|
chlozolinate
Fungicide
FRAC 2, F1; dicarboximide
NOMENCLATURE
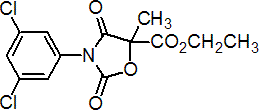
Common name chlozolinate (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name ethyl (?-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-2,4-dioxo-oxazolidine-5-carboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name (?-ethyl 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-2,4-dioxo-5-oxazolidinecarboxylate
CAS RN [84332-86-5] racemate; [72391-46-9] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 282-714-4 Development codes M 8164 (Agrimont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 332.1 M.f. C13H11Cl2NO5 Form Colourless, almost odourless solid. M.p. 112.6 °C V.p. 0.013 mPa (25 ºC, gas saturation method) KOW logP = 3.15 (22 °C) Henry 2.29 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.441 (20 °C) Solubility In water c. 2 ppm (25 °C). In acetone, ethyl acetate and 1,2-dichloroethane >250, ethanol c. 13, n-heptane c. 2, xylene c. 60 (all in g/kg, 22 °C). Stability Stable to 250 ºC (under nitrogen). Stable to light. In solution, hydrolysis occurs at pH 5-9.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by Di Toro et al. (Atti Giornate Fitopatol., Siusi, 1980). Introduced by Agrimont (now Isagro S.p.A.). Patents BE 874406; DE 2906574; IT 20579/78 Manufacturers Isagro
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Lipid peroxidation in mitochondrial membranes. Mode of action Contact fungicide with protective and curative action. Uses Control of Botrytis spp., Sclerotinia spp., and Monilia spp. in ornamentals, vegetables, vines, pome fruit, stone fruit, sunflowers and strawberries. Can be applied, at 750-1000 g/ha, as a foliar spray or as a soil drench. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected products: 'Manderol' (Isagro); 'Serinal' (Isagro)
ANALYSIS
Product and residues can be determined by glc. Details are available from Isagro.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >4500, mice >10 000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >10 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 200 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 200 mg/kg diet. Other Not mutagenic, not teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification R40| N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail and mallard ducks >4500 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout 27.5 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.18 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 30 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >100 mg/bee. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to Phytoseiulus persimilis at up to 2 ´ recommended application rate.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Chlozolinate is readily absorbed, metabolised and excreted. Metabolites identified in urine of rats are: 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyloxazolidin-2,4-dione, N-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2-hydroxypropionamide, O-1-carboxyethyl-N-3,5-dichlorophenyl carbamate, and N-(3,5-dichloro-2(or 4)-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropionamide and its sulfate and glucuronide conjugates. Plants In plants, chlozolinate undergoes hydrolysis and decarboxylation processes, giving the same metabolites as those identified in animals. Soil/Environment In silt-loam, sandy loam and clay loam soils, hydrolysis and decarboxylation occur; aerobic DT50 <7 h.
|