|
cycloprothrin
Insecticide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
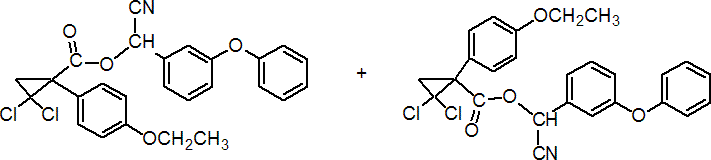
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cycloprothrin (BSI, draft E-ISO); cycloprothine ((f) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name (RS)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (RS)-2,2-dichloro-1-(4-ethoxyphenyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 2,2-dichloro-1-(4-ethoxyphenyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
CAS RN [63935-38-6] unstated stereochemistry Development codes GH-414 (CSIRO); NK-8116 (Nippon Kayaku) Official codes OMS 3049
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 482.4 M.f. C26H21Cl2NO4 Form Yellow to brown viscous liquid (tech.). B.p. 140-145 ºC/0.001 mmHg V.p. 2.13 ´ 10-3 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.19 S.g./density 1.256 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 0.091 mg/l (25 ºC). Readily soluble in most organic solvents, but only moderately soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Stability Stable £190 ºC and to light.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide invented at CSIRO and reported by G. Nolan et al. (Nature (London), 1978, 272, 734), and its development described by S. Kirihara & Y. Sakurai (Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1988, No. 53, 22). Introduced in Japan (1987) by Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd. Manufacturers Nippon Kayaku
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Insecticide with contact and stomach action. Also exhibits antifeeding and repellent activities. Uses Control of rice water weevils (Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus) and other insects in paddy rice, fruit, vegetables, tea, cotton, soya beans, and in forestry. Applied at 20-40 g/ha. Formulation types DP; EC; GR. Selected products: 'Cyclosal' (Nippon Kayaku)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by glc.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews J. Pestic. Sci., 16, 697-702 (1991). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg; no skin or eye irritation by tech., moderate irritation by GR and DP. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.5 mg/l air. NOEL (101 w) for rats 20 ppm. Other No teratogenic, carcinogenic or reproductive effects in rats in lifetime tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >5000, hens >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp >50, goldfish >10, rainbow trout 1.6 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) >10 mg/l. Bees Toxic to honeybees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In continual oral administration to rats, cycloprothrin is rapidly and completely excreted in urine and faeces (K. Seguchi et al., J. Pestic. Sci., 16, 591-598 (1991)). Plants For metabolism in rice plants, see K. Seguchi et al., J. Pestic. Sci., 16, 599-607 (1991). Soil/Environment When cycloprothrin was applied to simulated paddy water, the concentration absorbed in rice plants increased with time to a maximum within 7 days. The concentration was very low, and unchanged cycloprothrin was not found in the grain.
|