|
EPTC
Herbicide
HRAC N WSSA 8; thiocarbamate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name EPTC (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, WSSA, JMAF)
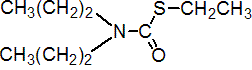
IUPAC name S-ethyl dipropylthiocarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name S-ethyl dipropylcarbamothioate
CAS RN [759-94-4] EEC no. 212-073-8 Development codes R-1608 (Stauffer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. material is 95% pure. Mol. wt. 189.3 M.f. C9H19NOS Form Colourless liquid, with an aromatic odour; (tech. is a yellow liquid). B.p. 127 ºC/20 mmHg V.p. 10 ´ 103 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.2 Henry 1.3 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 0.9546 (30 ºC) Solubility In water 375 mg/l (25 ºC). Miscible with common organic solvents, e.g. acetone, ethanol, isopropanol, benzene, xylene, kerosene. Stability Stable up to 200 ºC. Hydrolysed by strong acids on heating. F.p. 110 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by J. Antognini et al. (Proc. Northeast. Weed Control Conf., 1957, p. 2). Introduced by Stauffer Chemical Co. (now Syngenta AG). Patents US 2913327 Manufacturers ÉMV; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits lipid synthesis (not ACCase inhibition). Maize tolerance of thiocarbamates is attributed to oxidation to the sulfoxide and sulfone, followed by conjugation with glutathione. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots and shoots, with translocation acropetally to the leaves and stems. Kills germinating weed seeds and inhibits bud development from underground portions of some perennial weeds. Uses Control of annual and perennial grasses (especially couch grass), Cyperus spp., and some broad-leaved weeds in potatoes, beans, peas, forage legumes, beetroot, sugar beet, alfalfa, trefoil, clover, cotton, maize, flax, sweet potatoes, safflowers, sunflowers, strawberries, citrus, almonds, walnuts, ornamentals, pineapples, pine nurseries, and other crops. Applied pre-planting with soil incorporation. Combinations with the safener dichlormid are used for herbicidal control in maize. Formulation types EC; GR. Selected products: 'Eptam' (Syngenta); 'Eradicane' (Syngenta); 'Witox' (ÉMV); mixtures: 'Alirox' (+ dichlormid) (ÉMV)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Epitaph' (Cedar) mixtures: 'Double Play' (+ acetochlor) (Syngenta); 'Niptan' (+ AD 67) (Nitrokémia) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Capsolane' * (+ dichlormid) (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 974.05; CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1823; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 233). Residues determined by glc: for crops (W. Y. Ja et al., ibid., 1972, 6, 644; G. G. Patchett et al., Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 4, 117). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07). Analytical methods available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000, rabbits c. 10 000 mg/kg. Slight to mild eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 4.3, female rats 3.8 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for mice 20 mg/kg daily; (90 d) for rats 16, dogs 20 mg/kg daily. Rats fed 326 mg/kg daily for 21 d showed no symptoms other than excitability and weight loss. Not teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (7 d) for bobwhite quail 20 000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 19, bluegill sunfish 14 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 14 mg/l. Bees LD50 0.011 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 267 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 76 (WHO, 1988; general review of thiocarbamates). Plants In plants, EPTC is rapidly metabolised to CO2 and other metabolites. Soil/Environment In soil, EPTC rapidly undergoes microbial degradation to a mercaptan residue, an amino residue, and CO2 (J. P. Hubbell & J. E. Casida, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1977, 25, 404). Decomposes in 4-6 weeks in warm, moist soils.
|