|
cinmethylin
Herbicide
HRAC Z
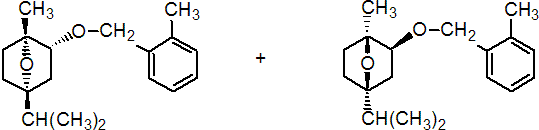
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cinmethylin (BSI, draft E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); cinméthyline ((f) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name (1RS,2SR,4SR)-1,4-epoxy-p-menth-2-yl 2-methylbenzyl ether
Chemical Abstracts name exo-(?-1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-2-[(2-methylphenyl)methoxy]-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane
CAS RN [87818-31-3] exo-(?- isomers; [87818-61-9] exo-(+)- isomer; [87819-60-1] exo-(-)- isomer Development codes SD 95 481 (Shell); WL 95 481 (Shell)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 274.4 M.f. C18H26O2 Form Dark amber liquid. B.p. 313 ºC/760 mmHg V.p. 10.1 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 3.84 Henry 4.40 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.014 g/ml (20 ºC) Solubility In water 63 mg/l (20 ºC). Miscible with a range of organic solvents. Stability Thermally stable up to 145 ºC. Hydrolytically stable from pH 5 to pH 9 at 25 ºC. Light-catalysed decomposition occurs in the presence of air. F.p. 147 °C (ASTM D93)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by J. W. Way et al. (Proc. 1985 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1, 265). Introduced by Shell International Chemical Co. Ltd (now BASF AG) in China (1989) and by E. I. du Pont de Nemours Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it). Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry May be metabolically activated, by cleavage of the benzyl ether, to form an analogue of naturally-occurring 1,4-cineole, which then inhibits asparagine synthetase (F. E. Dayan et al., Abstr. III Int. Weed Sci. Congr., Brazil, June 2000). Mode of action Absorbed from paddy water through the shoots and roots of germinating or emerging weeds. Moves upwards through the plant and disrupts meristematic development in growing points of roots and shoots. Uses Control of important weeds of rice, including Echinochloa spp., Monochoria vaginalis, and Cyperus difformis, by post-transplanting application, at 20-100 g/ha. Formulation types EC; GR. Compatibility Can be tank-mixed with broad-leaved weed herbicides. Selected products: 'Argold' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Discontinued products: 'Cinch' * (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by glc. Details available from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 3960 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and rabbits >2000 mg/kg; moderate skin and mild eye irritant to rabbits. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >3.5 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 100, mice 30 mg/kg diet. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R20| N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 6.6, bluegill sunfish 6.4, sheepshead minnow 1.6 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 7.2 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 for fiddler crab >1000 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals For a study of the metabolism of cinmethylin in the goat, see J. Agric. Food Chem., 1989, 37, 787. Soil/Environment Strongly adsorbed by soils (B. T. Grayson et al., Pestic. Sci., 1987, 21, 143), but relatively short-lived in the environment, being broken down in the soil under aerobic conditions with DT50 23-75 d, depending on soil texture. Under anaerobic conditions (as may be found in paddy rice), the rate of metabolism is reduced because of slower microbial breakdown.
|