|
diclofop-methyl
Herbicide
HRAC A WSSA 1; aryloxyphenoxypropionate
NOMENCLATURE
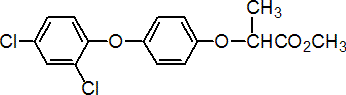
diclofop-methyl
Chemical Abstracts name methyl 2-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propanoate
CAS RN [51338-27-3] unstated stereochemistry; [71283-65-3] (R)- isomer; [75021-72-6] (S)- isomer EEC no. 257-141-8 Development codes Hoe 023408 (Hoechst); AE F023408 (AgrEvo)
diclofop
Common name diclofop (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA)
IUPAC name (RS)-2-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propionic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propanoic acid
CAS RN [40843-25-2] unstated stereochemistry Development codes Hoe 021079 (Hoechst)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
diclofop-methyl
Composition Tech. grade is ³93% pure. Mol. wt. 341.2 M.f. C16H14Cl2O4 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 39-41 ºC V.p. 0.25 mPa (20 ºC); 7.7 mPa (50 ºC) (vapour pressure balance) KOW logP = 4.58 S.g./density 1.30 at 40 ºC Solubility In water 0.8 mg/l (pH 5.7, 20 ºC). In acetone, dichloromethane, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethyl acetate, toluene >500 g/l; in polyethylene glycol 148, methanol 120, isopropanol 51, n-hexane 50 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable to light. In water, DT50 (25 ºC) 363 d (pH 5), 31.7 d (pH 7), 0.52 d (pH 9).
diclofop
Mol. wt. 327.2 M.f. C15H12Cl2O4 Form Yellowish-white solid. M.p. 118-122 °C V.p. 3.1 ´ 10-6 mPa (20 °C); 9.7 ´ 10-6 mPa (25 °C); 1.7 ´ 10-3 mPa (50 °C) (vapour pressure balance) KOW logP = 2.81 (pH 5), 1.61 (pH 7) S.g./density 1.4 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.453 (pH 5), 122.7 (pH 7), 127.4 (pH 9) (all in g/l, 20 °C). pKa 3.43
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicidal activity of diclofop-methyl reported by P. Langelüddeke et al. (Mitt. Biol. Bundesanst. Land.-Forstwirtsch. Berlin-Dahlem, 1975, 165, 169). Introduced by Hoechst AG (now Bayer CropScience). Patents DE 2136828; DE 2223894 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Jingma; Sharda; Sundat; Tide
APPLICATIONS
diclofop-methyl
Biochemistry Fatty acid synthesis inhibitor, by inhibition of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase). Destroys the cell membrane, prevents the translocation of assimilates to the roots, reduces the chlorophyll content, and inhibits photosynthesis and meristem activity. Mode of action Diclofop-methyl is a selective systemic herbicide, also with contact action, absorbed primarily by the leaves, with some absorption by the roots in moist soil. Undergoes rapid transformation to diclofop, which is translocated within the plant. Diclofop-methyl (R)-(+)- enantiomer shows significantly greater herbicidal activity by foliar application to 3 weed species than does the (S)-(-)- enantiomer, but there was less difference by soil application (H. J. Nestler & H. Bieringer, Z. Naturforsch. B. Anorg. Chem. Org. Chem., 1980, 35B, 366). Uses For post-emergence control of wild oats, wild millets, and other annual grass weeds in wheat, barley, rye, red fescue, and broad-leaved crops such as soya beans, sugar beet, fodder beet, flax, legumes, oilseed rape, sunflowers, clover, alfalfa, peanuts, brassicas, carrots, celery, beetroot, parsnips, lettuce, spinach, potatoes, cucumbers, peas, beans, tomatoes, fennel, alliums, herbs, etc. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to maize, sorghum, oats, sugar cane, rice, and cotton. Formulation types EC. Compatibility Incompatible with most other herbicides. Selected products: 'Hoegrass' (Bayer CropScience); 'Hoelon' (Bayer CropScience); 'Illoxan' (Bayer CropScience); 'Sperto' (Cequisa); 'Taiwan' (Rocca)
OTHER PRODUCTS
diclofop-methyl
'Cerlon' (Bayer CropScience); 'Colt' (Bayer CropScience); 'Iloxan' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Baghera' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl+ mefenpyr-diethyl) (Bayer CropScience); 'Corniche' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl) (Bayer CropScience); 'Dopler' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl+ mefenpyr-diethyl) (Bayer CropScience); 'Tigress Ultra' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl) (Bayer CropScience); 'Zeus' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl+ mefenpyr-diethyl) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Tigress' * (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl) (AgrEvo)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (CIPAC Handbook,1985, 1C, 2096). Details of glc methods for product and residue analysis are available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
diclofop-methyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 481-693 mg/kg (in sesame oil), dogs 1600 mg/kg (highest dose without induction of vomiting). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 for rats >1.36 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 0.1 mg/kg b.w.; (15 mo) for dogs 0.44 mg/kg b.w. ADI 0.001 mg/kg b.w. (AgrEvo proposed value). Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22, R43| N; R50, R53
diclofop
Oral Acute oral LD50 for female rats 586 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 1657 mg/kg.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
diclofop-methyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >10 000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail >1600, mallard ducks >1100 mg/kg b.w. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.23 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.23 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 1.5 mg/l, (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.53 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees under field conditions and application rate of 1.134 kg a.i./ha. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil, dry weight.
diclofop
Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 21.9, golden orfe 79.9 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals When fed to rats, diclofop-methyl is almost totally absorbed and then rapidly excreted; c. 90% is recovered unchanged in faeces and urine after 2 d, and 99% after 7 d. Accumulation of residues in the body is unlikely; low levels of total residues were found in organs and tissues 7 d after a single dose of 1.8 mg/kg b.w. Metabolites are identical with those in plants. Plants Diclofop-methyl is taken up rapidly and almost completely by plants, with little translocation. It is hydrolysed relatively quickly (DT50 in sugar beet 3 d), first to an isomeric mixture of hydrolysed free acids and their conjugates with glucuronic and sulfuric acid, and then to 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenol. Total radioactive residues at the time of harvest in wheat, sugar beet and soya beans are generally low, below or around the determination limits (0.01 to 0.1 mg/kg). The same applies to rotation crops. Soil/Environment In soil, diclofop-methyl is metabolised to diclofop, which then undergoes further degradation to 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenol, hydroxylated free acids and CO2. In various soils in field trials: DT50 1-57 d, DT90 30-281 d. Irrigation studies indicate low levels of leaching. From model calculations, a hazard to groundwater or to drinking water supplies can be excluded, even in sandy soil. Soil adsorption Koc 14 000-24 400 mg/kg.
|