|
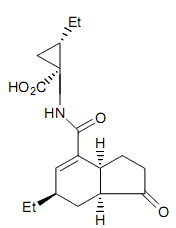
Coronatine
from Pseudomonas syringae pv. Glycinea
Storage Temperature –20 °C
CAS#: 62251-96-1
Synonyms: COR; Cyclopropanecarboxylic acid, 2-ethyl-
1-[[(6-ethyl-2,3,3a,6,7a-hexahydro-1-oxo-1H-inden-
4-yl)carbonyl] amino]
Product Description
Molecular weight: 319.4 Da
Molecular formula: C18H25NO4
Coronatine (COR) is a polyketide phytotoxin produced by several members of the Pseudomonas syringae group of pathovars.
The structure of COR has two distinct components: the polyketide coronafacic acid (CFA) and coronamic acid (CMA), an ethylcyclopropyl amino acid derived from isoleucine.
The primary symptom elicited by COR is a diffuse chlorosis that can be induced on a wide variety of plant species. The reaction of Arabidopsis thaliana to exogenously applied COR is atypical; instead of chlorosis, anthocyanins accumulate at the site of inoculation and the tissue develops a strong purple hue.
COR is also known to induce hypertrophy, to inhibit root elongation, and to stimulate ethylene production.
COR is reported to induce several changes in tomato tissue.
For example, the epidermal wall was significantly thicker and the chloroplasts stained more intensively and were smaller. One of the most pronounced effects was the appearance of proteinase inhibitors.
Striking structural and functional homologies between COR, methyl jasmonate, and 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid suggest that COR mimics the octadecanoid signaling molecules of higher plants.
Purity: >95% (HPLC)
Preparation Instructions : Coronatine is soluble in methanol (20 mg/ml), DMSO (20 mg/ml), and in water (0.2 mg/ml).
Storage/Stability: The supplied unopened vial is stable for 2 years if stored at –20 °C. A solution at 0.2 mg/ml in water, methanol, or DMSO is stable for 2 years at –20 °C (as
determined by HPLC).
|