|
ethion
Acaricide, insecticide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
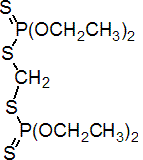
NOMENCLATURE
Common name ethion (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA, JMAF); diéthion ((m) France, Republic of South Africa, formerly India); no name (Italy, Portugal)
IUPAC name O,O,O',O'-tetraethyl S,S'-methylene bis(phosphorodithioate)
Chemical Abstracts name S,S'-methylene bis(O,O-diethyl) phosphorodithioate
CAS RN [563-12-2] EEC no. 209-242-3 Development codes FMC 1240 Official codes ENT 24 105
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 384.5 M.f. C9H22O4P2S4 Form Water-white to amber-coloured liquid. M.p. -15 to -12 ºC B.p. 164-165 ºC/0.3 mmHg V.p. 0.20 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.28 Henry 3.85 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.22 (20 ºC); (tech., 1.215-1.230) Solubility In water 2 ppm (25 ºC). Miscible with most organic solvents, e.g. acetone, methanol, ethanol, xylene, kerosene, petroleum oils. Stability Hydrolysed by aqueous acids and alkalis; DT50 390 d (pH 9). Slowly oxidised by air. F.p. 176 °C (Pensky-Martens closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported (Chem. Eng. News, 1957, 35, 87). Introduced by FMC Corp. Patents GB 872221; US 2873228 Manufacturers Aimco; Bayer CropScience; Bharat; Cheminova; Krishi Rasayan; Rallis; Sharda; Shaw Wallace
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic acaricide and insecticide with predominantly contact action. Uses Control of spider mites, aphids, scale insects, thrips, lepidopterous larvae, leafhoppers, suckers, soil-dwelling and other insects in pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, vines, vegetables, ornamentals, cotton, maize, sorghum, cucurbits, strawberries, turf, and other crops. Active against motile stages of mites when applied as a dormant spray, also against overwintering forms of many species. Typical application rate 0.5-1.0 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as directed, except to some varieties of apple (particularly early-maturing varieties, like Early McIntosh). Formulation types DP; EC; GR; WP; Seed treatment. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Cekuetion' (Cequisa); 'Cethion' (Cheminova); 'Challange' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Deviastra' (Devidayal); 'Dhanumit' (Dhanuka); 'Match' (Crop Health); 'MIT 505' (Shaw Wallace); 'Rayethion' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Tafethion' (Rallis); mixtures: 'Tomahawk' (+ endosulfan) (Calliope)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Ethion' (FMC); 'Nialate' (FMC); 'Ethanox' (Aimco); 'Ethiol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Fosmite' (Pesticides India); 'Indothion' (Indofil); 'Nilmite' (Biostadt); 'Raythion' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Rhodiacide' (Bayer CropScience); 'Rhodocide' (Bayer CropScience); 'Rukawat' (Sabero); 'Veer' (Parry); 'Vegfru Fosmite' (Pesticides India); 'Volthion' (Ralchem) mixtures: 'Nagata' (+ cypermethrin) (Rallis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by lc (CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1826; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 979.04). Residues determined by glc, with TID or FPD, by tlc or by paper chromatography (ibid., 968.24*, 970.52; Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-A, 201-G, 201-H, 201-I; D. C. Abbott et al., Pestic. Sci., 1970, 1, 10; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 396).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 59, 61 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 208 mg/kg (pure), 21 mg/kg (tech.); for mice and guinea pigs 40-45 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 838 mg/kg, guinea pigs and rabbits 915 mg/kg; (tech., for rabbits 1084 mg/kg). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.45 mg tech./l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 0.2 mg/kg daily, dogs 2.5 mg/kg diet (0.06 mg/kg daily). ADI (JMPR) 0.002 mg/kg b.w. [1990]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II (all formulations) EC classification T; R25| Xn; R21
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for quail 128, ducks >2000 mg tech./kg. Fish Toxic to fish. Average lethal concentration 0.72 mg/l (24 h); 0.52 mg/l (48 h). Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.056 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Metabolised in animals by oxidation to a phosphorothioate, followed by dealkylation and hydrolysis. Plants Break down is slow, and caused by weathering, rather than by plant metabolism. Soil/Environment Typical DT50 in soil 90 d.
|