|
cypermethrin
Insecticide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cypermethrin (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, BAN); cyperméthrine ((f) F-ISO)
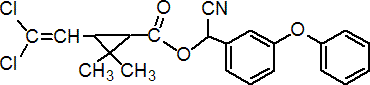
IUPAC name (RS)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1RS,3RS;1RS,3SR)-3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
Roth: (RS)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1RS)-cis-trans-3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 3-(2,2-dichloroethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
CAS RN [52315-07-8] (formerly [69865-47-0], [86752-99-0] and many other numbers) Development codes NRDC 149; PP383 (ICI); WL 43 467 (Shell); LE 79-600 (Rhône-Poulenc); FMC 30980 Official codes OMS 2002
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is 90% pure. Mol. wt. 416.3 M.f. C22H19Cl2NO3 Form Odourless crystals; (tech., yellow-brown viscous semi-solid at ambient temperatures). M.p. 61-83 °C, depending on isomer ratio V.p. 2.0 ´ 10-4 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 6.6 Henry 2.0 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.24 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.004 mg/l (pH 7). In acetone, chloroform, cyclohexanone, xylene >450, ethanol 337, hexane 103 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Relatively stable in neutral and weakly acidic media, with optimum stability at pH 4. Hydrolysed in alkaline media; DT50 1.8 d (pH 9, 25 °C); stable at pH 5 and 7 (20 °C). Relatively stable to light in field situations. Thermally stable up to 220 ºC. F.p. Not auto-flammable; non-explosive
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by M. Elliott et al. (Pestic. Sci., 1975, 6, 537). Developed by Ciba-Geigy, ICI (both now Syngenta AG), Mitchell Cotts and Shell International Chemical Co. (now BASF AG). Patents GB 1413491 to NRDC Manufacturers Agro-Chemie; Agrochem; Aimco; Ankur; Atabay; BASF; Bharat; DE-NOCIL; Dhanuka; Dow AgroSciences; Ficom; FMC; Gharda; Jiangsu Yangnong; Krishi Rasayan; Lucava; Meghmani; Mitchell Cotts; Mitsu; Parry; Rallis; Rotam; RPG; SC Enviro Agro; Sharda; Sundat; Syngenta; Tagros; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of the insect, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Also exhibits anti-feeding action. Good residual activity on treated plants. Uses Control of a wide range of insects, especially Lepidoptera, but also Coleoptera, Diptera, Hemiptera, and other classes, in fruit (including citrus), vines, vegetables, potatoes, cucurbits, lettuce, capsicums, tomatoes, cereals, maize, soya beans, cotton, coffee, cocoa, rice, pecans, oilseed rape, beet, ornamentals, forestry, etc. Control of flies and other insects in animal houses; and mosquitoes, cockroaches, houseflies and other insect pests in public health. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide. Formulation types EC; GR; UL; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Basathrin' (BASF); 'Cymbush' (Syngenta); 'Cymperator' (Syngenta); 'Ripcord' (BASF); 'Agrotrina' (Westrade); 'Alfa' (Trithin); 'Arrivo' (FMC); 'Cekumetrin' (Cequisa); 'Ciper QL' (Inquiport); 'Cynoff' (FMC); 'Cyperguard' (Gharda, Nufarm UK); 'Cyperil' (Agro-Chemie); 'Cypersan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Cyproid' (Aimco); 'Cyrux' (United Phosphorus); 'Cythrine' (Agriphar); 'Demar' (Mitsu); 'Devicyper' (Devidayal); 'Drago' (Inquiport); 'Durin' (Dhanuka); 'Grand' (Sanonda); 'Hilcyperin' (Hindustan); 'Kecip' (Kemio); 'Kruel' (Reposo); 'Lacer' (RPG); 'Mortal' (Crop Health); 'Ralothrin' (Rallis); 'Ranjer' (Ramcides); 'Rasayanrin' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Rocyper' (Rotam); 'Starcyp' (Shaw Wallace); 'Suraksha' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Termicidin' (Vapco); 'Visher' (Vipesco); 'Volcyper' (Ralchem); mixtures: 'Quick' (+ quinalphos) (Nagarjuna Agrichem)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Barricade' (BASF); 'Cyperkill' (Mitchell Cotts, Chiltern); 'Demon' (Syngenta); 'Flectron' (BASF); 'Folcord' (BASF); 'Gammexane' (Argentina) (Syngenta); 'Imperator' (Syngenta); 'Permasect C' (Mitchell Cotts, Nufarm UK); 'Stockade' (BASF); 'Toppel' (Syngenta); 'Agrocyde' (Tecomag); 'Agrocyper' (Chemvet); 'Agro-Cypethrin' (AgroSan); 'Ammo' (FMC); 'Arjun' (Parry); 'Auzar' (Biostadt); 'Cipermin' (Chemiplant); 'Combat' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Counter' (public health) (Vapco); 'Cypcord' (BEC); 'Cyper-Atac' (Trithin); 'Cypertox' (FCC, Crystal); 'Devicyprin' (Devidayal); 'Indothrin' (Indofil); 'Kepermin' (Kemio); 'Killer' (public health) (Vapco); 'Kripcord' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Kyclothrin' (Papaeconomou); 'MCC 25' (Chiltern); 'Prik' (Kemio); 'Pucara' (CAS); 'Record' (Ramcides); 'Rudra' (Parry); 'Scipio' (Bayer CropScience); 'Sherpa' (Bayer CropScience); 'Sniper' (public health) (Vapco); 'Syper' (Agrochem); 'Trofy' (RPG); 'Ustaad' (United Phosphorus) mixtures: 'Polytrin C' (+ profenofos) (Syngenta); 'Amber' (+ piperonyl butoxide+ tetramethrin) (Trithin); 'Anaconda' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Aimco); 'Baytan T' (+ triadimenol) (seed treatment) (Bayer CropScience); 'Concentrate 2' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Trithin); 'Dorsan-C' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Luxembourg); 'Fency' (+ fenitrothion) (Efthymiadis); 'Ideal-2' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Indofil); 'Mega C-505' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Crop Health); 'Murfothrin' (+ mecarbam) (Efthymiadis); 'Nagata' (+ ethion) (Rallis); 'Ninja' (+ methamidophos) (Reposo); 'NPB' (+ piperonyl butoxide+ bioallethrin S-cyclopentenyl isomer) (Trithin); 'Pestan super' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Efthymiadis); 'Premis 25' (+ triticonazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Raxil C' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Australia) (Bayer CropScience); 'SFB' (+ muscalure) (Trithin); 'Sherdiphos' (+ dimethoate+ triazophos) (Bayer CropScience); 'Ulka' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Biostadt) Discontinued products: 'Ambush C' * (Zeneca); 'Afrisect' * (Stefes); 'Cyper 10' * (Quadrangle); 'Cypercopal' * (Gilmore); 'Siege' * (Chemsearch) mixtures: 'Tifatol' * (+ CGA 50 439) (cypermethrin is rich in cis- isomers) (Novartis); 'Duracide Cyp' * (+ piperonyl butoxide+ tetramethrin) (Endura)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles. By glc with FID (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.03, 986.02; CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2047; A. Sapiets et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 33); total cypermethrin and diastereoisomer ratio by hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2052. 1994). Residues determined by glc with ECD (idem, ibid.; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 998.01). Details available from BASF or Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews See A. J. Gray & D. M. Soderlund, Chapt. 5 in "Insecticides". See also JECFA 47, FAO/WHO 36, 37 (see part 2 of Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 250-4150 (tech. 7180), mice 138 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >4920, rabbits >2460 mg/kg. Slight skin and eye irritant (rabbits). May be a weak skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 2.5 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for dogs 5, rats 7.5 mg/kg. ADI (JECFA evaluation) 0.05 mg/kg b.w. [1996]; (JMPR) 0.05 mg/kg b.w. [1981]. Other Oral toxicity values for cypermethrin depend on such factors as: carrier, cis:trans ratio of the sample, species, sex, age and degree of fasting. Values reported sometimes differ markedly. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification (Xn; R20/22| R43| N; R50)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >10 000, chickens >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.69, sheepshead minnow 2.37 mg/l; under field conditions, fish are not at risk from normal agricultural usage. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.15 mg/l. Bees Highly toxic to honeybees in laboratory tests, but field applications at recommended dosages do not put hives at risk. LD50 (24 h) (oral) 0.035 mg/bee; (topical) 0.02 mg/bee. Other beneficial spp. Not toxic to Collembola (J. A. Wiles & G. K. Frampton, Pestic. Sci., 47, 273 (1996)).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 82 (WHO, 1989). EHC review concludes that biological degradation is rapid, and consequently levels of cypermethrin and its degradation products in soil and surface waters are very low. Animals For studies of the biotransformation of cypermethrin in animal tissues, see Pestic. Sci., 1987, 21, 1 and ibid., 1990, 30, 159. Soil/Environment In soil, typical DT50 60 d (fine sandy loam); hydrolysis with cleavage of the ester bond occurs and also further hydrolytic and oxidative degradation; see T. R. Roberts & M. E. Standen, Pestic. Sci., 1977, 8, 305. Field dissipation is much faster. Koc 26 492-144 652; Kf 821-1042; not pH dependent. In river water, rapid degradation occurs, DT50 c. 5 d. DT50 for photochemical oxidative degradation in air 3.47 h.
|