|
clofentezine
Acaricide
IRAC 10A; mite growth inhibitor
NOMENCLATURE
Common name clofentezine (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (f) draft F-ISO)
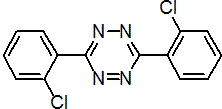
IUPAC name 3,6-bis(2-chlorophenyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
Chemical Abstracts name 3,6-bis(2-chlorophenyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
Other names bisclofentezin* (rejected common name proposal) CAS RN [74115-24-5] EEC no. 277-728-2 Development codes NC 21 314 (Fisons)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 303.1 M.f. C14H8Cl2N4 Form Magenta crystals. M.p. 182.3 ºC V.p. 1.3 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 ºC) (gas saturation and glc) KOW logP = 4.1 (25 ºC) Henry 1.97 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.51 (20 °C) Solubility In water 2.5 mg/l (pH 5, 22 ºC). In dichloromethane 37, acetone 9.3, hexane 1, ethanol 0.5 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability The a.i. and formulated products are stable to light, heat and air; on hydrolysis (22 ºC), DT50 248 h (pH 5), 34 h (pH 7), 4 h (pH 9). F.p. Low flammability
COMMERCIALISATION
History Acaricide reported by K. M. G. Bryan et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1981, 1, 67) and relationships between chemical structure and biological activity by P. J. Brooker et al. (Pestic. Sci., 1987, 18, 179). Introduced by FBC Limited (now Bayer CropScience) and transferred to Makhteshim-Agan Industries in 2001. Patents EP 5912 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Specific acaricide with contact action, and long residual activity. Inhibits embryo development. Uses Control of eggs and young motile stages (but not adults) of Panonychus ulmi and Tetranychus spp. on pome fruit and stone fruit (20 g/hl), citrus fruit (12.5-20 g/hl), nuts, vines (20 g/hl), hops, strawberries (200-300 g/ha), cucurbits (100-400 g/ha), cotton (150-250 g/ha), and ornamentals (20-30 g/hl). Has no effect on predatory mites or beneficial insect species. Phytotoxicity May cause slight injury to glasshouse roses. May cause a slight pink deposit on petals of white or pale flowers. Formulation types SC; WP. Compatibility 'Apollo' formulation is compatible with most pesticide products commonly used in orchards, except alkaline and copper products. Selected products: 'Apollo' (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); 'Niagara' (Rocca)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Apollo Plus' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Saran' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Acaristop' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Apolo' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cara' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Ovation' (Scotts) Discontinued products: 'Panatac' * (AgrEvo)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rp hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 18-23) or by visible spectroscopy. Residues in plants and soil determined by hplc. Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 47, 49 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5200 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2100 mg/kg. Mild eye and skin irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >9 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 40 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 50 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1986]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (company classification); EPA (formulation) III (50 SC)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >3000, bobwhite quail >7500 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >0.015, bluegill sunfish >0.25 mg/l (limits of solubility). Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >1.45 mg/l (limit of solubility). Algae Not toxic to Scenedesmus pannonicus up to limit of solubility. Other aquatic spp. Not toxic to aquatic organisms up to the limit of solubility. Bees Acute LD50 (oral) >20 mg/bee; LC50 (contact) >1500 ppm. Worms Not toxic to earthworms. Other beneficial spp. No known deleterious effects to beneficials, such as predatory mites and predaceous insects.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, undergoes metabolism by hydroxylation and exchange of the chlorine atoms on the rings for methylthio groups. Following oral administration, excretion occurs within 24-48 hours in the urine and faeces. Plants In metabolism studies, unchanged clofentezine was the major extractable residue. Trace amounts (4%) of 2-chlorobenzonitrile, the major photodegradation product, were also detected. Soil/Environment In soil, the major degradation route leads to 2-chlorobenzoic acid, and finally to CO2. DT50 in soil 65-85 d (15 ºC), 28-56 d (25 ºC), depending upon soil type. However, in laboratory studies, no leaching occurs. In water, 2-chlorobenzonitrile is the major product formed by hydrolysis and photodegradation, with smaller amounts of other compounds. Low solubility in water makes determination of soil adsorption constants difficult.
|