|
copper hydroxide
Fungicide, bactericide
FRAC M1; multi-site: inorganic
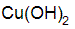
NOMENCLATURE
IUPAC name copper hydroxide; copper(II) hydroxide; cupric hydroxide
Chemical Abstracts name copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2)
CAS RN [20427-59-2]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 97.6 M.f. CuH2O2 Form Blue-green solid. Solubility In water 2.9 mg/l (pH 7, 25 ºC). Readily soluble in aqueous ammonia. Insoluble in organic solvents. Stability Dehydrated >50 ºC for extended periods. Decomposes at 140 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide introduced in USA (1968) by Kennecott Corp. Manufacturers Crystal; Griffin; Ingeniería Industrial; Sulcosa
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Non-specific thiol reactant, inhibiting respiration. Copper-II-ion (Cu++) is taken up by the spores during germination and accumulates until a sufficiently high concentration is achieved to kill the spore cell; the activity is limited to the prevention of spore germination. Mode of action Protectant fungicide and bactericide. Deposits must be on the crop before fungal spores begin to germinate. Uses For control of Peronosporaceae in vines, hops, and brassicas; Alternaria and Phytophthora in potatoes; Septoria in celery; and Septoria, Leptosphaeria, and Mycosphaerella in cereals, at 2-4 kg/ha or 300-400 g/100 l. Formulation types SC; WP. Compatibility Not compatible with acids, dicloran or calcium polysulfide. Selected products: 'Coproxide' (Vapco); 'Hidrocob' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Nu-Cop' (Micro Flo); 'Rameazzurro' (Agrimix); 'Vitra' (IQV); mixtures: 'Techlead-C' (+ ipconazole) (Kureha, Kumiai)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Blue Shield' (Cuproquim); 'Champ' (Nufarm SA, Nufarm Americas); 'Champion' (Nufarm SA, Nufarm Americas, Agrodan); 'Cupravit Blue' (Bayer CropScience); 'Cuproxyde' (Nufarm Americas); 'Danis' (Aragro); 'Funguran OH' (Spiess-Urania); 'Hidrocobre' (IQV); 'Hidroflow' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Kocide' (RPG, Cuproquim); 'KOP Hydroxide' (Drexel); 'Parasol' (Nufarm SA, Nufarm Americas); 'Spin Out' (Fargro); 'Sulcox OH' (Sulcosa) mixtures: 'GX-270' (+ copper sulfate) (Griffin); 'Kocide Combi' (+ mancozeb) (Griffin); 'ManKocide' (+ mancozeb) (Griffin); 'Control III' (+ cymoxanil) (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Nobact' (+ folpet) (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Oracle' (+ fenamidone) (Bayer CropScience); 'Ridomil Copper 70W' (+ metalaxyl) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold Copper' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Syngenta); 'Utilis' (+ fenamidone) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Kocide' * (Griffin)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by iodometric titration (AOAC Methods, 14th Ed., 6.015-6.016; CIPAC Handbook, 1970, 1, 226).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 489 mg/kg (tech.). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >3160 mg/kg. Severely irritating and corrosive to eyes, mild skin irritant. Inhalation LC50 > 2 mg/l air. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
High concentrations of this type of copper are toxic to aquatic organisms and may cause a significant decrease in populations of aquatic invertebrates, plants, and fish. Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 3400, mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg. Dietary LD50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >10 000 ppm. Fish LC50 (24 h) for rainbow trout 0.08 mg/l; (96 h) for fathead minnow 0.023, bluegill sunfish >180 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 6.5 ppb. Bees Non-toxic to honeybees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Copper is an essential element and is under homeostatic control in mammals. Plants Plants resist copper accumulation and translocation to stems, leaves or seeds. Most plants growing on soils containing up to 1000 ppm copper showed only slight elevation in copper content compared to plants grown in normal soils. Soil/Environment Copper is a basic chemical element and does not dissipate in the soil. Soluble copper ions in the soil water are rapidly complexed by organic matter, precipitated as hydroxides, or insolubilised as precipitates with sulfides, hydroxides, carbonates, or phosphates.
|