|
cyprodinil
Fungicide
FRAC 9, D1; anilinopyrimidine
NOMENCLATURE
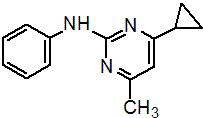
Common name cyprodinil (pa ISO)
IUPAC name 4-cyclopropyl-6-methyl-N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine
Chemical Abstracts name 4-cyclopropyl-6-methyl-N-phenyl-2-pyrimidinamine
CAS RN [121552-61-2] Development codes CGA 219417 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 225.3 M.f. C14H15N3 Form Fine beige powder, with a weak odour. M.p. 75.9 ºC V.p. 5.1 ´ 10-1 mPa (crystal modification A); 4.7 ´ 10-1 mPa (crystal modification B) (both 25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.9 (pH 5.0), 4.0 (pH 7.0), 4.0 (pH 9.0) (25 ºC) Henry 6.6 ´ 10-3 to 7.2 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc., depending on crystal modification) S.g./density 1.21 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 20 (pH 5.0), 13 (pH 7.0), 15 (pH 9.0) (all in mg/l, 25 ºC). In ethanol 160, acetone 610, toluene 440, n-hexane 26, n-octanol 140 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Hydrolytically stable: DT50 in pH range 4-9 (25 ºC) >>1 y. Photolysis DT50 in water 5-30 d. pKa 4.44, weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by U. J. Heye et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis.,1994, 2, 501). Developed and introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). First marketed in 1994. Patents EP 310550 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Proposed inhibitor of the biosynthesis of methionine and the secretion of fungal hydrolytic enzymes. There is no cross resistance to benzimidazoles, carbamates, dicarboximides, imidazoles, morpholines, quinolines, strobilurins or triazoles. Mode of action Systemic product, with uptake into plants after foliar application and transport throughout the tissue and acropetally in the xylem. Inhibits penetration and mycelial growth both inside and on the leaf surface. Uses As a foliar fungicide for use in cereals, grapes, pome fruit, stone fruit, strawberries, vegetables, field crops and ornamentals; and as a seed dressing on barley. Controls a wide range of pathogens, such as Tapesia yallundae and T. acuformis, Erysiphe spp., Pyrenophora teres, Rhynchosporium secalis, Botrytis spp., Alternaria spp., Venturia spp. and Monilinia spp., at 150-750 g/ha. Formulation types EC; WG. Compatibility Some incompatibility problems have been reported when added to liquid formulations, but not if mixed in reverse order. Selected products: 'Chorus' (Syngenta); 'Unix' (Syngenta); 'Amtrak' (Barclay); mixtures: 'Radius' (+ cyproconazole) (Syngenta); 'Stereo' (+ propiconazole) (Syngenta); 'Switch' (+ fludioxonil) (foliar) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Vangard' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Botryl' (+ fludioxonil) (ornamentals) (Syngenta); 'Celeste Orge' (+ fludioxonil+ tebuconazole+ anthraquinone) (seed treatment, France) (Syngenta); 'Erelia' (+ propiconazole) (Syngenta); 'Iridia' (+ cyproconazole) (France) (Syngenta); 'Koara' (+ propiconazole) (France) (Syngenta); 'Solitär' (+ fludioxonil+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment) (Syngenta); 'Podium' (+ fenpropidin) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Chieftain' * (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Play' * (+ difenoconazole) (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by hplc. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritant to eyes and skin (rabbits). Skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1200 mg/m3 air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 3 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1.5 y) for mice 196 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 65 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.03 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-mutagenic, non-teratogenic and non-oncogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III, IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for mallard ducks >500, bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5200 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 2.41 mg/l, bluegill sunfish 2.17 mg/l (static) and 3.2 mg/l (flow-through). Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.033 mg/l. Algae EbC50 (72 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 5.2 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 for Lemna gibba 7.71, Gammarus sp. 1.8, Ostracoda 1.1, Simocephalus vetulus 0.15, Tamnocephalus 0.12 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, oral and contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 192 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to Aleochara bilineata, Coccinella septempunctata, Aphidius rhopalosiphi, Poecilus cupreus, Episyrphus.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration, cyprodinil is rapidly absorbed and almost completely eliminated with urine and faeces. Metabolism proceeds by 4-hydroxylation of the phenyl and 5-hydroxylation of the pyrimidine rings, followed by mono- or di-sulfation. Residues in tissues were generally low and there was no evidence for accumulation or retention of cyprodinil or its metabolites. Plants Metabolism proceeded mainly via hydroxylation of the 6-methyl group of the pyrimidine ring, as well as hydroxylation of the phenyl and pyrimidine rings, followed by sugar conjugation. Soil/Environment In soil, the compound dissipated with DT5020-60 d at normal soil humidities and soil temperatures, whereby formation of bound residues represents the major route for dissipation. In leaching and adsorption/desorption experiments, the compound proved to be immobile in soil. Photolytic DT50 in water 13.5 d.
|