|
dimethenamid
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; chloroacetamide
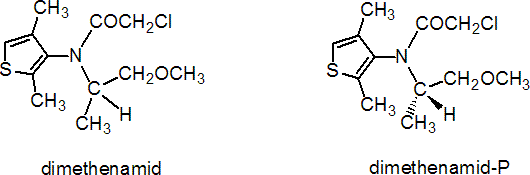
NOMENCLATURE
dimethenamid
Common name dimethenamid (BSI, pa E-ISO)
IUPAC name (RS)-2-chloro-N-(2,4-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-N-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acetamide
Chemical Abstracts name (RS)-2-chloro-N-(2,4-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-N-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acetamide
CAS RN [87674-68-8] Development codes SAN 582 H (Sandoz)
dimethenamid-P
Common name dimethenamid-P (BSI, pa E-ISO)
IUPAC name (S)-2-chloro-N-(2,4-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-N-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acetamide
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-(2,4-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-N-((1S)-2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acetamide
Other names s-dimethenamid CAS RN [163515-14-8] Development codes BAS 656H (BASF); SAN 1289H (Sandoz)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
dimethenamid
Mol. wt. 275.8 M.f. C12H18ClNO2S Form Yellowish-brown, viscous liquid. B.p. 127 ºC/26.7 Pa V.p. 36.7 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.15?.02 (25 ºC) Henry 8.32 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.187 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 1.2 g/l (pH 7, 25 ºC). In heptane 282, iso-octane 220 (both in g/kg, 25 ºC). In ether, kerosene, ethanol all >50% (25 ºC). Stability Stable in storage at 54 ºC for 4 weeks, and at 70 ºC for 2 weeks. Estimated decomposition at 20 ºC within 2 years is <5%. Stable at pH 5-9 (buffered, 25 ºC) for 30 d. F.p. 91 °C (Pensky-Martens closed cup)
dimethenamid-P
Mol. wt. 275.8 M.f. C12H18ClNO2S Form Yellow-brown clear liquid. B.p. 122.6 °C/0.07 mmHg V.p. 2.51 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 1.89 (25 °C) Henry 4.80 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.195 (25 °C) Solubility In water 1449 mg/l (25 °C). In hexane 20.8 g/100ml; miscible with acetone, acetonitrile, toluene, and n-octanol (25 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5, 7, and 9 for 31 d (25 °C). F.p. 79 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
dimethenamid
History Reported by J. Harr et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1991, 1, 87). Introduced by Sandoz AG (became Novartis Crop Protection AG); sold to BASF in 1996. Manufacturers BASF
dimethenamid-P
History BASF introduced the resolved (S)- isomer in 2000. Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits cell division and tissue differentiation. Chloroacetamides may inhibit synthesis of very long chain fatty acids (J. Schmalfuss et al., Abstr. Meeting WSSA, Toronto, 40, 117-118, 2000; P. Böger, Abstr. III Int. Weed Control Congr., Brazil 2000). Maize tolerance of chloroacetamides is due mainly to conjugation with glutathione; P450 metabolism may also be a factor. Mode of action Primarily a soil-applied herbicide but also can be applied post-emergence. The herbicide enters the plant via root and epicotyl uptake; there is little or no foliar activity, and little translocation in the plant. Uses Control of annual grass and broad-leaved weeds pre- or early post- emergence, in maize, soya beans, sugar beet, potatoes, dry beans, and other crops. Applied at 0.85 - 1.44 kg/ha (dimethenamid), 0.65-1.0 kg/ha (dimethanimid-P). Formulation types EC.
dimethenamid
Selected products: 'Frontier' (BASF) Formulation types EC.
dimethenamid-P
Selected products: 'Frontier X2' (BASF); 'Isard' (BASF); 'Outlook' (BASF); 'Spectrum' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
dimethenamid
'Wing' (BASF); 'Zeta 900' (BASF) mixtures: 'Century' (+ atrazine) (BASF); 'Detail' (+ imazaquin-ammonium) (BASF); 'Guardsman' (+ atrazine) (BASF); 'OpTill' (+ dicamba) (BASF); 'Leadoff' (+ atrazine) (DuPont)
dimethenamid-P
'Frontier Extra' (BASF); 'Frontier Optima' (BASF); 'Frontier Super' (BASF) mixtures: 'G-Max Lite' (+ atrazine) (BASF); 'Guardsman Max' (+ atrazine) (BASF)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
dimethenamid
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1570 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; mild eye irritant (rabbits). Sensitising to skin. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4990 mg/m3 air. NOEL for rats 6.0, dogs 10, mice 4.3 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.04 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test and chromosome aberration assay; no carcinogenic or teratogenic potential.
dimethenamid-P
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 466 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute dermal LD50 rats >2000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant, slight skin irritant (rabbits). Skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2200 mg/m3 air NOEL NOAEL (90 d) for rats 39 mg/kg b.w., (13 w) for male mice 46 mg/kg b.w., (13 w) for dogs 5 mg/kg/ b.w. ADI 0.05 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test and chromosome aberration assay; no carcinogenic or teratogenic potential.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
dimethenamid
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1908 mg/kg b.w. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg b.w. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 6.4, rainbow trout 2.6 mg/l. LC50 for sheepshead minnow 7.2 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 16 mg/l. Algae LC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.062 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 4.8, eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) 5.0 mg/l. Bees Contact LD50 >1 mg/bee. Worms LC50 459.8 mg/kg dry soil. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to Poecilus cupreus and Aleochara bilineata (IOBC).
dimethenamid-P
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1068 mg/kg b.w. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg b.w. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 10, rainbow trout 6.3 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 12 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum 0.017 ppm, Anabaena 0.38 ppm. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (14 d) for Lemna 0.0089 ppm; LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp 3.2 mg/l. Bees Acute oral LD50 (24 h) >1000 mg/bee. Worms LC50 294 mg/kg dry soil. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to Poecilus, Chrysoperla, and Typhlodromus (IOBC).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
dimethenamid
Animals Rapidly and extensively metabolised in animals, primarily via glutathione conjugation followed by complexes with cysteine, thioglycolic acid, and mercapturate. Plants Rapid metabolism in maize and sugar beet leads to conjugates with glutathione, cysteine, thiolactic acid and thioglycolic acid. Metabolism pathways in plants is similar to that in animals. No accumulation of parent. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soil, probably through microbial action, with DT50 8-43 d, depending upon soil type and weather conditions. Photolysis DT50 on soil c. 7.8 d, in water 23-33 d. Kd (4 soils) 0.7-3.5.
dimethenamid-P
Animals Rapidly and extensively metabolised in animals, primarily via glutathione conjugation followed by complexes with cysteine, thioglycolic acid, and mercapturate. Plants Rapid metabolism in maize and sugar beet via conjugation to glutathione, subsequent hydrolysis to cysteine conjugate, and then further oxidation, deamination, and decarboxylation. Metabolism pathways in plants is similar to that in animals. No accumulation of parent. Soil/Environment Extensively degraded in soil via glutathione and/or cysteine conjugation, leading to mineralisation and formation of bound residues. Major metabolites include an oxalamide and a sulfonate, but these are transient. DT50 of parent in soil 8-43 d, depending of soil type and conditions. Kd (10 soils) 1.23-13.49. Photolytic DT50 in top layers of aqueous solution <1 d; in soil 14-16 d.
|