|
杀螨杀菌剂
二硝巴豆酸酯
生态毒性:
CAS NO: 39300-45-3
分子量: 364.4
分子式:C18H24N2O6
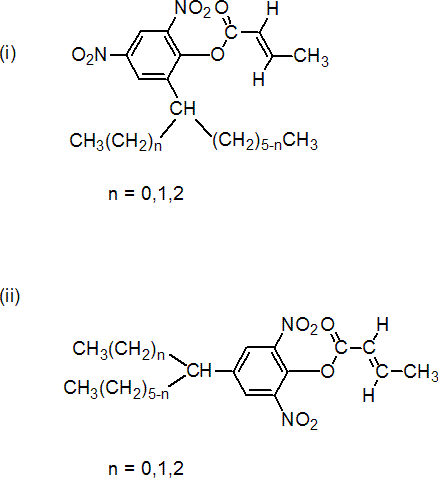
二硝巴豆酸酯 (dinocap;商品名称:敌螨普,消螨普) 是两个异构体的混合物。异构体Ⅰ:2,6-二硝基-4-异辛基苯基豆酸酯,简称敌螨普-4,约占混合物的30%;异构体Ⅱ:2,4-二硝基-6-异辛基苯基豆酸酯,简称敌螨普-6,约占混合物的70%。敌螨普-4 代表的异构体杀菌活性较强,敌螨普-6 代表的异构体杀螨活性较强。
化 学 名: 它是两个异构体的混合物,(1)消螨普-4,巴豆酸2,6-二硝基-4-辛基苯酚;2,6-Dinitro-4-Octylphenylcrotonate(II),约占30%;(2)消螨普-6,巴豆酸2,4-二硝基-6-辛基苯酯;2,4- Dinitro -6- Octylphenyl crotonate(I),约占70%。
理化性质:
性 状: 深红色粘稠液体有刺激性气味
熔点:-22.5 °C
沸点: 138-140 ºC/0.05 mmHg; 环境气压下, 超过200 °C即分解。
蒸气压: 3.33 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 ºC, 蒸气压平衡)
KOW: logP = 4.54 (20 °C)
Henry: 1.36 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.)
密度/比重: 1.10 (20 ºC)
溶解度:水中0.151 mg/l. 2,4-异构体在丙酮,1,2-二氯乙烷,乙酸乙酯,正庚烷,甲醇,二甲苯中溶解度>250 g/l; 2,6异构体在丙酮,1,2-二氯乙烷,乙酸乙酯,甲苯中溶解度>250 g/l,在正庚烷中8.5-10.2 g/l, 在甲醇中20.4-25.3 g/l.
稳定性: 在光照下快速分解。 >32 ºC即分解。 在酸性介质中稳定。在碱性介质中,可在酯基中水解。在甲醇水溶液中水解为2-(1- 甲基庚基)-4,6-二硝基苯基巴豆酸。 (25 ºC) DT50 229 d (pH 5), 56 h (pH 7), 17 h (pH 9).
闪点:67 ºC (Pensky-Martens closed cup)
使用:
二硝巴豆酸酯产品主要用于防治苹果、葡萄、烟草、蔷薇、菊花、黄瓜、啤酒花的白粉病,可用于防治苹果全瓜螨,还可用作种子处理剂。该产品由Rohm & Hass 公司开发并商品化生产,产品主要制剂剂型有EC、WP 和DF。该产品市场主要在欧洲、美洲和中东地区,与内吸性杀菌剂复配使用,美国陶氏化学公司2005 年将该产品在欧洲申请登记。
生物化学:使线粒体氧化磷酸化分开。
作用方式:触杀型杀菌剂,兼有保护和治疗作用。另外还可以作为非内吸性杀螨剂。
用途:在欧洲主要作为杀霉剂用于防治葡萄白粉病(210克/公顷)。也可用于防治其它各种作物的白粉病,包括梨果和核果,如柑橘,黄瓜,蔬菜,烟草,啤酒花和观赏植物等。另外,可以防治植食性螨类,如苹果Panonychus ulmi红蜘蛛,和Hemitarsonemus latus 柑橘银螨。
植物毒性:无植物毒性,在一定条件下的温室玫瑰除外。高温易导致药害。
配方类型:DP EC; WP。
相容性:与油和油基喷雾剂及碱性物质不相容。
毒性:
口服:急性经口LD50雄性大鼠990毫克/公斤,雌性大鼠1212毫克/公斤。
眼睛和皮肤:兔急性经皮LD50³2000毫克/公斤。对皮肤和眼睛(兔)刺激。
吸入:LC50(4小时)大鼠³3毫克/升空气。
NOEL:NOEL(18个月)雌性小鼠2.7毫克/公斤体重每天,雄性小鼠14.6毫克/ 公斤体体重每天;(2年)对大鼠6-8毫克/公斤体重每天,狗0.4毫克/公斤体重每天,对啮齿动物有致癌作用;每天。在3个品种上可造成致畸作用,相关的NOAEL为小鼠4毫克/公斤体重每天。
ADI:(JMPR)0.008毫克/ kg体重[2000]。
毒性等级:WHO III(AI),EPA(配方)III
EC分类:: Xn; R22| Xi; R38 (混合异构体)
环境毒性:
鸟:鹌鹑急性经口LD50>2150毫克/公斤。绿头野鸭膳食LC50=2204 ppm(8天),鹌鹑LC50=2204 PPM。
鱼:对鱼类有毒。 LC50: 虹鳟鱼13, 蓝鳃太阳鱼5.3,鲤鱼14,大翻车鱼20毫克/升。
水蚤: LC50(48小时)4.2毫克/升。
海藻:EC50(72小时)> 105毫克/升。
其他水生菌。:摇蚊(Chironomus riparius) LC50=390毫克/升。
蜜蜂:低毒,对蜜蜂的急性LD50(接触)29毫克/蜜蜂, 急性LC50(口服)6.5毫克/蜜蜂。
蠕虫:LC50(14天)120毫克/公斤。
其他益虫:在实验室条件下,对蚜茧蜂(Aphidius rhopalosiphi)和捕食性螨(Typhlodromus pyri)有害。然而,在田间条件下,由于快速降解,影响被最小化。在野外条件下按标签用量使用时,敌螨普对捕食螨无不良影响。
|
|
dinocap
Fungicide, acaricide
FRAC 29, C5
NOMENCLATURE
Common name dinocap (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO); DPC (JMAF); no name (Republic of South Africa)
IUPAC name 2,6-dinitro-4-octylphenyl crotonates and 2,4-dinitro-6-octylphenyl crotonates in which 'octyl' is a mixture of 1-methylheptyl, 1-ethylhexyl and 1-propylpentyl groups
Chemical Abstracts name (E)-2-(1-methylheptyl)-4,6-dinitrophenyl 2-butenoate
CAS RN [131-72-6] single compound; [39300-45-3] mixed isomers but unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 254-408-0 (for mixed isomers) Development codes CR-1693
Official codes ENT 24 727
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition: Originally thought to be 2-(1-methylheptyl)-4,6-dinitrophenyl crotonate (i, n=0). Now known that the commercial material is a mixture comprising 2.0-2.5 parts of 6-octyl isomers (i) to 1.0 part of 4-octyl isomers (ii). See IUPAC definition for specification of 'octyl'.
Mol. wt.: 364.4
M.f.: C18H24N2O6
Form: Dark red viscous liquid with a pungent odour.
M.p.: -22.5 °C
B.p.: 138-140 ºC/0.05 mmHg; at ambient pressure, decomp. above 200 °C
V.p.: 3.33 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 ºC, vapour pressure balance)
KOW: logP = 4.54 (20 °C)
Henry: 1.36 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.)
S.g./density: 1.10 (20 ºC)
Solubility: In water 0.151 mg/l. 2,4- isomer in acetone, 1,2-dichloroethane, ethyl acetate, n-heptane, methanol and xylene >250 g/l; 2,6- isomer in acetone, 1,2-dichloroethane, ethyl acetate and xylene >250 g/l, in n-heptane 8.5-10.2 g/l, in methanol 20.4-25.3 g/l.
Stability: Rapidly decomposed by light. Decomposes >32 ºC. Stable in acidic media. Hydrolysis of the ester group occurs in alkaline media. 2-(1-methylheptyl)-4,6-dinitrophenyl crotonate hydrolysed in aqueous methanol; (25 ºC) DT50 229 d (pH 5), 56 h (pH 7), 17 h (pH 9).
F.p.: 67 ºC (Pensky-Martens closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History: Introduced by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences).
Patents: US 2526660; US 2810767
Manufacturers: Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry: Uncouples mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation.
Mode of action: Contact fungicide with protective and curative action. Secondary effect as a non-systemic acaricide.
Uses: Primarily sold as a mildewicide for use on Uncinula necator in grapes in Europe (at 210 g/ha). Also used to control powdery mildews of various crops including pome and stone fruit, citrus, cucurbits, vegetables, tobacco, hops and ornamentals. Secondarily causes some suppression of phytophagous mites such as Panonychus ulmi, and Hemitarsonemus latus (citrus silver mite).
Phytotoxicity: Non-phytotoxic, except for glasshouse roses under certain conditions. Phytotoxicity is increased at higher temperatures.
Formulation types: DP; EC; WP.
Compatibility: Incompatible with oils and oil-based sprays, and alkaline materials.
Selected products: 'Karathane' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sialite' (Siapa)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Korthane' (Dow AgroSciences)
mixtures: 'Dikar' (+ mancozeb) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Karamat' (+ fenbuconazole) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sabithane' (+ myclobutanil) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Neptune' (+ difenoconazole) (Syngenta); 'Preface' (+ penconazole) (Syngenta)
Discontinued products: 'Arathane' * (Rohm & Haas); 'Crotothane' * (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by spectrophotometry (R. F. Black et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1974, 57, 653), or by lc; details available from Dow AgroSciences.
Residues determined by glc (A. Ambrus et al., ibid., 1981, 64, 733; Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-A, 201-G, 201-I; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part II; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 568).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews: FAO/WHO 89 (see part 2 of the Bibliography).
Oral: Acute oral LD50 for male rats 990, female rats 1212 mg/kg.
Skin and eye: Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits ³2000 mg/kg . Irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits).
Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats ³3 mg/l air.
NOEL: NOEL (18 months) for female mice 2.7 mg/kg b.w. daily, for male mice 14.6 mg/kg b.w. daily; (2 y) for rats 6-8 mg/kg b.w. daily; there were no carcinogenic effects in rodents; for dogs 0.4 mg/kg b.w. daily. Teratogenic effects were produced in 3 species, with the relevant NOAEL in mice being 4 mg/kg b.w. daily.
ADI: (JMPR) 0.008 mg/kg b.w. [2000].
Toxicity class: WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III
EC classification: Xn; R22| Xi; R38 (for mixed isomers)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds: Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 2204 ppm, for bobwhite quail 2298.
Fish: Toxic to fish. LC50 for rainbow trout 13, bluegill 5.3, carp 14, fathead minnow 20 mg/l.
Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 4.2 mg/l.
Algae: EC50 (72 h) >105 mg/l.
Other aquatic spp.: LC50 for Chironomus riparius 390 mg/l.
Bees: Low toxicity to bees; acute LD50 (contact) 29 mg/bee; acute LC50 (oral) 6.5 mg/bee.
Worms: LC50 (14 d) 120 mg/kg.
Other beneficial spp.: Under laboratory conditions, dinocap is harmful to Aphidius rhopalosiphi and Typhlodromus pyri. However, under field conditions, effects are minimised due to rapid degradation. Dinocap has no adverse effects to predatory mites under field conditions when used to label recommendations (M. Miles & E. Green, Proc. 2002 Br. Crop Prot. Conf .- Pests Dis., 297-302).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Dinocap is readily degraded in plants, animals and the environment to give 2,4- and 2,6- dinitrophenol (DNOP). Dinocap and its residues have no significant leaching potential and pose no threat to groundwater.
Animals: In rats, following oral administration, dinocap is almost entirely eliminated rapidly in the urine and faeces. In dairy cows, dinocap and its metabolites are excreted almost completely in the faeces, with only a small amount in the urine. The nitro groups are enzymically reduced to amino groups, and ester hydrolysis also takes place, to give DNOP.
Plants: Metabolism follows the same course as in animals.
Soil/Environment: Soil: DT50 (lab, aerobic, 20°C) 4-24 d; DT90 13.5-113 d. DT50 (lab, anaerobic, 20°C) 8 d. No significant soil photolysis. The major metabolite is DNOP, formed by ester hydrolysis, with subsequent microbial degradation to CO2. Koc 2889-310 200, depending on soil type; dinocap and its residues have no leaching potential. Water: DT50 (sterile, dark, 20°C) >1 y (pH 4), 16-30 d (pH 7), 3.6-9 d (pH 9). Photolysis in water is more rapid; DT50 <1 d (25°C, pH 4). In dark water/sediment systems, dinocap rapidly dissipates from water to sediment, DT50 (lab) <7 d, and is readily degraded. In aquatic systems, the major metabolite is DNOP. Air: No significant volatile losses are expected following application. Any small amounts present in air are estimated to degrade with atmospheric t½ 1.9 h.
|