|
chloropicrin
Insecticide, nematicide
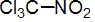
NOMENCLATURE
Common name chloropicrin (BSI, E-ISO, ESA, accepted in lieu of common name); chloropicrine (F-ISO, accepted in lieu of common name)
IUPAC name trichloronitromethane
Chemical Abstracts name trichloronitromethane
CAS RN [76-06-2] EEC no. 200-930-9
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 164.4 M.f. CCl3NO2 Form Colourless liquid with a lachrymatory action. M.p. -64 ºC B.p. 112.4 ºC/757 mmHg V.p. 3.2 kPa (25 ºC) S.g./density 1.6558 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 2.27 (0 ºC), 1.62 (25 ºC) (both in g/l). Miscible with most organic solvents, e.g. acetone, benzene, ethanol, methanol, carbon disulfide, diethyl ether, carbon tetrachloride. Stability Stable in acidic media, unstable in alkali. F.p. Non-flammable
COMMERCIALISATION
History Used as an insecticide since 1908. Patents GB 2387 Manufacturers Great Lakes; Mitsui; Niklor
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Fumigant. Uses An insecticide used for the fumigation of stored grain. Also of soil to control nematodes and other soil-dwelling pests. Phytotoxicity Highly phytotoxic. Formulation types OL; TB; TC. Compatibility Compatible with other fumigants. Selected products: 'Chlor-O-Pic' (Great Lakes); 'Dorochlor' (Mitsui); mixtures: 'Brom-O-Gas' (+ methyl bromide) (Great Lakes); 'Midas' (+ methyl iodide) (Arvesta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Chlorofume' (K&S Fumigation); 'Hd-Pic' (Hendrix & Dail); 'Nutrapic' (Applied Agrosciences) mixtures: 'Bro-Mean C-33' (+ methyl bromide) (Reddick); 'Double Stopper' (+ 1,3-dichloropropene) (Nippon Kayaku, Yashima, DAS Ryosho); 'Inline' (+ 1,3-dichloropropene) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sobrom BM 98' (+ methyl bromide) (Brian Jones); 'Telone C-17' (+ 1,3-dichloropropene) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Telone C-35' (+ 1,3-dichloropropene) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Telopic' (+ 1,3-dichloropropene) (Dead Sea); 'Terr-O-Gas' (+ methyl bromide) (Great Lakes) Discontinued products: 'Picrin 80' * (Mitsui Toatsu) mixtures: 'Trizone' * (+ methyl bromide+ propargyl bromide) (Dow)
ANALYSIS
Chloropicrin is determined by glc. For determination in air, collect in propan-2-ol and convert to a derivative which is measured colorimetrically (L. Feinsilver & F. W. Oberst, Anal. Chem., 1953, 25, 820). Methods reviewed by J. L. Daft in Comp. Analyt. Profiles, Chapter 11.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 3, 5 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 250 mg/kg. Skin and eye Severe irritant to skin of rabbits. Inhalation At 0.008 mg/l air, it can be clearly detected; at 0.016 mg/l, it produces coughing and lachrymation; and at 0.12 mg/l, 30 to 60 minutes exposure can be fatal. Exposure of cats, guinea pigs and rabbits to concentrations of 0.8 mg/l air was lethal in 20 min. ADI (JMPR) No ADI [1965]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) FM; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R22| T+; R26| Xi; R36/37/38
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Fish TLm (48 h) for carp 0.168 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) 0.91 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment In the atmosphere, chloropicrin is extensively degraded to CO2 by photolysis; DT50 in natural sunlight 4 d (calc.) (K. Sato et al., Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London, 1998, 2, 6E-018).
|