|
diphenamid
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; alkanamide (acetamide)
NOMENCLATURE
Common name diphenamid (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF); difénamide ((f) F-ISO); no name (Germany)
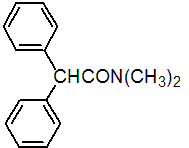
IUPAC name N,N-dimethyldiphenylacetamide
Chemical Abstracts name N,N-dimethyl-a-phenylbenzeneacetamide
CAS RN [957-51-7] EEC no. 213-482-4 Development codes L-34 314 (Lilly)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 239.3 M.f. C16H17NO Form Colourless crystals; (tech., off-white solid). M.p. 134.5-135.5 ºC; (tech., 132-134 ºC) V.p. Negligible at 20 ºC S.g./density 1.17 (23.3 ºC) Solubility In water 260 mg/l (27 ºC). Moderately soluble in polar organic solvents. In acetone 189, dimethylformamide 165, xylene 50 (all in g/l, 27 ºC). Stability Relatively resistant to degradation by u.v. light. Moderately stable to heat (some decomposition occurs at 210 ºC). Decomposed by strong acids and alkalis.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by E. F. Alder et al. (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 1960, p. 55). Introduced by Eli Lilly & Co. and by The Upjohn Co. (neither now manufacture or market it). Patents US 3120434
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cell division inhibitor. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots, with translocation throughout the plant. Inhibits root elongation. Uses Pre-emergence control of annual grasses and some broad-leaved weeds in a wide range of crops, including cotton, potatoes, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, vegetables, capsicums, okra, soya beans, peanuts, tobacco, pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, bush fruit, strawberries, forestry nurseries, and ornamental plants, shrubs, and trees. Generally used at 4-6 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to many crops, including cereals, maize, sorghum, sugar beet, beetroot, carrots, and spinach. Formulation types WP. Compatibility Incompatible with highly alkaline materials.
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Rideon' (Richter Gedeon) Discontinued products: 'Dymid' * (Lilly); 'Enide' * (Zeneca)
ANALYSIS
Residues determined by glc with FID (G. A. Boyack et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1966, 14, 312; J. B. Tepe et al., Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1967, 5, 375; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 637). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1050, mice 600, rabbits 1500, dogs 1000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >225 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats and dogs receiving 2000 mg/kg diet showed no unusual effects on physiology and fertility. Other Acute i.p. LD50 for mice 569 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22| N; R52, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Fish Slightly toxic to fish.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, N-demethylation occurs, followed by elimination as the O-glucuronide; p-hydroxylation is reported as a minor route of metabolism (R. E. McMahon & H. R. Sullivan, Biochem. Pharmacol., 1965, 14, 1085-1092). Plants In plants, metabolism involves N-demethylation. Soil/Environment In soil, diphenamid undergoes microbial degradation. Persistence under warm damp conditions is c. 3-6 months.
|