|
chlorpyrifos-methyl
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name chlorpyrifos-methyl (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, ESA); chlorpyriphos-methyl ((m) F-ISO, JMAF)
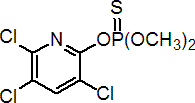
IUPAC name O,O-dimethyl O-3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl phosphorothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-dimethyl O-(3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinyl) phosphorothioate
CAS RN [5598-13-0] Development codes Dowco 214 (Dow) Official codes OMS 1155; ENT 27 520
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition 97% pure. Mol. wt. 322.5 M.f. C7H7Cl3NO3PS Form White crystals, with a slight mercaptan odour. M.p. 45.5-46.5 ºC V.p. 3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 4.24 Henry 3.72 ´ 10-1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.64 (23 °C) Solubility In water 2.6 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone >400, methanol 190, hexane 120 (all in g/kg, 20 ºC). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 27 d (pH 4), 21 d (pH 7), 13 d (pH 9). Aqueous photolysis DT50 1.8 d (June), 3.8 d (December). F.p. 182 ºC (COC)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by R. H. Rigterink & E. E. Kenaga (J. Agric. Food Chem., 1966, 14, 304). Introduced by Dow Chemical Co. (now Dow AgroSciences). First marketed in the US in 1985. Patents US 3244586 Manufacturers Aimco; Dow AgroSciences; Sharda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Uses Control of Coleoptera, Diptera, Homoptera and Lepidoptera in cereals (including stored grains), and various foliar crop pests in pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, bush and cane fruit, vines, strawberries, vegetables, tomatoes, tea, rice, cotton, and other crops. Applied to stored grain at 6-10 cc/ton; foliar application at 250-1000 g/ha. Industrial and public health uses include control of Muscidae and crawling insects; also employed in disease vector control programs (e.g. Anopheles spp., vectors of malaria). Formulation types EC; HN; UL. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline and strongly acidic materials. Selected products: 'Reldan' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Decisprime' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Nuvagrain' * (Ciba); 'Pyriban M' * (Aimco); 'Smite' * (AgrEvo EH)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by glc (Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5; Analyst (London), 1979, 104, 425; 1985, 110, 765; P. Bottomley & P. G. Baker, ibid., 1984, 109, 85). Details available from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67, 92 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >3000, mice 1100-2250, guinea pigs 2250, rabbits 2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000, rats >3700 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.67 mg/l. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, NOEL, based on plasma cholinesterase levels, 0.1 mg/kg daily for dogs and rats. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [2001, 1992]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >1590, bobwhite quail 923 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 2500-5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.41, bluegill sunfish 0.88 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (24 h) 0.016-0.025 ppm. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.57 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. Toxic to crustaceans. LC50 (36 h) for crayfish 0.004 mg/l. Bees Very toxic to bees. LD50 (contact) 0.38 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (15 d) for Eisenia foetida 182 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In rats and other mammals, following oral administration, rapid metabolism occurs, the principal metabolite being 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-ol. Excretion is principally in the urine. Soil/Environment In soil, undergoes microbial degradation to 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-ol, which is subsequently degraded to organochlorine compounds and CO2; DT50 1.5-33 d, DT90 14-47 d, depending upon soil type and microbial activity. Kd 3.5-407 ml/g, depending on soil type. Koc is more constant: 1190-8100 ml/g.
资
|