|
diniconazole
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
diniconazole
Common name diniconazole (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
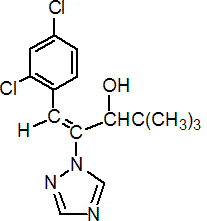
IUPAC name (E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol
Chemical Abstracts name (E)-(?-b-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methylene]-a-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol
CAS RN [83657-24-3]; [76714-88-0] (E)- isomers Development codes S-3308 L (Sumitomo); XE-779 (Chevron)
diniconazole-M
IUPAC name (E)-(R)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol
CAS RN [83657-18-5]; [83657-19-6] (E)-(S)- isomer
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
diniconazole
Mol. wt. 326.2 M.f. C15H17Cl2N3O Form Colourless crystals. M.p. c. 134-156 ºC V.p. 2.93 mPa (20 ºC); 4.9 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.3 (25 ºC) S.g./density 1.32 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 4 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone, methanol 95, xylene 14, hexane 0.7 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to heat, light, and moisture.
diniconazole-M
Mol. wt. 326.2 M.f. C15H17Cl2N3O
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by H. Takano et al. (Noyaku Kagaku, 1983, 8, 575); diniconazole-M is more potent than diniconazole. Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd and Valent.
diniconazole
Patents US 4203995; GB 2004276 Manufacturers Sumitomo
diniconazole-M
Patents US 4435203; EP 54431 Manufacturers Sumitomo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Steroid demethylation (ergosterol biosynthesis) inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Uses Control of leaf and ear diseases (e.g. powdery mildew, Septoria, Fusarium, smuts, bunt, rusts, scab, etc.) in cereals; powdery mildew in vines; powdery mildew, rust, and black spot in roses; leaf spot in peanuts; Sigatoka disease in bananas; and Uredinales in coffee. Also used on fruit, vegetables, and other ornamentals. Formulation types EC; SC; WG; WP.
diniconazole
Selected products: 'Spotless' (Sumitomo); 'Sumi-8' (Sumitomo)
OTHER PRODUCTS
diniconazole
'Dinizol' (AgroSan); 'Embassador' (Sanonda)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis details available from Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. Residues determined by glc with FTD.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
diniconazole
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 639, female rats 474 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2770 mg/m3. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53 ((E)- isomers)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
diniconazole
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1490, mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 5075 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.58, Japanese killifish 6.84, carp 4.0 mg/l. Bees Acute contact LD50 for bees >20 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, diniconazole is rapidly metabolised by hydroxylation of the tert-butyl methyl groups. Within 7 days, 52-87% is excreted in the faeces and 13-46% in the urine. Plants Half-life in cereals is a few weeks.
|