|
chlorsulfuron
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
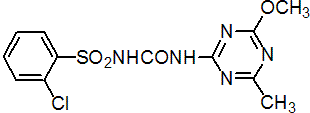
NOMENCLATURE
Common name chlorsulfuron (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA)
IUPAC name 1-(2-chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-[[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]carbonyl]benzenesulfonamide
CAS RN [64902-72-3] EEC no. 265-268-5 Development codes DPX 4189 (DuPont); W4189
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 357.8 M.f. C12H12ClN5O4S Form White crystalline solid. M.p. 170-173 °C (purity 98%) V.p. 3 ´ 10-6 mPa (25 ºC, Knudsen gas effusion) KOW logP = -0.99 (pH 7) Henry 5 ´ 10-10 (pH 5); 3.5 ´ 10-11 (pH 7); 3.2 ´ 10-12 (pH 9) (all Pa m3 mol-1, calc.) S.g./density 1.48 Solubility In water 590 (pH 5), 31800 (pH 7) (both mg/l, 25 ºC). In dichloromethane 1.4, acetone 4, methanol 15, toluene 3, hexane <0.01 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to light when dry. Decomposes at 192 ºC. In aqueous solutions, DT50 23 d (pH 5, 25 ºC); >31 d (pH 7 and above). Hydrolysis is also promoted by polar organic solvents such as methanol and acetone. pKa 3.4
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by P. G. Jensen (Weed Control, 1980, 21st, 24). Introduced in USA in 1982, by E. I. du Pont de Nemours Co. Patents US 4127405 Manufacturers DuPont; Sharda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the foliage and roots, with rapid translocation acropetally and basipetally. Uses Control of most broad-leaved weeds and some annual grasses in wheat, barley, oats, rye, triticale, flax, and on non-crop land. Applied pre-emergence, early post-emergence, pre-plant, or early post-plant incorporated, at 9-35 g/ha in crops, 140 g/ha in non-crop situations. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to many broad-leaved crops, particularly sugar beet and brassicas. Formulation types WG. Selected products: 'Glean' (DuPont); 'Telar' (USA) (DuPont); 'Granonet' (Agrimix); 'Lasher' (Sanonda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Pilargreen' (Pilarquim); 'Press' (AgroSan); 'Uron' (Probelte) mixtures: 'Finesse' (+ metsulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Valinate' (+ linuron) (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 89; R. V. Slates & M. W. Watson, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 53). Residues determined by hplc (idem, ibid.; E. W. Zahnow, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1982, 30, 854) and by immunoassay (Kelly et al.,ibid.,1985, 33, 962). Methods for sulfonylurea residues in crops, soil and water reviewed (A. C. Barefoot et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 2, 707; C. R. Powley, in, Handbook of Residue Analytical Methods).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 5545, female rats 6293 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 3400 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; non-irritating and non-sensitising to skin. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.9 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 100, mice 500 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 2000 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.05 mg/kg. Other No oncogenic, mutagenic or teratogenic activity detected in standard tests. Acute i.p. LD50 for rats 1450 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV (75 WG) EC classification N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >250, bluegill sunfish >300 mg/l. LC50 for fathead minnow >300, catfish >50, sheepshead minnow >980 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >112 mg/l. Algae EC50 50 mg/l. Bees LD50 (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 >2000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment In soil, degradation and deactivation is through biotic (microbial) and abiotic (hydrolysis) processes, followed by complete degradation to low-molecular-weight compounds through continuing soil microbial processes. Rate of hydrolysis is increased at lower pH. Average half-life under growing-season conditions is c. 4-6 weeks. Koc 40 (pH 7).
|