|
cyanazine
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,3,5-triazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cyanazine (BSI, E-ISO, (f) F-ISO, WSSA)
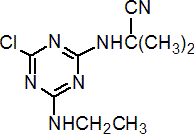
IUPAC name 2-(4-chloro-6-ethylamino-1,3,5-triazin-2-ylamino)-2-methylpropiononitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[[4-chloro-6-(ethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]-2-methylpropanenitrile
CAS RN [21725-46-2] EEC no. 244-544-9 Development codes WL 19 805; SD 15 418 (both Shell); DW 3418
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade ³95% pure. Mol. wt. 240.7 M.f. C9H13ClN6 Form Tech. cyanazine is a white crystalline solid. M.p. 167.5-169 ºC; (tech., 166.5-167 ºC) V.p. 2 ´ 10-4 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 2.1 S.g./density 1.29 kg/l (20 ºC) Solubility In water 171 mg/l (25 ºC). In methylcyclohexanone, chloroform 210, acetone 195, ethanol 45, benzene, hexane 15, carbon tetrachloride <10 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to heat (1.8% decomposition after 100 h at 75 ºC), and to light. Stable in solution between pH 5 and 9, hydrolysed by strong acids and alkalis. pKa 0.63, v. weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by W. J. Hughes et al. (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 21st, 1967, p. 27). Introduced by Shell Research Ltd (now BASF AG, who sold commercial rights in EU to Feinchemie Schwebda in 2001). Patents GB 1132306 Manufacturers BASF; Griffin
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Maize tolerance of triazines is attributed to conjugation with glutathione. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots (with translocation acropetally to the leaves), and also by the foliage. Uses Used for general weed control (a) pre-emergence to the crop, at 1-3 kg/ha, in broad beans, maize and peas; (b) post-emergence in barley and wheat during the early tillering stage, at 0.26-0.33 kg/ha in combination with a variety of other herbicides for the control of broad-leaved weeds. Other crops for which it is used include: cotton, oilseed rape, forestry, potatoes, soya beans, sugar cane. Phytotoxicity Selective if applied according to label recommendations. Formulation types GR; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Bladex' (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Cy-Pro' (Griffin)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Gramex' (Japan) (BASF); 'Canter' (Barclay); 'Fortrol' (Feinchemie Schwebda) mixtures: 'Bellater' (+ atrazine) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Bullet' (+ pendimethalin) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Halbard' (+ diflufenican) (Feinchemie Schwebda) Discontinued products: 'Match' * (BASF); 'Reply' * (Cyanamid); 'Urlac' * (BASF) mixtures: 'Activus' * (+ pendimethalin) (Cyanamid); 'Topshot' * (+ 2,4-DB+ bentazone) (Cyanamid); 'Angle' * (+ terbuthylazine) (Novartis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2039) or by glc or hplc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.32; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 275). Residues in plants determined by glc with ECD or FID (ibid.), and in soils by glc or hplc (ibid.). In water, by lc with u.v. detection (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 992.14).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 182-334, mice 380, rabbits 141 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >1200, rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes. Inhalation LC50 >2460 mg/m3 air, as cyanazine dust. NOEL (2 y) for rats 12, dogs 25 mg/kg diet. Water GV 0.6 mg/l (TDI 0.198 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II (DF, SC and WP), III (GR) EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2000, quail 400 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for harlequin fish 10 mg/l; LC50 (96 h) for fathead minnow 16 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 42-106 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) <0.1 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees. LD50 (topical) >100 mg/bee (tech. in acetone); (oral) >190 mg/bee (tech. as dust).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats and dogs, following oral administration, cyanazine is rapidly metabolised and eliminated within c. 4 days. Plants In plants, the nitrile group is hydrolysed to a carboxylic acid group, and the chlorine atom is replaced by a hydroxy group (K. I. Beynon et al., Pestic. Sci., 1972, 3, 293-305). Soil/Environment Microbial degradation in soil occurs within one growth period. Metabolism is similar to that in plants. DT50 in soil c. 2 w. (K. I. Beynon et al., Pestic. Sci., 1972, 3, 293-305, 379-401).
|