|
硫丹
硫丹,有机化合物,即1,2,3,4,7,7-六氯双环2.2.1庚-2-烯-5,6-双羟甲基亚硫酸酯。棕色结晶。硫丹有毒,对眼和上呼吸道有一过性刺激作用。对中枢神经系统有损害。主要用作农用杀虫剂,但却是一个极具争议的农药。由于其剧毒性、生物蓄积性和内分泌干扰素作用,已经在50多个国家被禁止使用,包括欧盟、一些亚洲和西非国家。但它仍然广泛应用于许多其他国家,包括印度,巴西和澳大利亚。由于硫丹对环境的威胁,硫丹正在被考虑纳入斯德哥尔摩公约中禁止在全球使用和制造。
简介
化学品中文名称: 硫丹
化学品英文名称: endosulfan
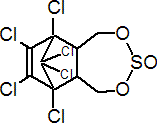
中文名称2: 1,2,3,4,7,7-六氯双环[2.2.1]庚-2-烯-5,6-双羟甲基亚硫酸酯
英文名称2: benzoepin
技术说明书编码: 2521
CAS No.: 115-29-7
分子式: C9H6CI6O3S
分子量: 406.91
成分
有害物成分 CAS No.
硫丹 115-29-7
危险性概述
危险性
危险性类别:
侵入途径:
健康危害: 吸入、摄入或经皮吸收会中毒。对眼和上呼吸道有一过性刺激作用。对中枢神经系统有损害。一般表现为头痛、头晕、瞳孔收缩、恶心、痉挛、口吐泡沫。
环境危害: 对环境有危害。
燃爆危险: 本品可燃,高毒。
急救措施
皮肤接触: 立即脱去污染的衣着,用大量流动清水冲洗。就医。
眼睛接触: 提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。
吸入: 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入: 饮足量温水,催吐。就医。
消防措施
危险特性: 遇明火、高热可燃。其粉体与空气可形成爆炸性混合物, 当达到一定浓度时, 遇火星会发生爆炸。受高热分解放出有毒的气体。
有害燃烧产物: 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢、氧化硫。
灭火方法: 消防人员须戴好防毒面具,在安全距离以外,在上风向灭火。灭火剂:雾状水、泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。
第六部分:泄漏应急处理
应急处理: 隔离泄漏污染区,限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴防尘口罩,穿防毒服。不要直接接触泄漏物。小量泄漏:避免扬尘,小心扫起,收集于干燥、洁净、有盖的容器中。大量泄漏:收集回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
制备
注意事项
操作注意事项: 密闭操作,提供充分的局部排风。防止粉尘释放到车间空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴防尘面具(全面罩),穿胶布防毒衣,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与氧化剂、酸类、碱类接触。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。
储存注意事项: 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。包装必须密封,切勿受潮。应与氧化剂、酸类、碱类、食用化学品等分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。
接触控制/个体防护
职业接触限值
中国MAC(mg/m3): 未制定标准
前苏联MAC(mg/m3): 0.1
TLVTN: 0.1mg/m3(皮)
TLVWN: 未制定标准
监测方法
工程控制: 严加密闭,提供充分的局部排风。
呼吸系统防护: 可能接触其粉尘时,必须佩戴防尘面具(全面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,应该佩戴空气呼吸器。
眼睛防护: 呼吸系统防护中已作防护。
身体防护: 穿胶布防毒衣。
手防护: 戴橡胶手套。
其他防护: 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作完毕,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。
理化特性
主要成分: 含量:(8-80%)可湿性粉剂、粉剂;(2-80%)乳剂。
外观与性状: 二种异构体的混合物,是棕色结晶。
pH:
熔点(℃): 70~100
沸点(℃): 无资料
相对密度(水=1): 1.745(20℃ )
相对蒸气密度(空气=1): 14.0
饱和蒸气压(kPa): 0.133×10-5(25℃)
燃烧热(kJ/mol): 无资料
临界温度(℃): 无资料
临界压力(MPa): 无资料
辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: 无资料
闪点(℃): 无意义
引燃温度(℃): 无资料
爆炸上限%(V/V): 无资料
爆炸下限%(V/V): 无资料
溶解性: 不溶于水,溶于多数有机溶剂。
主要用途: 用作农用杀虫剂。
其它理化性质:
稳定性和反应活性
稳定性:
禁配物: 强氧化剂、强酸、强碱、潮湿空气。
避免接触的条件:
聚合危害:
分解产物:
第十一部分:毒理学资料
急性毒性: LD50:18 mg/kg(大鼠经口); 7.36 mg/kg(小鼠经口);34 mg/kg(大鼠经皮)
LC50:无资料
亚急性和慢性毒性:
刺激性:
致敏性:
致突变性:
致畸性:
致癌性:
生态学资料
生态毒理毒性:
生物降解性:
非生物降解性:
生物富集或生物积累性:
其它有害作用: 该物质对环境有危害,不要让该物质进入环境。
第十三部分:废弃处置
废弃物性质:
废弃处置方法: 建议用焚烧法处置。破损容器禁止重新使用,要在规定场所掩埋。
废弃注意事项:
运输信息
危险货物编号: 61127
UN编号: 2761
包装标志:
包装类别:
包装方法: 塑料袋或二层牛皮纸袋外全开口或中开口钢桶。
运输注意事项: 运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与酸类、氧化剂、食品及食品添加剂混运。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶,勿在居民区和人口稠密区停留。
第十五部分:法规信息
法规信息 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定;常用危险化学品的分类及标志 (GB 13690-92)将该物质划为第6.1 类毒害品。
应用
农业中的应用
35%硫丹 乳油
中文名称: 硫丹
又名: 安杀丹 硕丹 赛丹 雅丹
高效广谱杀虫杀螨剂
产品特点
1、 广谱杀虫杀螨,对果树、蔬菜、茶树、棉花、大豆、花生等多种作物害虫害螨有良好防效。
2、兼具触杀、胃毒和熏蒸多种作用,害虫不易产生抗性。
3、杀虫速度快,杀虫谱广,对天敌和益虫友好。
4、低残留,对作物安全,且有一定壮苗绿叶作用。
使用范围和使用方法:
作物 防治对象 使用浓度或商品用量 使用方法
苹果 黄蚜绵蚜、食心虫、瘤蚜、潜叶蛾 3000-4000倍液 2000-2500倍液 均匀喷雾
梨树 食心虫、梨木虱、介壳虫、梨二叉蚜、毛虫、蝽象 1500-2500倍液 均匀喷雾
其他果树 蚜虫、食心虫、尺蠖、卷叶蛾、介壳虫、叶蝉、毒蛾、天牛、瘿蚊、多种螨类 1500-2500倍液 均匀喷雾
茶树 茶尺蠖、茶细蛾、小绿叶蝉、蓟马、茶蚜 45-130ml 兑水喷雾
棉花 棉蚜、棉铃虫、斜纹夜蛾、蓟马、造桥虫 60-130ml 兑水喷雾
蔬菜 菜青虫、小菜蛾、菜蚜、甘蓝夜蛾、瓢虫 30ml 均匀喷雾
注意事项
1、喷药时避免吸入口鼻和接触皮肤,施药后用肥皂清洗并漱口。
2、本品不能与强酸强碱农药混用。
3、本品对鱼高毒,药液避免流入鱼塘、河流,谨慎清洗喷雾器和处理废弃物。
4、食用作物、饲料作物收获前三周停止用药。
5、贮存与阴凉干燥,避免儿童接触,避免与食物、种子、饲料混放。
中毒解救:
施用时有头痛、痉挛、昏迷等中毒症状,用肥皂清水清洗皮肤;误服用活性炭催吐并到医院诊治。有效解毒剂为巴比妥酸盐。
学名1,2,3,4,7,7-六氯双环[2.2.1]庚-2-烯-5,6-双羟甲基亚硫酸酯。是有机氯杀虫剂。纯品是白色晶体。粗制品是棕色无定形粉末。熔点70~100℃。它是两种异构体的混合物,熔点分别是108~110℃和208~210℃。不溶于水。溶于二甲苯、氯仿、丙酮等有机溶剂。在碱性溶液中易分解放出二氧化硫。遇湿气逐渐分解失效。对白鼠LD50是40~60毫克/公斤。可加工成可湿性粉剂、乳油和粉剂。主要用来防治马铃薯甲虫、棉铃虫、玉米穗虫以及烟草和蔬菜害虫等。对鱼的毒性较大,使用时应避免流入河渠中。可由六氯环戊二烯与1,4-丁烯二醇先制得硫丹醇,再与亚硫酰二氯作用而制得。
谨以此文献给UD,以表我的歉意——Tydus
2005年8月1日欧盟批准了硫丹重新评估决议硫丹不能继续作为农药有效成分在欧盟各成员国使用。同时,该决议还规定,截止2006年6月2日撤销所有含有硫丹的农药产品登记,已登记产品使用截止日期为2007年6月2日;自2005年12月3日起,不在新增批准含有硫丹的产品登记。
2010年10月斯特哥尔摩公约第六次委员会会议在瑞士日内瓦召开,国际专家建议把有机氯杀虫剂硫丹列入持久有机污染物(POPs)附件A中,列入附件A意味着全面禁止硫丹的生产和使用。
|
|
endosulfan
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 2A; cyclodiene
NOMENCLATURE
Common name endosulfan (BSO, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA); thiodan (Iran, USSR); benzoepin (JMAF); no name (Italy)
IUPAC name (1,4,5,6,7,7-hexachloro-8,9,10-trinorborn-5-en-2,3-ylenebismethylene) sulfite; 6,7,8,9,10,10-hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3-benzodioxathiepine 3-oxide
Chemical Abstracts name 6,7,8,9,10,10-hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3-benzodioxathiepine 3-oxide
CAS RN [115-29-7] endosulfan; [959-98-8] formerly [33213-66-0], alpha-endosulfan; [33213-65-9] formerly [891-86-1] and [19670-15-6], beta-endosulfan EEC no. 204-079-4 Development codes Hoe 02 671 (Hoechst); FMC 5462 Official codes OMS 204 (a); OMS 205 (b); OMS 570; ENT 23979
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Endosulfan is a mixture of two stereoisomers: alpha-endosulfan, endosulfan (I), stereochemistry 3a,5ab,6a,9a,9ab-, comprises 64-67% of the tech. grade; beta-endosulfan, endosulfan (II), stereochemistry 3a,5aa,6b,9b,9aa-, 29-32%. Earlier reports on the stereochemistry of these isomers gave conflicting reports (W. Riemschneider, World Rev. Pest Control, 1963, 2(4), 29). Mol. wt. 406.9 M.f. C9H6Cl6O3S Form Colourless crystals; (tech., cream to brown, mostly beige). M.p. ³80 ºC (tech.); a- 109.2 ºC; b- 213.3 ºC V.p. 0.83 mPa (20 ºC) for 2:1 mixture of a- and b- isomers KOW logP for a- = 4.74; b- = 4.79 (both at pH 5) Henry a- 1.48; b- 0.07 (both Pa m3 mol-1, 22 °C, calc.) S.g./density c. 1.8 (20 ºC) (tech.) Solubility In water alpha-endosulfan 0.32, beta-endosulfan 0.33 (both in mg/l, 22 ºC). In ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, toluene 200, ethanol c. 65, hexane c. 24 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable to sunlight. Slowly hydrolysed in aqueous acids and alkalis, with the formation of the diol and sulfur dioxide.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by W. Finkenbrink (Nachrichtenbl. Dtsch. Pflanzenschutzdienstes (Braunschweig), 1956, 8, 183). Introduced by Hoechst AG (now Bayer CropScience) and, in the USA, by FMC Corp. Patents DE 1015797; US 2799685; GB 810602 all to Hoechst Manufacturers Aako; Bayer CropScience; Drexel; Excel; Hindustan; Makhteshim-Agan; Milenia; Parry; Seo Han; Sharda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Antagonist of the GABA receptor-chloride channel complex. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of sucking, chewing, and boring insects and mites on a very wide range of crops, including fruit (including citrus), vines (0.1-0.2%), olives, vegetables including potatoes (0.1-0.2%), ornamentals, cucurbits, cotton (1.5-2.5 l/ha), tea (1.0-2.0 l/ha), coffee (1.5-2.0 l/ha), rice (1.5-2.0 l/ha), cereals (1.0-2.0 l/ha), maize and sorghum (1.5-2.5 l/ha), oilseed crops (1.0-2.0 l/ha), hops, hazels, sugar cane (1.5-2.5 l/ha), tobacco (0.8-1.5 l/ha), alfalfa, mushrooms, forestry, glasshouse crops, etc. Also controls tsetse flies. Phytotoxicity Glasshouse geraniums and chrysanthemums, alfalfa, and lima beans may be injured. Formulation types DP; EC; GR; UL; SC; WP; Powder concentrate. Compatibility Incompatible with strongly alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Fan' (FMC); 'Afidanil' (Efthymiadis); 'Algodán 350' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Cekulfan' (Cequisa); 'Davonil' (Vapco); 'Devisulfan' (Devidayal); 'Endocel' (Excel); 'Endodhan' (Dhanuka); 'Endosol' (Aimco); 'Endostar' (Shaw Wallace); 'Hildan' (Hindustan); 'Lucasulfan' (Lucava); 'Mentor' (Crop Health); 'Phaser' (Bayer CropScience); 'Speed' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Thiodan' (Bayer CropScience); 'Thionex' (Makhteshim-Agan); mixtures: 'Tomahawk' (+ ethion) (Calliope)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Golden Leaf Tobacco Spray' (FMC); 'Afidan 5' (Tecniterra); 'Arasulfan' (Aragro); 'Fantom' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Master' (Chemiplant); 'Mortero' (CAS); 'Parrysulfan' (Parry); 'R Sulfa' (Ramcides); 'Sulfanex' (AgroSan); 'Thionate' (Crystal); 'Thiosulfan' (Platte); 'Trysulphone' (BEC) mixtures: 'Afidan M 40' (+ parathion-methyl) (Tecniterra); 'Asgrow Thirethrin' (+ piperonyl butoxide+ pyrethrins (pyrethrum)) (Agriliance); 'Decisdan' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Methofan' (+ methomyl) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Metofan forte' (+ methomyl) (Aragro); 'Pull Up' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Probelte); 'Serk' (+ thiometon) (Syngenta); 'Sulfanex-Methyl' (+ parathion-methyl) (AgroSan) Discontinued products: 'Cyclodan' * (Hoechst); 'Beosit' * (Stähler); 'Laipuran' * (Lainco); 'Rasayansulfan' * (Krishi Rasayan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2110; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 983.08). Residues determined by glc with MCD (ibid., 976.23; Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, 201-A, 201-G, 201-I; 405; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 773; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 5, 6, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M1, M12). Endosulfan isomers in drinking water by glc with ECD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 990.06). Further methods available on request from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 83, 85 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 70 mg (in aqueous suspension)/kg, 110 mg tech. (in oil)/kg, 76 mg alpha- isomer/kg, 240 g beta- isomer/kg; for dogs 77 mg tech./kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 359 mg (in oil)/kg; for male rats >4000, female rats 500 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 0.0345, female rats 0.0126 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 15 ppm diet; (1 y) for dogs 10 ppm diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.006 mg/kg b.w. [1998]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) I (tech.) EC classification T; R24/25| Xi; R36| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 205-245, ring-necked pheasants 620-1000 mg/kg. Fish Highly toxic (LC50 (96 h) for golden orfe 0.002 mg/l water) but, in practical use, should be harmless to wildlife. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 75-750 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for green algae >0.56 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees under field conditions at an application rate of 1.6 l/ha (560 g endosulfan/ha). Worms NOEC 0.1 mg/kg dry weight.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 40 (WHO, 1984). Animals The principal route of elimination is faeces; most of the radioactivity is excreted within the first 48 hours. The amounts excreted are independent of dose level, number of dosages and isomerism. There are indications of species-specificity. Residues of endosulfan accumulate in the kidneys rather than in fat. Elimination from the kidneys takes place with DT50 7 d, but there is no sign of accumulation in the kidneys even after long-term feeding. Endosulfan is metabolised rapidly in mammalian organisms to less-toxic metabolites and to polar conjugates. Plants The plant metabolites (mainly endosulfan sulfate) were also found in animals and have thus been investigated from a toxicological point of view. 50% of residues are lost in 3-7 days (depending on plant species). Soil/Environment Endosulfan (alpha- and beta-) is degraded in soil with DT50 30-70 d. The main metabolite usually found was endosulfan sulfate, which is degraded more slowly and is, for this reason, the most important metabolite. DT50 for total endosulfan (alpha- and beta- endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate) in the field is 5-8 mo. No leaching tendency was observed. Koc 3000-20 000; Kd <3%.
|