|
esfenvalerate
Insecticide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name esfenvalerate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
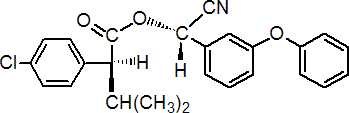
IUPAC name (S)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutyrate
Chemical Abstracts name [S-(R*,R*)]-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 4-chloro-2-(1-methylethyl)benzeneacetate
Other names fenvalerate-U CAS RN [66230-04-4] Development codes S-1844; S-5602 Aa (both to Sumitomo); DPX-YB656 (DuPont) Official codes OMS 3023
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³98% total isomers and ³75% resolved (S,S)- isomers. Mol. wt. 419.9 M.f. C25H22ClNO3 Form Colourless crystals; (tech., yellow-brown viscous liquid or solid at 23 ºC). M.p. 59.0-60.2 ºC; (tech., 43.3-54 °C) B.p. 151-167 ºC (tech.) V.p. 2 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 6.22 (25 ºC) Henry 4.20 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.26 (4-26 ºC) Solubility In water 0.002 mg/l (25 ºC). In xylene, acetone, chloroform, ethyl acetate, dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide >600, hexane 10-50, methanol 70-100 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Relatively stable to heat and light. Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5, 7 and 9 (25 °C). Specific rotation [a]D25 -15.0?(c 2.0 in methanol) F.p. 256 °C (Pensky-Martens)
COMMERCIALISATION
History The enhanced insecticidal activity of esfenvalerate over fenvalerate reported by I. Nakayama et al. (Advances in Pestic. Sci., 1979, Part 2, p. 174), and its properties reviewed by H. Oo'uchi (Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1985, No. 46, p. 21). Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd and developed under licence by Shell International Chemical Co., Ltd and E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. 'Asana' registered by US EPA in 1986 and first marketed in 1987. Manufacturers JIE; Sharda; Sumitomo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Voltage dependent sodium channel agonist. Mode of action Insecticide with contact and stomach action. Uses A potent contact and ingested insecticide with a very broad range of activity, especially effective against Coleoptera, Diptera, Hemiptera, Lepidoptera and Orthoptera on cotton, fruit, vegetables and other crops, at 5-25 g/ha. It is effective against strains resistant to organochlorine, organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides. Phytotoxicity Some injury has been noted on crucifers, cucumbers, aubergines, tomatoes, pears and mandarin oranges. Formulation types EC; SC; UL. Selected products: 'Asana' (DuPont); 'Sumi-alfa' (Sumitomo); 'Sumi-alpha' (Sumitomo); 'Fast' (Vapco); 'Vifen alpha' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Evercide 2668' (MGK); 'Halmark' (BASF); 'Mandarin' (Philagro) mixtures: 'Broxer' (+ fenitrothion) (Sumitomo); 'Kabuto' (+ pirimicarb) (Philagro)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis commonly by glc or by hplc. Details available from Sumitomo. Analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 75-88 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000, rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Slight skin irritant; mild eye irritant. Not a skin sensitiser. NOEL No effect on sub-chronic studies at ³2 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.02 mg/kg. Other Acute LD50 values vary with the vehicle, concentration, route and species, etc.; values reported sometimes differ markedly. No carcinogenic, developmental or reproductive toxicity in animal tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification T; R23/25| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 381 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail >5620, mallard ducks 5247 ppm. Fish Extremely toxic to aquatic animals. LC50 (96 h) for fathead minnows 0.690, bluegill sunfish 0.26, rainbow trout 0.26 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.24 mg/l. Bees LD50 (contact) 0.017 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapid metabolism and elimination occurs in rats and other animals. Primary metabolism involves hydroxylation of 2'- and 4'- hydroxyl moieties, ester cleavage, hydroxylation and oxidation of the alcohol derivatives, oxidation of the cyano moiety and conjugation of the acidic metabolites with sulfate, glycine and glucuronic acid. Plants The major metabolite was decarboxylated fenvalerate. Ester cleavage, hydration of the cyano group to carboxamide and carboxylic acid, hydroxylation of the 2'- and 4'- phenoxy positions, conversion of the alcohol moiety to 3-phenoxybenzyl alcohol and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid, and conjugation of the resulting carboxylic acids and alcohols with sugars, also occur. Soil/Environment In sand (0.38% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 4.4; in sandy loam (pH 7.3, 1.1% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 6.4, DT50 88 d; in silty loam (pH 5.3, 2.0% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 71, DT50 114 d; in clay loam (pH 5.7, 0.2% o.m.), DT50 287 d; in clay loam (pH 6.4, 1.5% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 105. Koc 5300.
|