|
chlorthal-dimethyl
Herbicide
HRAC K1 WSSA 3; benzenedicarboxylic acid
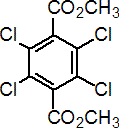
NOMENCLATURE
chlorthal-dimethyl
Common name chlorthal-dimethyl (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO (before 1990)); DCPA (WSSA); TCTP (JMAF)
Chemical Abstracts name dimethyl 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-1,4-benzenedicarboxylate
Other names dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate CAS RN [1861-32-1] Development codes DAC 893
chlorthal
Common name chlorthal (WSSA; BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO (since 1990))
IUPAC name tetrachloroterephthalic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid
CAS RN [2136-79-0]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
chlorthal-dimethyl
Mol. wt. 332.0 M.f. C10H6Cl4O4 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 156 ºC V.p. 0.21 mPa (25 ºC, gas saturation method) KOW logP = 4.28 (25 ºC) Henry 1.39 ´ 10-1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water c. 0.5 mg/l (25 ºC). In benzene 250, toluene 170, xylene 140, dioxane 120, acetone 100, carbon tetrachloride 70 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to heat and u.v. light. Decomposes at c. 360-370 ºC.
chlorthal
Mol. wt. 303.9 M.f. C8H2Cl4O4
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by P. H. Schuldt et al. (Proc. Northeast. Weed Control Conf., 1960, p. 42). Chlorthal-dimethyl introduced by Diamond Alkali Co. (later ISK Biosciences Corp.). Patents US 2923634 Manufacturers Amvac
APPLICATIONS
chlorthal-dimethyl
Biochemistry Microtubule assembly inhibition. Mode of action Selective non-systemic herbicide, absorbed by the coleoptiles (grasses) and hypocotyls. Kills germinating seeds. Uses Pre-emergence control of annual grasses and some annual broad-leaved weeds in onions, garlic, leeks, tomatoes, lettuce, cucurbits, capsicums, aubergines, brassicas, potatoes, sweet potatoes, horseradish, field beans, soya beans, cotton, strawberries, ornamentals, established turf, and other crops. Applied at 6.9-11.5 kg 75 WP formulation/ha for sandy-sandy soil, 11.5 -16.1 kg formulation/ha for heavy silt loam. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to beet, spinach, flax, and trefoil. Formulation types GR; SC; WP. Selected products: 'Dacthal' (Amvac); 'Erazor' (Amvac); mixtures: 'Decimate' (+ propachlor) (Amvac); 'Ringo' (+ propachlor) (Amvac)
OTHER PRODUCTS
chlorthal-dimethyl
Discontinued products: 'Dimethyl-T' * (Amvac)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by i.r. spectrophotometry (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 970.06; CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2034) or by glc with FID (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 970.05; CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2032). Residues determined by glc (H. P. Burchfield & E. E. Storris, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 4, 67; Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 616). In drinking water, by glc with ECD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 990.06); the acid metabolites by conversion to methyl ester with diazomethane, then glc with ECD (ibid., 992.32).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
chlorthal-dimethyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and dogs >10.0 g/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for albino rabbits >2 g/kg. Mild dermal irritant; slight eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.5 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for mice 142, rats 1 mg/kg daily. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
chlorthal-dimethyl
Birds LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish Non-toxic to fish. LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >4.7, bluegill sunfish >5.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >4.6 mg/l. Bees Slightly toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, chlorthal-dimethyl is metabolised to monomethyl tetrachloroterephthalate and 2,3,5,6-tetrachloroterephthalic acid (chlorthal), which are eliminated in the urine. Plants Chlorthal-dimethyl is not metabolised by plants. Soil/Environment Soil DT50 100 d. In soil, microbial degradation leads to monomethyl tetrachloroterephthalate and 2,3,5,6-tetrachloroterephthalic acid (chlorthal). Duration of residual activity in soil is c. 3 months.
|