|
fenbuconazole
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenbuconazole (BSI, draft E-ISO, ANSI)
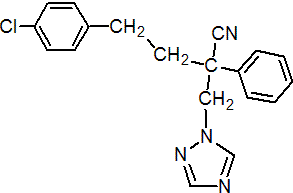
IUPAC name 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-phenyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)butyronitrile
Chemical Abstracts name a-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-a-phenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-propanenitrile
CAS RN [114369-43-6] unstated stereochemistry Development codes RH-7592; RH-57592 (both Rohm & Haas)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 336.8 M.f. C19H17ClN4 Form Off-white solid with a faint sulfur-like odour. M.p. 126.5-127 °C B.p. unstable above 300 °C V.p. 3.4 ´ 10-1 mPa (25 °C, vapour pressure balance) KOW logP = 3.23 (25 °C) Henry 3.01 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.27 (20 °C) Solubility In water 3.8 mg/l (25 °C). In acetone and 1,2-dichloroethane >250, ethyl acetate 132, methanol 60.9, octanol 8.43, xylene 26.0, n-heptane 0.0677 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis in the dark, DT50 >2210 d (pH 5), 3740 d (pH 7), 1370 d (pH 9). Thermostable up to 300 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by D. Briant et al. (Proc. 1988 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1, 33). Introduced by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences) in 1992. Patents US 5087635 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Steroid demethylation inhibitor. Mode of action Penetrant fungicide with residual protectant activity and low translocation in the plant. Uses Initial registration was obtained for control of Septoria species and rusts on cereals (at 75 g/ha). Subsequent registrations have been obtained in Europe for use in vines for control of powdery mildew (Uncinula necator) and black rot (Guignardia bidwellii), in stone fruit for control of powdery mildew and Monilinia spp., and in pome fruit for control of apple scab and powdery mildew (at 30-50 g/ha). In North America, product registration for use on pecans and stone fruit was obtained in 1995. Further global markets include a wide range of diseases on fruits, tree nuts, citrus, bananas, rice and vegetables. Formulation types EC; EW; OD; SC. Selected products: 'Enable' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Indar' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Kruga 5EC' (Interfarm); 'Kruga' (Headland); 'Reward' (Interfarm); 'Surpass 5' (Interfarm) mixtures: 'Karamat' (+ dinocap) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Graphic' (+ propiconazole) (Syngenta); 'Mirage Extra' (+ prochloraz) (PBI, Makhteshim-Agan); 'Myriad' (+ fenpropimorph) (Bayer CropScience); 'Nordika' (+ prochloraz) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Troika' (+ carbendazim) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Reward' * (Headland); 'Surpass' * (Headland); 'Tenere' * (Ciba) mixtures: 'Unison' * (+ tridemorph) (PBI)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by gc. Details from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 80, 82 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (tech.); severe irritant to eyes and skin (EC formulation) (rabbits). No dermal sensitisation (Buehler test). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.1 mg/l air (for tech.). NOEL NOEL for reproductive effects 6.3 mg/kg b.w. daily; NOEL for developmental effects 30 mg/kg b.w. daily. No adverse reproductive or foetal effects have been observed at rates below a maternally toxic dose. NOAEL based on results of chronic feeding, oncogenicity and reproductive studies 3 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1997]. Other Non-mutagenic in a variety of tests. Toxicity class EPA (formulation) II, (tech., III)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 4050, mallard ducks 2110 mg/kg diet. LC50 (21 d) for bobwhite quail 2150 mg/kg daily. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.68 mg/l (tech.), for rainbow trout 1.5 mg/l. Chronic NOEC for rainbow trout 0.33 mg/l. Daphnia Acute EC50 2.2 mg/l; chronic NOEC 0.078 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.47 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. Chronic NOEC to sediment dweller (Chironomus riparius) 1.73 mg/l. Bees LC50 (96 h, dust exposure) >0.29 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 98 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Harmless in laboratory studies on Poecilus cupreus, Chrysoperla carnea, Coccinella septempunctata, and Typhlodromus pyri (IOBC).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Plants In peanuts, degraded by three routes: oxidation at the benzylic carbon, leading to oxidative degradation products including a ketone and some lactones, substitution on the carbon next to the triazole ring, leading to triazolylalanine and triazolylacetic acid (presumably via free triazole), and hydroxylation followed by conjugation at the 3- position of the chlorophenyl ring. Soil/Environment Soil adsorption Koc 2100-9000 (clay, loam, sand, sandy loam, silty clay loam).
|