|
fenamidone
Fungicide
FRAC 11, C3; strobilurin type: imidazolinone
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenamidone (BSI, pa ISO (not Japan))
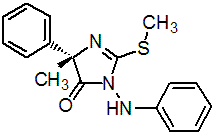
IUPAC name (S)-1-anilino-4-methyl-2-methylthio-4-phenylimidazolin-5-one
Chemical Abstracts name (S)-3,5-dihydro-5-methyl-2-(methylthio)-5-phenyl-3-(phenylamino)-4H-imidazol-4-one
CAS RN [161326-34-7] Development codes RPA 407213 ((S)- enantiomer, Rhône-Poulenc)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 311.4 M.f. C17H17N3OS Form White woolly powder, with no characteristic odour. M.p. 137 °C V.p. 3.4 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 2.8 (20 °C) S.g./density 1.285 Solubility In water 7.8 mg/l (20 °C). In acetone 250, acetonitrile 86.1, dichloromethane 330, methanol 43, n-octanol 9.7 (mg/l, 20 °C). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 (sterile conditions) 41.7 d (pH 4), 411 d (pH 7), 27.6 d (pH 9); phototransformation DT50 5 d. Other properties Surface tension 72.9 mN m-1 (20 °C).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by R. T. Mercer et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1998, 2, 319). Discovered by Rhône-Poulenc Agro and developed by Aventis; now owned and distributed by Bayer CropScience. First registration and launch in 2001. Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits mitochondrial respiration by blocking electron transport at ubihydroquinone: cytochrome c oxidoreductase. Mode of action Protectant and curative fungicide with antisporulant and trans-laminar systemic activity. Uses Foliar fungicide with activity against Oomycete fungi, such as grape and vegetable downy mildew including Bremia, Peronospora, Plasmopara, Pseudoperonospora spp. and diseases caused by Phytophthora infestans (at 75-150 g/ha). It can also be used as a seed treatment or soil drench to control Pythium spp. It also suppresses other pathogens, including Alternaria spp., as well as certain leaf spot diseases, powdery mildews and rusts. Formulation types SC; WG (for mixtures). Selected products: 'Censor' (Bayer CropScience); 'Reason' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Elicio' (+ fosetyl-aluminium) (Bayer CropScience); 'Mildex' (+ fosetyl-aluminium) (Bayer CropScience); 'Noblite' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience); 'Oracle' (+ copper hydroxide) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sagaie' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience); 'Secure' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sereno' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sonata' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience); 'Tertio' (+ fosetyl-aluminium+ cymoxanil) (Bayer CropScience); 'Utilis' (+ copper hydroxide) (Bayer CropScience); 'Verita' (+ fosetyl-aluminium) (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Pure active substance by hplc. Methods for the determination of residues are available upon request from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for female rats 2028, male rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 2.1 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 32.5 mg/kg/day; (52 w) for dogs 100 mg/kg/day. ADI 0.028 mg/kg. Other Negative in Ames and micronucleus tests. Not teratogenic in rats and rabbits; no reproductive, developmental or carcinogenic effects.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5200 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout and bluegill sunfish 0.74 mg/l. Algae EbC50 (72 h) 3.84 mg/l; ErC50 (72 h) 12.29 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. NOEC for Chironomus riparius 0.05 mg/l. Bees LD50 (96 h, oral) >159.8 mg/bee; LD50 (96 h, contact) 74.8 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 25 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals At low doses (3 mg/kg) in mammals, fenamidone was relatively well absorbed in both sexes and intensively metabolised by phase I reactions (oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis) and phase II reactions (conjugation); the majority of the administered dose was relatively rapidly excreted via the biliary route. At high doses, absorbtion was low: 50-60% of the parent compound was found in faeces. Plants The pattern of metabolite formation is similar in all crops; fenamidone forms the largest part of the residue and the only significant metabolite is RPA 405862, formed by hydrolysis of the thio-methyl side chain. Soil/Environment Hydrolysis (see Stability) follows pseudo first-order reaction kinetics, resulting in three hydrolysis products that exceed 10% of applied radioactivity. Fenamidone is readily photodegraded in aqueous conditions. The active compound is considered to be not readily biodegradable, non-volatile and therefore not found in air.
|