|
chlorimuron-ethyl
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
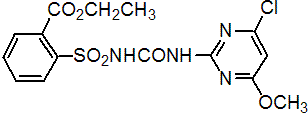
NOMENCLATURE
chlorimuron-ethyl
Common name chlorimuron-ethyl
IUPAC name ethyl 2-(4-chloro-6-methoxypyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)benzoate
Chemical Abstracts name ethyl 2-[[[[(4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]benzoate
CAS RN [90982-32-4] Development codes DPX-F6025 (DuPont)
chlorimuron
Common name chlorimuron (BSI, ANSI, WSSA, draft E-ISO, draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name 2-(4-chloro-6-methoxypyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)benzoic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[[[[(4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]benzoic acid
CAS RN [99283-00-8]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
chlorimuron-ethyl
Composition Tech. is >95%. Mol. wt. 414.8 M.f. C15H15ClN4O6S Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 181 ºC V.p. 4.9 ´ 10-7 mPa KOW logP = 0.11 (pH 7) Henry 1.7 ´ 10-10 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.51 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 9 (pH 5), 1200 (pH 7) (both in mg/l, 25 ºC). Low solubility in organic solvents. Stability In water DT50 17-25 d (pH 5, 25 ºC). pKa 4.2
chlorimuron
Mol. wt. 386.8 M.f. C13H11ClN4O6S
COMMERCIALISATION
History Chlorimuron-ethyl introduced as a herbicide by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. First US registration in 1986. Patents US 4394506; US 4547215 Manufacturers DuPont; IPESA; JIE; Sharda; Shenyang; Tide
APPLICATIONS
chlorimuron-ethyl
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Crop selectivity derives from plant metabolism both by homoglutathione conjugation and by de-esterification (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Uses Used post-emergence for control of important broad-leaved weeds, such as cocklebur, pigweed, sunflower and annual morning glory, in soya beans and peanuts. Active at 9-13 g/ha. Formulation types WG. Selected products: 'Classic' (DuPont); 'Darban' (IPESA); 'Sponsor' (Reposo); 'Tirimiron' (Tide)
OTHER PRODUCTS
chlorimuron-ethyl
'Kloben' (India) (DuPont); 'Glicincas' (CAS); 'Skirmish' (FMC) mixtures: 'Almix' (+ metsulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Canopy XL' (+ sulfentrazone) (DuPont); 'Canopy' (+ metribuzin) (DuPont); 'Concert' (+ thifensulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Preview' (+ metribuzin) (DuPont); 'Reliance' (+ thifensulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Synchrony STS' (+ thifensulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Authority Broadleaf' (+ sulfentrazone) (FMC) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Gemini' * (+ linuron) (DuPont); 'Lorox Plus' * (+ linuron) (DuPont); 'New Lorox Plus' * (+ linuron) (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (R. A. Guinivan et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 37). Residues determined by hplc (J. L. Prince & R. A. Guinivan, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1988, 36, 1). Methods for sulfonylurea residues in crops, soil and water reviewed (A. C. Barefoot et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 2, 707).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
chlorimuron-ethyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 4102 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant or eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 250 mg/kg diet (12.5 mg/kg b.w. daily); (1 y) for dogs 250 mg/kg diet (6.25 mg/kg b.w. daily). NOEL in: reproduction (2-generation) in rats 250 mg/kg diet; teratogenicity in rats 30, rabbits 15 mg/kg. ADI 0.020 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
chlorimuron-ethyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 (14 d) for mallard ducks >2510 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout >1000, bluegill sunfish >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1000 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. For Lemna gibba,EbC50 0.45 ppb, ErC50 45 mg/l, EC50 (frond counts) 0.27 ppb. LC50 for crayfish >1000 ppm. Bees LD50 (48 h) >12.5 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms (Eisenia foetida) >4050 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Chlorimuron-ethyl is rapidly and extensively metabolised in the hen; 18 metabolites in the excreta were resolved by hplc. Soil/Environment In soil, Kd >1.60 (pH 4.5, 5.6% o.m.), 0.28 (pH 5.8, 4.3 % o.m.), <0.03 (pH 6.5, 2.1% o.m.), <0.03 (pH 6.6, 1.1 % o.m.).
|