|
etofenprox
Insecticide
IRAC 3; non-ester pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name etofenprox ((m) draft F-ISO, INN; BSI, draft E-ISO both since 1988); ethofenprox* (before 1988)
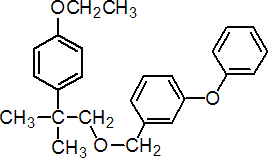
IUPAC name 2-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl 3-phenoxybenzyl ether
Chemical Abstracts name 1-[[2-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropoxy]methyl]-3-phenoxybenzene
CAS RN [80844-07-1] Development codes MTI-500 (Mitsui) Official codes OMS 3002
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 376.5 M.f. C25H28O3 Form White crystals. M.p. 36.4-38.0 ºC B.p. 200 ºC/0.18 mmHg V.p. 32 mPa (100 ºC) KOW logP = 7.05 (25 ºC) S.g./density 1.157 (23 ºC, solid); 1.067 (40.1 ºC, liquid) Solubility In water <1 mg/l (25 ºC). In chloroform 9, acetone 7.8, ethyl acetate 6, xylene 4.8, methanol 0.066 (all in kg/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable in acidic and alkaline media at 80 ºC for >90 days, and to light.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide introduced in Japan (1987) by Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals, Inc. (now Mitsui Chemicals Inc.). Patents GB 2118167; US 4570005 Manufacturers Mitsui; RPG
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Insecticide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of rice water weevils, skippers, leaf beetles, leafhoppers, planthoppers, and bugs on paddy rice; and aphids, moths, butterflies, whitefly, leaf miners, leaf rollers, leafhoppers, thrips, borers, etc. on pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, tea, soya beans, sugar beet, brassicas, cucumbers, aubergines, and other crops. Also used to control public health pests, and on livestock. Formulation types CS; DP; EW; EC; GR; SL; UL; WP. Selected products: 'Trebon' (Mitsui); 'Boxer' (Vapco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Nukil' (Mitsui, Dhanuka); 'Vectron' (Mitsui); 'Primo' (RPG) mixtures: 'Achieve Moncut Trebon' (+ fenoxanil+ flutolanil) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Kasu-rab-validatrebon' (+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate+ phthalide+ validamycin) (Hokko); 'Mon-Rab Trebon F' (+ flutolanil+ phthalide) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Vicidi-M' (+ phenthoate) (Vipesco)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 56-61). Residues determined by glc with ECD.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats >42 880, male mice >107 200, dogs >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and male and female mice >2140 mg/kg; non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 5900 mg/m3. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 32 mg/kg diet; (2 y) for male rats 3.7, female rats 4.8, male mice 3.1, female mice 3.6 mg/kg diet. In life-span feeding studies on rats and mice, at doses up to 4900 ppm, and on dogs, at doses up to 10 000 ppm, no adverse effects were observed. Mutagenicity, teratogenicity, and three-generation reproduction studies showed no noticeable abnormalities. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1993]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Fish TLm (48 h) for carp 5.0 ppm. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) >40 mg/l. Worms LC50 for earthworms (7 d) 43.1 ppm, (14 d) 24.6 ppm.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, parent compound, 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl 3-(phenoxybenzyl) ether, and 2-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl) ether are found. Plants In rice, the main metabolite is 2-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl 3-phenoxybenzoate. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil c. 6 d.
|