|
difenoconazole
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name difenoconazole (BSI, draft E-ISO)
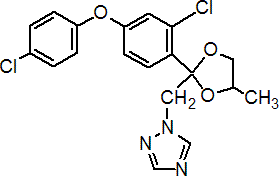
IUPAC name cis,trans-3-chloro-4-[4-methyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-2-yl]phenyl 4-chlorophenyl ether
Chemical Abstracts name 1-[2-[2-chloro-4-(4-chlorophenoxy)phenyl]-4-methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole
CAS RN [119446-68-3] unstated stereochemistry Development codes CGA 169 374 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Ratio of cis- to trans- isomers is in the range 0.7 to 1.5. Mol. wt. 406.3 M.f. C19H17Cl2N3O3 Form White to light beige crystals. M.p. 82.0-83.0 °C V.p. 3.3 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.4 (25 ºC) Henry 1.5 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.40 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 15 mg/l (25 ºC). In ethanol 330, acetone 610, toluene 490, n-hexane 3.4, n-octanol 95 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable up to 150 ºC. Hydrolytically stable. pKa 1.1
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by W. Ruess et al. (Proc. 1988 Br. Crop Prot. Conf., 2, 543). Introduced in France (1989) by Ciba-Geigy (now Syngenta AG). Patents EP 65485 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Sterol demethylation inhibitor. Inhibits cell membrane ergosterol biosynthesis, stopping development of the fungus. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with preventive and curative action. Absorbed by the leaves, with acropetal and strong translaminar translocation. Uses Systemic fungicide with a novel broad-range activity protecting the yield and crop quality by foliar application or seed treatment. Provides long-lasting preventive and curative activity against Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes including Alternaria, Ascochyta, Cercospora, Cercosporidium, Colletotrichum, Guignardia, Mycosphaerella, Phoma, Ramularia, Rhizoctonia, Septoria, Uncinula, Venturia spp., Erysiphaceae, Uredinales and several seed-borne pathogens. Used against disease complexes in grapes, pome fruit, stone fruit, potatoes, sugar beet, oilseed rape, banana, cereals, rice, soya beans, ornamentals and various vegetable crops, at 30-125 g/ha. Used as a seed treatment against a range of pathogens in wheat and barley, at 3-24 g/100 kg seed. Phytotoxicity In wheat, early foliar applications at growth stages 29-42 might cause, in certain circumstances, chlorotic spotting of leaves, but this has no effect on yield. Formulation types DS; EC; FS; SC; WG. Selected products: 'Dividend' (seed treatment) (Syngenta); 'Score' (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Bardos' (Syngenta); 'Bogard' (Syngenta); 'Geyser' (Syngenta); 'Plandom' (Syngenta); 'Plover' (Syngenta); 'Polyscore' (Syngenta); 'Purugen' (Syngenta); 'Sico' (Syngenta); 'Slick' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Arix' (+ propiconazole) (Syngenta); 'Armure' (+ propiconazole) (Syngenta); 'Dividend XL' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Syngenta); 'Eria' (+ carbendazim) (Syngenta); 'Helix' (+ fludioxonil+ metalaxyl-M+ thiamethoxam) (Syngenta); 'Landor CT' (+ fludioxonil+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Germany) (Syngenta); 'Neptune' (+ dinocap) (Syngenta); 'Spyrale' (+ fenpropidin) (Syngenta); 'Taspa' (+ propiconazole) (Syngenta); 'Trial' (+ carbendazim) (Syngenta) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Play' * (+ cyprodinil) (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
Residue determination by glc. Details from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1453, mice >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2010 mg/kg. Non-irritant to eyes and skin (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats ³3300 mg/m3 air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 1.0 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1.5 y) for mice 4.7 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 3.4 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.01 mg/kg b.w. Other Not teratogenic or mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III EC classification (R22)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 (9-11 d) for mallard ducks >2150, Japanese quail >2000 mg/kg. LC50 for bobwhite quail 4760, mallard ducks >5000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.81, bluegill sunfish 1.2, sheepshead minnow 0.82 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.77 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.032-1.2 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp 0.15 mg/l; EC50 (96 h) for Eastern oysters 0.45 mg/l; (14 d) for duckweed (Lemna gibba)18.5 mg/l. NOEC (28 d) for reproduction in the sediment dweller, Chironomus riparis ³50 mg/kg sediment. Bees Non-toxic to honeybees; LD50 (oral) >187 mg/bee; LC50 (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms >610 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. NOEC (28 d) for reproduction in Collembola (Folsomia candida) 500 mg/kg soil. Use under field conditions is not expected to result in adverse effects on soil micro-organisms or on soil and foliar dwelling non-target arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration, difenoconazole was rapidly eliminated practically to entirety, with urine and faeces. Residues in tissues were not significant and there was no evidence for accumulation. Plants Two routes of metabolism: one by a triazole route to triazolylalanine and triazolylacetic acid; the other by hydroxylation of the phenyl ring followed by conjugation. Soil/Environment Practically immobile in soil, strong adsorption to soil particles (mean adsorption coefficient normalised to organic carbon, Koc,ads 3759 ml/g), low potential to leach below top soil layer. Soil dissipation rate is slow and dependent on application rate; DT50 50-150 d. DT50 from water 2 d.
|