faecal route (61%), whereas renal excretion accounted for 15-36% of the total administered dose. Plants The metabolic pathway is similar in all crops; in all plant samples, the unchanged active ingredient was identified as the largest single constituent. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil £1 d (4 soils, 20 °C). Studies and calculation show that the compound can be classified as having no, or only low, leaching potential; no problems of groundwater contamination will be expected. In sterile aquatic systems, fenhexamid was stable to hydrolysis. In natural water/sediment systems, fenhexamid degrades rapidly and completely, ultimately forming CO2; overall DT50 (calc.) was a few days (C. Anderson, et al., Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. Bayer, 1999,52, 2).
|