|
dichlobenil
Herbicide
HRAC L WSSA 20; benzonitrile
NOMENCLATURE
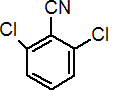
Common name dichlobenil (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); DBN (JMAF)
IUPAC name 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile
CAS RN [1194-65-6] EEC no. 214-787-5 Development codes H 133
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade dichlobenil is ³98% pure. Mol. wt. 172.0 M.f. C7H3Cl2N Form White crystalline solid with a musty odour. M.p. 143.8-144.3 ºC (tech.) B.p. 270 ºC/760 mmHg V.p. 144 mPa (25 °C, gas saturation method) KOW logP = 2.70 Henry 1.14 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density D420 = 1.55 Solubility In water 21 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 86.0, methanol 17.2, dichloromethane 151 (all in g/l, 20 ºC); in xylene 53, ethanol 15, cyclohexane 3.7 (all in g/l, 25 °C). Stability Stable to heat, <270 ºC. Stable to acids, but rapidly hydrolysed by strong alkalis to 2,6-dichlorobenzamide. In sterile aqueous solutions at pH 5, 7 and 9 in the dark (22 °C), decomposition only 5-10% after 150 d. Photolytic DT50 in water 10.2 d (natural sunlight at 40?Northern latitude).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicidal properties reported by H. Koopman & J. Daams (Nature (London), 1960, 186, 89). Introduced by Philips-Duphar B.V. (now Crompton Europe B.V., subsidiary of Crompton Corporation). Patents NL 572662; US 3027248 Manufacturers Crompton
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibition of cell wall (cellulose) biosynthesis. Has no effect on cell respiration or photosynthesis. Mode of action Systemic herbicide. Inhibits actively dividing meristems, germination of seeds and damages rhizomes. Its selectivity can be ascribed to the fact that it is bound to the top 5-10 cm of the soil. Uses For selective weed control of annual and many perennial weeds in woody ornamentals, fruit orchards, vineyards, bush fruit, forest plantations, public green areas, at dosages between 2.7 and 5.4 kg/ha. For total weed control in non-crop areas, at dosages up to 8.1 kg/ha. Control of floating, emergent or submerged aquatic plant growth in non-flowing water, at 2.7-8.1 kg/ha, depending on water depth. Phytotoxicity Some conifers are susceptible to dichlobenil vapour, due to their bark structure. Formulation types GR; WP. Selected products: 'Casoron' (Crompton); 'Barrier' (PBI/Gordon)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Casoron G' (Crompton); 'Decabane' (BASF); 'Sierraron' (Scotts UK); 'Silbenil' (Isagro) Discontinued products: 'Prefix D' * (Cyanamid)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1769; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 979.03; A. van Rossum, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 311), by capillary gc (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E ,65), or by spectrometry. Residues determined by glc (K. I. Beynon et al., J. Sci. Food Agric., 1966, 17, 151).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin or eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >250 mg/m3. NOEL Combined oral toxicity study NOEL (2 y) for rats 2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. In the reproduction study for rats NOEL 60 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.025 mg/kg b.w. Other Not mutagenic in Ames, cell mutation, chromosomal abberation, cell transformation, DNA repair and micronucleus tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R21| N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 683 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail c. 5200, mallard ducks >5200 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) 5-13 mg/l (various fish species). Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 6.2 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 2.0, Anabaena flos-aquae 2.7 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 (contact) >11 mg/bee. Worms LD50 for earthworms >1000 mg 'Casoron G'/kg substrate. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to carabids (Poecilus cupreus and Pardosa spp.). Semi-field testing on Aleochara bilineata showed adequate recovery after initial adverse effects. No effect on soil microflora.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Metabolised and excreted mainly as hydroxylated conjugates. For fate in animals, see K. I. Beynon & A. N. Wright, Residue Rev., 1972, 43, 23; A. Verloop, ibid., 1972, 43, 55. Plants The soil metabolite 2,6-dichlorobenzamide can be taken up by plants via the roots. Plant metabolism involves ring hydroxylation (at the 3-position and, to a lesser extent, at the 4-position) of both dichlobenil and 2,6-dichlorobenzamide, and subsequently conjugation with a sugar. See K. I. Beynon & A. N. Wright, Residue Rev., 1972, 43, 23; A. Verloop, ibid., 1972, 43, 55. Soil/Environment Has a low leaching potential. In soil, dichlobenil gradually undergoes microbial degradation to 2,6-dichlorobenzamide, which is slowly broken down to 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid. Half-life of dichlobenil in soil may vary between 1 and 6 months, depending on soil type. See K. I. Beynon & A. N. Wright, Residue Rev., 1972, 43, 23; A. Verloop, ibid., 1972, 43, 55.
|