|
cyromazine
Insecticide
IRAC 17
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cyromazine (BSI, draft E-ISO, (f) draft F-ISO, ANSI)
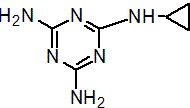
IUPAC name N-cyclopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine
Chemical Abstracts name N-cyclopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine
CAS RN [66215-27-8] Development codes CGA 72 662 (Ciba-Geigy) Official codes OMS 2014
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 166.2 M.f. C6H10N6 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 224.9 °C V.p. 4.48 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = -0.061 (pH 7.0) (OECD 107) Henry 5.8 ´ 10-9 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.35 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 13 g/l (OECD 105) (pH 7.1, 25 ºC). In methanol 22, isopropanol 2.5, acetone 1.7, n-octanol 1.2, dichloromethane 0.25, toluene 0.015, hexane 0.0002 (all in g/kg, 20 ºC). Stability Stable up to 310 ºC. Stable to hydrolysis for 28 days at up to 70 ºC. pKa 5.22, weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insect growth regulator reported by R. D. Hall et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1980, 73, 564) and by R. E. Williams et al. (Poultry Sci., 1980, 59, 2207). Introduced as an insecticide by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents GB 1587573; BE 857896 Manufacturers Gilmore; Sannong; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor. Mode of action Insect growth regulator with contact action, which interferes with moulting and pupation. When used on plants, action is systemic: applied to the leaves, it exhibits a strong translaminar effect; applied to the soil, it is taken up by the roots and translocated acropetally. Uses Control of Diptera larvae in chicken manure by feeding to the poultry or treating the breeding sites. Also used to control flies on animals. Used as a foliar spray to control leaf miners (Liriomyza spp.) in vegetables (e.g. celery, melons, tomatoes, lettuce), mushrooms, potatoes and ornamentals, at 75-225 g/ha; also used at 190-450 g/ha in drench or drip irrigation. Formulation types SL; WP. Selected products: 'Trigard' (plant protection) (Syngenta); 'Cyclon' (Cequisa); 'Genialroc' (Rocca); 'Gilzine' (Gilmore); 'Neporex' (veterinary use) (Novartis A H); 'Trivap' (Vapco); 'Vetrazin' (veterinary use) (Novartis A H)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Armor' (Syngenta); 'Citation' (Syngenta); 'Larvadex' (Syngenta); 'Patron' (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by glc or hplc. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 59, 61 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 3387 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >3100 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant; non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.720 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 300, mice 1000 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1990]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1785, Japanese quail 2338, Pekin ducks >1000, mallard ducks >2510 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish >90, carp, catfish and rainbow trout >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >9.1 mg/l. Algae LC50 124 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to adult honeybees (no contact action up to 5 mg/bee). Worms LC50 >1000 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Non-toxic.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, cyromazine is efficiently excreted, mainly as the parent compound. Plants Rapidly metabolised in plants. The principal metabolite is melamine. Soil/Environment Cyromazine and its main metabolite melamine are moderately mobile. Numerous studies conducted (laboratory and field) demonstrate that cyromazine is efficiently degraded by biological mechanisms.
|