|
cyazofamid
Fungicide
FRAC 21, C4; Qil
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cyazofamid (BSI, pa ISO)
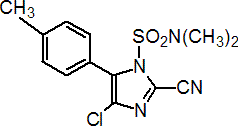
IUPAC name 4-chloro-2-cyano-N,N-dimethyl-5-p-tolylimidazole-1-sulfonamide
Chemical Abstracts name 4-chloro-2-cyano-N,N-dimethyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole-1-sulfonamide
CAS RN [120116-88-3] Development codes IKF-916 (Ishihara Sangyo)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 324.8 M.f. C13H13ClN4O2S Form Ivory, odourless powder. M.p. 152.7 °C V.p. 1.3 ´ 10-2 mPa (35 °C) KOW logP = 3.2 (25 °C) Henry >4.03 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (20°C, calc.) S.g./density 1.446 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.121 ppm (pH 5), 0.107 (pH 7), 0.109 (pH 9) (all 20 °C) Stability In water DT50 24.6 d (pH4), 27.2 d (pH 5), 24.8 d (pH 7).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by S. Mitani et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1998, 2, 351). First registered in UK and Korea in 2001, by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd. Manufacturers Ishihara Sangyo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Both cyazofamid and the strobilurin fungicides inhibit at complex III (ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase) in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. However, cyazofamid inhibits Qi (the ubiquinone reducing site) of cytochrome bc1, whereas the strobilurins inhibit Qo (the ubiquinol oxidising site) of cytochrome bc1. Selectivity appears to be due to a difference in the susceptibility of the target enzyme Mode of action Foliar and soil preventative fungicide with residual activity and rainfastness, together with moderate translaminar and curative activity. Inhibits all stages in the lifecycle of Phytophthora infestans. Uses For control of Oomycete and Plasmodiophora diseases, such as potato and tomato late blight (Phytophthora infestans), downy mildews (e.g. of cucumber, Pseudoperonospora cubensis), at 60-100 g/ha. Its use as a foliar treatment on other crops, such as, vines, onions, lettuce, rice and crucifers is under investigation. Soil treatments are being evaluated for turf and crucifers. Formulation types SC Selected products: 'Docious' (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Mildicut' (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Ranman' (Ishihara Sangyo)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not irritating to eyes or skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats >5.5 mg/l. Other Negative in Ames, REC assay, chromosomal aberration and mouse micronucleus tests.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD 50 for quail and ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC 50 for quail and ducks >5 mg/ml. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >0.510, carp > 0.14 mg/l (both the highest achievable concentration in water). Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >0.14 mg/l (highest achievable concentration in water). Algae EbC50 (72 h) for Selenastrum 0.858 mg/l. Bees LD50 for honey bees (oral) >151.7 mg/bee; (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms Acute LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to Aphidius rhopalosiphi, Typhlodromus pyri, Chrysoperla carnea, Aleochara bilineata.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soil, DT50 3-5 d. Koc 736-2172.
|