|
difenacoum
Rodenticide
coumarin anticoagulant; hydroxycoumarin
NOMENCLATURE
Common name difenacoum (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
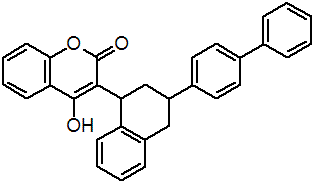
IUPAC name 3-(3-biphenyl-4-yl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin
Chemical Abstracts name 3-[3-(1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthalenyl]-4-hydroxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
CAS RN [56073-07-5] EEC no. 259-978-4
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. material is >90% pure. Mol. wt. 444.5 M.f. C31H24O3 Form Colourless, odourless crystals; (tech., buff/beige powder). M.p. 215-217 ºC V.p. 0.16 mPa (45 ºC) KOW logP >7 (calc., unionised) Solubility In water 31 ´ 10-3 (pH 5.2), 2.5 (pH 7.3), 84 (pH 9.3) (all in mg/l, 20 °C). Slightly soluble in alcohols. In acetone, chloroform >50, ethyl acetate 2, benzene 0.6 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to light, and to temperatures up to 100 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Rodenticide reported by M. Hadler (J. Hyg., 1975, 74, 441). Introduced by Sorex (London) Ltd (now Sorex Ltd) and later by ICI Agrochemicals, now Syngenta AG, who sold their rights to Sorex in 2003. First marketed in 1976. Patents GB 1458670 to Sorex Manufacturers Sorex
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Second-generation anticoagulant rodenticide. Inhibits the vitamin K-dependent steps in the synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX and X. Mode of action Indirect anticoagulant rodenticide. Uses Effective against rats and most mice resistant to other anticoagulants. For a review, see A. P. Buckle & R. H. Smith, "Rodent Pests and their Control", CABI. Formulation types AB; BB; CB; RB. Selected products: 'Neosorexa' (Sorex); 'Ratak' (Sorex); 'Kemifen' (Kemio); 'Ratzenmice Baits' (Trithin); mixtures: 'Sorexa CD Concentrate' (+ ergocalciferol) (Sorex); 'Sorexa CD3 Concentrate' (+ vitamin D3) (Sorex)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Sorexa Gel' (Sorex); 'Rataway' (Deosan); 'Sakarat D' (Killgerm) mixtures: 'Sorexa CD Mouse Bait' (+ vitamin D3) (Sorex); 'Sorexa CD Mouse Killer' (+ vitamin D3) (Sorex) Discontinued products: 'Neokil' * (Sorex); 'Rat Rods' * (Killgerm); 'Ratak' * (Killgerm); 'Ridak' * (Zeneca); 'Wax Bait' * (Killgerm)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (K. Hunter, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 151) or by u.v. spectrometry (details from Sorex Ltd). Residues determined by hplc (idem, ibid.).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1.8, female rats 2.45, male mice 0.8, rabbits 2.0, female guinea pigs 50, dogs >50, cats >100, pigs >50 mg/kg. Sub-acute oral LD50 (5 d) for male rats 0.16 mg/kg/day. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats 27.4, female rats 17.2, rabbits 1000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia EC classification T+; R28| T; R48/25| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for chickens >50 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.10 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.52 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 175 (WHO, 1995) Soil/Environment DT50 (average) 290 d (range 146-439 d). Unlikely to leach; no leaching in 30 cm lab. columns.
|