|
chlorfluazuron
Insecticide
IRAC 15; benzoylurea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name chlorfluazuron (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
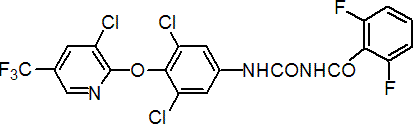
IUPAC name 1-[3,5-dichloro-4-(3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy)phenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[[3,5-dichloro-4-[[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]oxy]phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
CAS RN [71422-67-8] Development codes IKI-7899 (Ishihara Sangyo); CGA 112 913 (Ciba-Geigy); PP145 (ICI); UC 64 644 (Rhône-Poulenc)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 540.7 M.f. C20H9Cl3F5N3O3 Form White crystals. M.p. 226.5 ºC (decomp.) V.p. <1 ´ 10-5 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 5.8 (unionised) Henry <5.41 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.663 (20 °C) Solubility In water <0.01 mg/l (20 ºC). In hexane <0.01, n-octanol 1, xylene 2.5, methanol 2.5, toluene 6.6, isopropanol 7, dichloromethane 22, acetone 55, cyclohexanone 110 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable to heat and light, and to hydrolysis. pKa 8.10, v. weak acid F.p. 224.0-224.5 °C (OECD 102)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by T. Haga et al. (Abstr. 5th IUPAC Congr. Pestic. Chem., 1982, IId-7). Discovered by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd, also evaluated by other companies; first marketed in 1988 in Japan. Manufacturers Ishihara Sangyo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor (R. Neumann & W. Guyer, Proc. 10th Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 1983, 1, 445). Mode of action Insect growth regulator which acts as an anti-moulting agent, leading to death of the larvae and pupae. Uses Control of Heliothis, Spodoptera, Bemisia tabaci and other chewing insects on cotton; and Plutella, Thrips and other chewing insects on vegetables. Also used on fruit, potatoes, ornamentals and tea. Applied at 2.5 g/hl. Formulation types EC; SC. Selected products: 'Aim' (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Atabron' (ISK Biosciences); 'Jupiter' (Ishihara Sangyo)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Helix' (seed treatment) (ISK Biosciences, Crop Care)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc or glc. Residues by hplc with u.v. detection. Details from Ishihara Sangyo.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >8500, mice 7000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >1000, rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; mild eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.4 mg/l. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail and mallard ducks >2510 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1071 µg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.908 mg/l. Algae EC50 (12 d) for green algae >1.8 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (28 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Metabolised in rats by cleavage of the urea bridge. Plants Slowly degraded in plants. Soil/Environment Half-life in soil varies from c. 6 weeks to a few months. Kd 120-990. Slowly degraded in water, DT50 for aqueous photodegradation 20 h.
|