|
chlorothalonil
Fungicide
FRAC M5; multi-site: chloronitrile
NOMENCLATURE
Common name chlorothalonil (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI); TPN (JMAF)
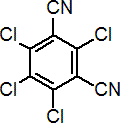
IUPAC name tetrachloroisophthalonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 2,4,5,6-tetrachloro-1,3-benzenedicarbonitrile
CAS RN [1897-45-6] EEC no. 217-588-1 Development codes DS-2787 (Diamond Shamrock)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is c. 97%. Mol. wt. 265.9 M.f. C8Cl4N2 Form Colourless, odourless crystals; (tech. has a slightly pungent odour). M.p. 252.1 °C B.p. 350 ºC/760 mmHg V.p. 0.076 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.92 (25 °C) Henry 2.50 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C) S.g./density 2.0 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.81 mg/l (25 ºC). In xylene 80, cyclohexanone, dimethylformamide 30, acetone, dimethyl sulfoxide 20, kerosene <10 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Thermally stable at ambient temperatures. Stable to u.v. light in aqueous media and in crystalline state. Stable in acidic and moderately alkaline aqueous solutions; slow hydrolysis at pH >9.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by N. J. Turner et al. (Contrib. Boyce Thompson Inst., 1964, 22, 303). Introduced by the Diamond Alkali Co. (later ISK Biosciences Corp.) and sold to Zeneca Agrochemicals (now Syngenta AG) in 1997. Patents US 3290353; US 3331735 Manufacturers Agrochem; GB Biosciences; Gharda; Gilmore; Isagro; SDS Biotech KK; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Conjugation with, and depletion of, thiols (particularly glutathione) from germinating fungal cells, leading to disruption of glycolysis and energy production, fungistasis and fungicidal action. Mode of action Non-systemic foliar fungicide with protective action. Uses Control of many fungal diseases in a wide range of crops, including pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, bush and cane fruit, cranberries, strawberries, pawpaws, bananas, mangoes, coconut palms, oil palms, rubber, pepper, vines, hops, vegetables, cucurbits, tobacco, coffee, tea, rice, soya beans, peanuts, potatoes, sugar beet, cotton, maize, ornamentals, mushrooms, and turf. Application rates for food crops are 1-2.5 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Russetting is possible with flowering ornamentals, apples, and grapes. Some varieties of flowering ornamentals may be injured. Pittosporum foliage is sensitive. Phytotoxicity may be increased with oils or oil-containing substances. Formulation types SC; WG; WP; Fogging concentrate. Compatibility Not compatible with oils. Selected products: 'Bravo' (Syngenta); 'Daconil' (Syngenta, SDS Biotech KK); 'Banko' (Calliope); 'Bombardier' (Unicrop); 'Chloronil' (Vapco); 'Clortosip' (Sipcam); 'Corrib' (Barclay); 'Equus' (Nations Ag); 'Fungiless' (Sanonda); 'Gilonil' (Gilmore); 'Mycoguard' (Chiltern, Gharda); 'Oranil' (Cequisa); 'Talonil' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Teren' (Efthymiadis); 'Visclor' (Vischim)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Countdown L&G' (Syngenta); 'ISK 375' (Syngenta); 'Jupital' (Syngenta); 'Kvach' (Syngenta); 'Nuocide' (Syngenta); 'Ole' (Syngenta); 'Tuffcide' (Syngenta); 'Atlas Cropgard' (Nufarm UK); 'Clortocaffaro' (Isagro); 'Dragonil' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Echo' (Sipcam); 'Estampe' (France) (Bayer CropScience); 'Faber' (Tripart); 'Flute' (Sipcam UK); 'Mainstay' (Quadrangle); 'Orchid' (GreenCrop); 'Passport' (SDS Biotech KK); 'Pilarich' (Pilarquim); 'Pugil' (Sipcam); 'Repulse' (Hortichem); 'Rover' (Sipcam); 'Rumble' (Probelte); 'Talone' (Chemiplant); 'Terranil 90DF' (Agriliance); 'Thayonil' (Agrochem); 'Ultrafaber' (Tripart) mixtures: 'Alto Elite' (+ cyproconazole) (Syngenta); 'Bravo C/M' (+ copper oxychloride) (Syngenta); 'Bravocarb' (+ carbendazim) (Syngenta); 'Folio Gold' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Syngenta); 'Folio' (+ metalaxyl) (Syngenta); 'Lynx' (+ hexaconazole) (Syngenta); 'Reach' (+ triadimefon) (Syngenta); 'Sambarin' (+ propiconazole) (Syngenta); 'Sirius' (+ hexaconazole) (Syngenta); 'Abitre' (+ tetraconazole) (Bayer CropScience); 'Adagio' (+ mancozeb) (Interfarm); 'Allure' (+ prochloraz) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Arbitre' (+ tetraconazole) (Bayer CropScience); 'Blizzard' (+ cymoxanil) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Bravo S' (+ sulfur) (Helena); 'Diva' (+ iprodione) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Eminent Star' (+ tetraconazole) (Isagro); 'Flouronil' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Nufarm Americas); 'Guru' (+ mancozeb) (Interfarm); 'Halo' (+ flutriafol) (Cheminova); 'Impact Excel' (+ flutriafol) (Cheminova); 'Moncut CL' (+ flutolanil) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Music' (+ tetraconazole) (Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Prospa' (+ flutriafol) (Cheminova); 'Soleyou' (+ carbendazim) (Calliope); 'Spectro' (+ thiophanate-methyl) (Cleary); 'Tattoo C' (+ propamocarb hydrochloride) (Bayer CropScience); 'Terranil CU' (+ copper oxychloride) (Agriliance); 'Terranil S' (+ sulfur) (Agriliance); 'Vista CT' (+ fluquinconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Voodoo' (+ tetraconazole) (UK) (Sipcam); 'Walabi' (+ pyrimethanil) (Bayer CropScience, BASF) Discontinued products: 'Exotherm Termil' * (Zeneca); 'Baton' * (Bayer); 'Miros' * (Sipcam); 'Strada' * (Sipcam UK); 'UK Rover 500' * (Sipcam) mixtures: 'PP 375' * (+ flutriafol) (Zeneca); 'Adagio' * (+ mancozeb) (PBI); 'Ashlade Mancarb Plus' * (+ maneb+ carbendazim) (Ashlade); 'Merlin' * (+ propamocarb hydrochloride) (Aventis); 'Octolan' * (+ cyproconazole) (Novartis); 'Triumph' * (+ flusilazole) (DuPont); 'Victor' * (+ maneb+ carbendazim) (Tripart); 'Voodoo' * (+ tetraconazole) (Monsanto)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 999.04; D. L. Ballee et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1976, 8, 263). Residues determined by gc-ms, details available from Syngenta. In drinking water by glc with ECD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 990.06). Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews CAG (see part 2 of Bibliography). IARC ref. 30; 73 class 2B Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for albino rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Severe eye irritant; mild skin irritant (rabbits). Evidence in humans of contact dermatitis with repeated exposure. Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for rats 0.52 mg/l air; (4 h) for rats 0.10 mg/l air. NOEL Chronic administration of chlorothalonil has been associated with renal hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis of the forestomach in the kidney and forestomach of rats and male mice. These pre-neoplastic lesions precede subsequent tumour development in the rodent kidney and forestomach. The mode of action has been demonstrated to be epigenetic with a NOEL of 1.8 in rats and 1.6 in mice. In dogs, the pattern of toxicity is different from that in rodents with no evidence of toxicity in the kidney or forestomach, and a NOEL of at least 3 mg/kg b.w. (JMPR 1994). ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg [1994]; (EPA) 0.02 mg/kg (RED 1998). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) II ('Bravo' SC) EC classification R40| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >4640 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >10 000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 47, bluegill sunfish 59, channel catfish 43 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 70 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 210 mg/l; EC50 (72 h) for Navicula pelliculosa 5.1 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (48 h) for Crangonyx pseudogracilis 64 mg/l, Chironomus riparius 110 mg/l, Cloeon dipterum 600 mg/l; LC50 (24 h) for Brachionus calyciflorus 24 mg/l. Bees LD50 for honeybees (oral) >63 mg/bee; (contact) >101 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >404 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. LR50 (7 d) for Typhlodromus pyri >18.75 kg/ha; LR50 (48 h) for Aphidius rhopalosiphi >18.75 kg/ha.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 183 (WHO, 1996) Animals Chlorothalonil is not well absorbed following oral dosing. It reacts with glutathione in the gut rumen, or immediately on absorption into the body, to give mono-, di- or tri- glutathione conjugates. These may be excreted through urine or faeces, or subject to further metabolism resulting in thiol or mercapturic acid derivatives. Excretion of these in urine is believed to be significantly greater in rats than in dogs or primates. In ruminants, the major identified metabolite is the the 4-hydroxy derivative; no parent material is found. Plants In plants the majority of residues remain as parent compound; 4-hydroxy-2,5,6-trichloroisophthalonitrile is found as a metabolite to a limited extent. Soil/Environment Koc 1600 (sand) to 14 000 (silt), indicating low mobility to immobile. In aerobic and anaerobic soil studies, DT50 is 0.3-28 d (20 ºC). Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5-7, at pH 9 (22 °C), DT50 is 38 d. Degradation is faster in biotic aquatic systems, typical DT50 (aerobic) <8 h, (anaerobic) <10 d. A wide variety of metabolites are formed which are in turn degraded further..
|