|
ethofumesate
Herbicide
HRAC N WSSA 8; benzofuran
NOMENCLATURE
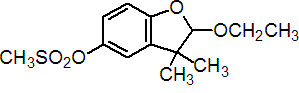
Common name ethofumesate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA)
IUPAC name (?-2-ethoxy-2,3-dihydro-3,3-dimethylbenzofuran-5-yl methanesulfonate
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-ethoxy-2,3-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl-5-benzofuranyl methanesulfonate
CAS RN [26225-79-6] EEC no. 247-525-3 Development codes AE BO49913 (AgrEvo); NC 8438 (Fisons); SN 49913 (Schering); ZK 49913
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 286.3 M.f. C13H18O5S Form White, crystalline solid; (tech. is a light brown crystalline solid; mild aromatic odour). M.p. 70-72 ºC; tech., 69-71 °C V.p. 0.12 to 0.65 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 2.7 (pH 6.5-7.6, 25 °C) Henry 3.7 ´ 10-3 to 6.8 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.29 (20 °C, tech.) Solubility In water 50 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone, dichloromethane, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethyl acetate >600, toluene, p-xylene 300-600, methanol 120-150, ethanol 60-75, isopropanol 25-30, hexane 4.67 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to hydrolysis in water at pH 7 and 9. At pH 5.0, DT50 940 d, forming the hydroxy analogue. Phototransformed in water, DT50 31 h. Degraded in air, DT50 4.1 h.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by R. K. Pfeiffer (Symp. New Herbic., 3rd, 1969, p. 1). Introduced by Fisons Ltd, Agrochemical Division (now Bayer CropScience) in 1974. Patents GB 1271659 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Feinchemie Schwebda; Griffin; Punjab; Sharda; Synthesia; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits lipid synthesis (not ACCase inhibition). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the emerging shoots (grasses) and roots (broad-leaved plants), with translocation to the foliage. Not readily absorbed by leaves after the plant has generated a mature cuticle. Inhibits the growth of meristems, retards cellular division, and limits formation of waxy cuticle. Uses Used pre- and/or post-emergence in sugar and other beet crops, turf, ryegrass and the other pasture grasses, at 0.3-2.0 kg/ha. It is effective in controlling a wide range of important grasses and broad-leaved weeds, with a good persistence of activity in the soil. In beet crops, 1.0-2.0 kg/ha can be used, but ethofumesate is normally recommended at 0.2-2.0 kg/ha in tank-mixtures or co-formulations with other residual or contact herbicides for use in beet. A high degree of tolerance is also shown by strawberries, sunflowers, Phaseolus beans and tobacco, depending on the time of application. Phytotoxicity Onions, peas, beans, carrots, and cotton are tolerant to some extent. Formulation types EC; SC. Selected products: 'Betanal Progress' (Bayer CropScience); 'Ethosat' (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Ethosin' (Agriphar); 'Keeper' (Barclay); 'Kubist' (Griffin); 'Nortron' (Bayer CropScience); 'Prograss' (Bayer CropScience); 'Tramat' (Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Betanal Tandem' (+ phenmedipham) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Aran' (Barclay); 'Boxer' (Sipcam); 'Darby' (Barclay); 'Kemiron' (Bayer CropScience); 'Legclene' (Bayer CropScience); 'MSS Thor' (Nufarm UK); 'Salute' (United Phosphorus); 'Stapler' (Barclay); 'Stemat' (Stefes) mixtures: 'Beetup Pro' (+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (United Phosphorus Ltd); 'Beetup Trio' (+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (United Phosphorus Ltd); 'Betamix Progress' (+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (Bayer CropScience); 'Betanal Progress OF' (+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (Bayer CropScience); 'Betanal Quattro' (+ metamitron+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (Bayer CropScience); 'Betanal Trio' (+ metamitron+ phenmedipham) (Bayer CropScience); 'Betasana Trio' (+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (United Phosphorus Ltd); 'Betosip Combi' (+ phenmedipham) (Sipcam); 'Bettix Triple' (+ metamitron+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (United Phosphorus Ltd); 'Contatto' (+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Goalpost' (+ phenmedipham) (Barclay); 'Goldpost' (+ phenmedipham) (Barclay); 'Gremlin' (+ chloridazon) (Sipcam UK); 'Kontakt Twin' (+ phenmedipham) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Leyclene' (+ ioxynil+ bromoxynil) (as salts) (Bayer CropScience); 'MagicTandem' (+ phenmedipham) (Stefes); 'Magnum' (+ chloridazon) (BASF); 'Powertwin' (+ phenmedipham) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Progress' (+ phenmedipham+ desmedipham) (Bayer CropScience); 'Saherb' (+ phenmedipham+ trifluralin+ desmedipham) (Azot); 'Spectron' (+ chloridazon) (Bayer CropScience); 'Synbetan D Forte' (+ desmedipham) (Synthesia); 'Synbetan P Forte' (+ phenmedipham) (Synthesia); 'Torero' (+ metamitron) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Twin' (+ phenmedipham) (Feinchemie Schwebda, Headland) Discontinued products: 'Atlas Thor' * (Atlas); 'Fumat' * (Stefes); 'MSS Ethosan' * (Mirfield); 'Primasan' * (Nufarm Whyte) mixtures: 'Medimat 2' * (+ phenmedipham) (Stefes); 'Tandem' * (+ phenmedipham) (Stefes)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by glc with FPD (R. J. Whiteoak et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 353). Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >3.97 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats >1000 mg/kg diet (37.6 mg/kg b.w. daily). ADI 0.4 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >3552, bobwhite quail >8743 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks >1082, bobwhite quail >839 mg/kg b.w. daily. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 11.91-20.2, bluegill sunfish 12.37-21.2, mirror carp 10.92 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 13.52-22.0 mg/l. Algae EC50 3.9 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (growth) (96 h) for Crassostrea virginica (Eastern oyster) 1.7 mg/l; LC50 (96 h) Mysidopsis bahia (mysid shrimp) 5.4 mg/l. Bees LC50 (contact and oral) >50 mg/bee. Worms LC50 134 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. LD50 for Aleochara bilineata >1250, for Poecilus cupreus and Chrysoperla carnea >2000 g/ha.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Major metabolite is the lactone or free acid form of the respective 2-oxo compound. Plants In plants, ethofumesate is metabolised to the 2-hydroxy and 2-oxo derivatives, methanesulfonic acid, and CO2. Soil/Environment Ethofumesate is biologically degraded in soil to transient degradates which are rapidly converted to soil-bound residues and mineralised to CO2. Photodegradation also occurs. DT50 ranges from 10-122 d (lab.) and 84-407 d (field). It has been demonstrated under field conditions that ethofumesate does not accumulate in soil and that uptake by succeeding crops is negligible. It is weakly/moderately adsorbed to soil (mean Koc 203), but field lysimeter studies have demonstrated only low mobility, most residues being located in the top 30 cm. It does not leach into groundwater.
|