|
cycloxydim
Herbicide
HRAC A WSSA 1; cyclohexanedione oxime
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cycloxydim (BSI, draft E-ISO); cycloxydime ((f) draft F-ISO)
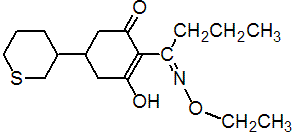
IUPAC name (?-2-[1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-thian-3-ylcyclohex-2-enone
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-(tetrahydro-2H-thiopyran-3-yl)-2-cyclohexene-1-one; in an early publication, the tautomer 2-[1-(ethoxyamino)butylidene]-5-(tetrahydro-2H-thiopyran-3-yl)-1,3-cyclohexanedione was named
CAS RN [101205-02-1] cycloxydim; [99434-58-9] for tautomer Development codes BAS 517H (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 325.5 M.f. C17H27NO3S Form Colourless, odourless crystals; (tech., yellow beige crystals, with a weak aromatic odour; dark brown oil above m.p.). M.p. c. 41 ºC V.p. 0.01 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = c. 1.36 (pH 7, 25 ºC). Henry 6.1 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.165 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 53 mg/l (pH 4.3, 20 ºC). In acetone, ethanol, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, toluene >250 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). In n-hexane 29 g/kg (20 ºC). Stability Stable at room temperature for ³1 y; unstable above 30 ºC; decomposes c. 200 ºC. DT50 in argon atmosphere at 20 000 lux (simulated sunlight, 15-20 ºC) >192 h; in air at 80 000 lux (simulated sunlight, 20 ºC) 0.8 h. pKa c. 4.17 F.p. 89.5 ºC (tech.)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by W. Zwick et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1985, 1, 85) and by N. Meyer et al. (ibid., p. 93). Introduced by BASF AG; first marketed in France 1989. Patents EP 70370; EP 71707; US 4422864; DE 3121355 Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Fatty acid synthesis inhibitor, by inhibition of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase). Mitosis inhibitor. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed rapidly by the foliage, with translocation both acropetally and basipetally. Uses Post-emergence control of annual and perennial grasses (except red fescue and Poa spp.) in broad-leaved crops (e.g. oilseed rape, beans, potatoes, brassicas, cotton, celery, fennel, beetroot, sugar beet, fodder beet, sunflowers, soya beans, flax, alfalfa, crucifers, alliums). Applied at 100-400 g/ha against annual grasses, 500-600 g/ha against Agropyron repens. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to all broad-leaved crops, when used as directed. Phytotoxic to graminaceous crops. Formulation types EC. Compatibility Should not be mixed with broad-leaved herbicides. Selected products: 'Focus' (BASF); 'Laser' (BASF); 'Stratos' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Valentia' (GreenCrop)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues analysed by derivatisation to glutaric acid derivatives and measurement by glc with S-FPD. Details available from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats c. 5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.28 mg/l. NOEL (18 mo) for rats 7 mg/kg b.w. daily; (2 y) for mice 32 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.07 mg/kg [1992]. Other Non-mutagenic, non-carcinogenic, non-teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout 220, bluegill sunfish >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 132 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata >100 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 for Lemna gibba >100 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees; LD50 >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals See Soil/Environment. Plants See Soil/Environment. Soil/Environment Rapidly broken down in plants, animals and in the soil by oxidation, conjugation, rearrangement, hydroxylation, and reductive ether-cleavage (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1988, 1, 335-341). DT50 (lab.) 0.5-12 d (20 ºC). Koc <10-183.
|