|
fenarimol
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: pyrimidine
NOMENCLATURE
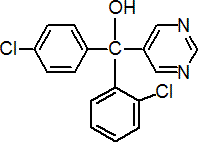
Common name fenarimol (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name (?-2,4'-dichloro-a-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzhydryl alcohol
Chemical Abstracts name (?-a-(2-chlorophenyl)-a-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-pyrimidinemethanol
CAS RN [60168-88-9] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 262-095-7 Development codes EL-222 (Lilly)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 98%. Mol. wt. 331.2 M.f. C17H12Cl2N2O Form Off-white crystals. M.p. 117-119 ºC V.p. 0.065 mPa (25 ºC) by vapour pressure balance KOW logP = 3.69 (pH 7, 25 ºC) Henry 1.57 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.40 Solubility In water 13.7 mg/l (pH 7, 25 ºC). In acetone 151, methanol 98.0, xylene 33.3 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Readily soluble in most organic solvents, but only slightly soluble in hexane. Stability Decomposed rapidly by sunlight, aqueous DT50 c. 12 h. Hydrolytically stable up to ³52 ºC (pH 3-9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by I. F. Brown et al. (Proc. Am. Phytopathol. Soc., 1975, 2, 31). Introduced in Lebanon (1977) by Eli Lilly & Co. (agrochemical interests now Dow AgroSciences). Rights sold to Margarita Internacional in 2002. Patents GB 1218623 Manufacturers Margarita
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitor (demethylation inhibitor). Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective, curative, and eradicant action. Translocated acropetally within the plant. Uses Control of powdery mildews in pome fruit, stone fruit, vines, roses and other ornamentals; scab on pome fruit; dollar spot, brown patch and snow mould of turf. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as directed. If used in excessive amounts, abnormal leaf development and darker green colouration may result. Formulation types EC; SC; WP. Selected products: 'Rubigan' (Gowan, Margarita); 'Rimidin' (Margarita)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Porter' (+ quinoxyfen) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sonic' (+ quinoxyfen) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trisave' (+ quinoxyfen) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Vento' (+ quinoxyfen) (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Bloc' * (DowElanco)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (E. W. Day & O. D. Decker, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 173). Residues in soil and plant tissue determined by glc with ECD (idem, ibid.). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07). Details available from Gowan Co.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 74, 76 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2500, mice 4500, dogs >200 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation No adverse effect seen when rats exposed for 1 h to 2.04 mg tech./l air. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats receiving 25 mg/kg diet and mice receiving 600 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1995] (environmental assessment also performed). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification R62, R63| R64| N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 4.1, bluegill sunfish 5.7 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 5.1 mg/l, NOEC 4.0 mg/l. Algae For Scenedesmus subspicatus ErC50 5.1 mg/l, NOEC 0.59 mg/l; for Raphidocellis subcapitata ErC50 1.5 mg/l, NOEC 0.59 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h) (oral) >10 mg/bee; (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms Not toxic to earthworms. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to Typhlodromus pyri, Aphidius rhopalosiphi, Poecilus cupreus and Chrysoperla carnea.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, fenarimol is rapidly excreted. Plants Forms numerous photodegradation products. Soil/Environment DT50 >365 d under aerobic conditions in laboratory soil (28% sand, 14.7% clay, 57.3% silt, 2.3% o.m., pH 6.1). Field DT50 14-130 (average 79) d. Koc 500-992 (average 734) l/kg, Kd 1.5-11.9 (average 6.7) l/kg, depending on soil type. Hydrolytically stable, but undergoes rapid photolysis, DT50 4-12 h.
|