|
diclosulam
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; triazolopyrimidine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name diclosulam (BSI, pa ISO, ANSI)
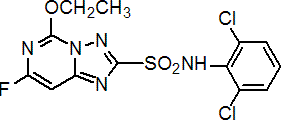
IUPAC name N-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-ethoxy-7-fluoro[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine-2-sulfonamide
Chemical Abstracts name N-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-ethoxy-7-fluoro[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine-2-sulfonamide
CAS RN [145701-21-9] Development codes XDE-564; DE-564 (both Dow)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 406.2 M.f. C13H10Cl2FN5O3S Form Off-white solid. M.p. 218-221 °C V.p. 6.67 ´ 10-10 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 0.85 (pH 7) S.g./density 1.602 (20 °C) Solubility In water 6.32 mg/ml (20 °C). In acetone 0.797, acetonitrile 0.459, dichloromethane 0.217, ethyl acetate 0.145, methanol 0.0813, octanol 0.00442, toluene 0.00588 (all in g/100 ml, 20 °C). Stability Stable 28 d at 50 °C. pKa 4.0 (20 °C)
COMMERCIALISATION
Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits the acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme. The primary site of activity is within the chloroplasts in plant meristems. Selectivity is attributed to limited translocation in soya beans and peanuts, and rapid metabolism into a non-active form; DT50 in soya beans 3 h. Mode of action Taken up by both roots and foliage and translocated to new growing points. Lethal amounts of diclosulam accumulate in meristems, halting cell division and resulting in plant death. Very little diclosulam accumulates in plant roots. Uses Soil applied (including pre-emergence, pre-plant, and pre-plant incorporated), broad-leaved weed control, in peanuts and soya beans. Application rates for peanuts 17.5-26 g/ha; for soya beans 26-35 g/ha. Formulation types WG. Selected products: 'Crosser' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Snake' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Spider' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Discontinued products: 'Strongarm' * (Dow AgroSciences)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.04 mg/l. NOEL NOEL (2 y) for rats 5 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.05 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III (WG)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg. Acute dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >110, bluegill sunfish >137, sheepshead minnow >120 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 72 mg/l; life-cycle NOEC 5.66 mg/l; LOEC 9.16 mg/l. Algae EC50 (14 d) for green algae (Selenastrum capricornutum) 1.6, bluegreen algae (Anabaena flos-aquae) 83 mg/l; NOEC for green algae 1.6, bluegreen algae 561 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for grass shrimp >120, Eastern oyster >120 mg/l. EC50 for Lemna sp. 1.16 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, contact) for honeybees >25 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >991 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Classed as practically non-toxic to slightly toxic.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Metabolised primarily by dealkylation of the ethoxy group and hydrolysis of the sulfonamide linkage. Soil/Environment Dissipation of diclosulam occurs primarily through microbial degradation and is minimally influenced by soil pH. Soil DT50 (in a wide variety of soils) c. 33-65 d. Koc 90. Low application rates and half-life mean diclosulam is not likely to contaminate groundwater.
|