|
chlorfenapyr
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 13; arylpyrrole
NOMENCLATURE
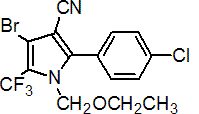
Common name chlorfenapyr (BSI, pa ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-ethoxymethyl-5-trifluoromethylpyrrole-3-carbonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(ethoxymethyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile
CAS RN [122453-73-0] Development codes AC 303,630; CL 303,630 (both Cyanamid); MK-242 (Mitsubishi Chemical)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 407.6 M.f. C15H11BrClF3N2O Form White solid. M.p. 100-101 ºC V.p. <1.2 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.83 S.g./density 0.355 (24 ºC) Solubility Practically insoluble in water. Soluble in acetone, diethyl ether, dimethyl sulfoxide, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile, and alcohols. Stability In air DT50 0.88 d (10.6 h, calc.). In water (direct photodegradation) DT50 4.8-7.5 d. Stable to hydrolysis (pH 4, 7 and 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Developed by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG). Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Oxidative removal in vivo of the N-ethoxymethyl group generates the active species, which is a mitochondrial uncoupler. Mode of action Insecticide and acaricide with mainly stomach and some contact action. Exhibits good translaminar but limited systemic activity in plants. Uses Control of many species of insects and mites, including those resistant to carbamate, organophosphate and pyrethroid insecticides and also chitin-synthesis inhibitors, in cotton, vegetables, citrus, top fruit, vines and soya beans. Among pests resistant to conventional products which are controlled by chlorfenapyr are Brevipalpus phoenicis (leprosis mite), Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Colorado potato beetle), Helicoverpa spp., Heliothis spp., Plutella xylostella (diamond-back moth) and Tetranychus spp. Also control of many species of structural and household Formicidae (especially Camponotus, Iridomyrmex, Monomorium, and Solenopsis), Blattellidae (especially Blatta, Blattella, Periplaneta and Supella spp.), Kalotermitidae (especially Incisitermes) and Rhinotermitidae (especially Reticulitermes, Coptotermes, Heterotermes) at use rates of between 0.125 to 0.50% a.i. w/w. Phytotoxicity No phytotoxicity observed at field use rates. Formulation types EC; SC. Selected products: 'Phantom' (professional pest control) (BASF); 'Pylon' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Alert' (citrus, cotton) (BASF); 'Chu-Jin' (China) (BASF); 'Grizli' (E. Europe) (BASF); 'Intrepid' (Europe) (BASF); 'Kotetsu' (Japan) (BASF, Nihon Nohyaku); 'Pirate' (cotton) (BASF); 'Rampage' (S.E. Asia) (BASF); 'Secure' (ornamentals) (BASF); 'Stalker' (BASF) mixtures: 'Oonata' (+ fluacrypyrim) (Nippon Soda)
ANALYSIS
Product by glc. Residues by hplc. Details from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 441, female rats 1152 mg tech./kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Moderate eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 for rats 1.9 mg tech./l air. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames, CHO/HGPRT, mouse micronucleus and unscheduled DNA synthesis tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) III (240 g/l 'Pylon', 'Phantom')
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 10, bobwhite quail 34 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 9.4, bobwhite quail 132 ppm. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 500 mg/l. LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 7.44, bluegill sunfish 11.6 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (96 h) 6.11 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum 132 ppb. Bees LD50 0.2 mg/bee. Worms NOEC (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 8.4 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, >60% of orally administered chlorfenapyr was excreted primarily through faeces within 24 hours. The absorbed residues were metabolised via N-dealkylation, dehalogenation, hydroxylation and conjugation. Parent and less polar metabolites were found in egg, milk and tissues such as fat and liver. Metabolism in hens and goats is similar to that in rats, however in these species, 80% of orally administered chlorfenapyr was rapidly excreted. Un-excreted residues were present in kidney and liver. At the potential maximum dietary burden, all residues are <0.01 ppm. Chlorfenapyr is the only significant residue component. Plants In cotton, citrus, tomato, lettuce and potato, chlorfenapyr is dealkylkated to the insecticidally active component (AC 303268) or debrominated to less toxic metabolites. Chlorfenapyr does not translocate out of treated plant parts. Parent compound is the prominent residue. Soil/Environment In soil, chlorfenapyr is the major residue. Debromination to a less toxic metabolite is the primary route; dealkylation is not a primary route of degradation in soil. Koc >10 000 ml/g, indicating chlorfenapyr is likely to be strongly bound in soils. In water DT50 (direct photodegradation) 4.8-7.5 d; stable to hydrolysis at pH 4, 7 and 9.
|