|
cartap hydrochloride
Insecticide
IRAC 4C; 2-dimethylaminopropane-1,3-dithiol
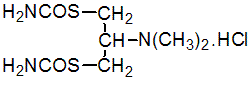
NOMENCLATURE
cartap hydrochloride
Common name cartap hydrochloride
CAS RN [15263-52-2] cartap monohydrochloride; [22042-59-7] cartap, unspecified hydrochloride EEC no. 239-309-2
cartap
Common name cartap (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, JMAF)
IUPAC name S,S'-(2-dimethylaminotrimethylene) bis(thiocarbamate)
Chemical Abstracts name S,S'-[2-(dimethylamino)-1,3-propanediyl] dicarbamothioate
CAS RN [15263-53-3] Development codes TI-1258 (Takeda)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
cartap hydrochloride
Mol. wt. 273.8 M.f. C7H16ClN3O2S2 Form White crystalline, slightly hygroscopic solid with slight odour. M.p. 179-181 ºC (decomp.) V.p. Negligible Solubility In water c. 200 g/l (25 ºC). Very slightly soluble in methanol and ethanol. Insoluble in acetone, diethyl ether, ethyl acetate, chloroform, benzene, and hexane. Stability Stable in acidic conditions, but hydrolysed in neutral or alkaline media.
cartap
Mol. wt. 237.3 M.f. C7H15N3O2S2 Form White crystalline powder. M.p. 187-188 °C V.p. 2.5 ´ 10-2 mPa (25 °C) Solubility In hexane, toluene, chloroform, acetone and ethyl acetate <0.01, methanol 16.0 (all g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable at 150 °C.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by M. Sakai et al. (Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool., 1967, 11, 125), its action and structure-activity relationships reviewed (K. Konishi, Pestic. Chem. [Congr. Pestic. Chem., 2nd, 1971], 1972, 1, 179; M. Sakai & Y. Sato, ibid., p. 445; M. Sakai, Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1971, No. 6, p. 15; 1978, No. 34, p. 22). The hydrochloride introduced by Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd (now Sumitomo Chemical Takeda Agro Company Ltd) and first marketed in Japan in 1967. Patents GB 1126204; US 3332943; FR 1452338 Manufacturers Hunan Linxiang; Kuo Ching; Sharda; Sumitomo Chemical Takeda; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Analogue or propesticide of the natural toxin nereistoxin. Nicotinergic acetylcholine blocker, causing paralysis by blocking cholinergic transmissions in the central nervous systems of insects. Mode of action Systemic insecticide with stomach and contact action. Insects discontinue feeding, and die of starvation.
cartap hydrochloride
Uses Cartap hydrochloride is used, at c. 0.4-1.0 kg/ha, for control of chewing and sucking insects (particularly Lepidoptera and Coleoptera), at almost all stages of development, on many crops, including rice (Chilo suppressalis, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus and rice-leaf beetle), potatoes, cabbage and other vegetables (Agromyzidae, Leptinotarsa decemlineata and Plutella xylostella); also on soya beans, peanuts, sunflowers, maize, sugar beet, wheat, pearl barley, pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, vines, chestnuts, ginger, tea, cotton, and sugar cane. Phytotoxicity May be phytotoxic to cotton, tobacco, and apples, under certain soil and climatic conditions. Formulation types DP; GR; SP. Compatibility Not compatible with pesticides which are alkaline. Selected products: 'Padan' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Sanvex' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda, Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Hilcartap' (Hindustan); 'Mahadan' (Crop Health)
cartap
Selected products: 'Vicarp' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
cartap hydrochloride
'Cadan' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Patap' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Thiobel' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Vegetox' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Kritap' (Krishi Rasayan) mixtures: 'Dantotsupadan' (+ clothianidin) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Dantotsupadanvalida' (+ clothianidin+ validamycin) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Hustler' (+ clothianidin+ ferimzone+ phthalide+ validamycin) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda)
cartap
'Caldan' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda, Dhanuka); 'Pilartap' (Pilarquim) mixtures: 'Vipami' (+ isoprocarb) (Vipesco)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by colorimetry on a derivative (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 24). Residue analysis by glc or by polarography (K. Nishi et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 371).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 74 (see part 2 of the Bibliography).
cartap hydrochloride
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 345, female rats 325, male mice 150, female mice 154 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for mice >1000 mg/kg; no irritation to skin or eyes in rabbits. Inhalation LC50 (6 h) for rats >0.54 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 10 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1.5 y) for mice 20 mg/kg b.w. daily. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R21/22| N; R50, R53
cartap
ADI (JMPR) ADI withdrawn [1995].
ECOTOXICOLOGY
cartap hydrochloride
Fish LC50 for carp 1.6 mg/l (24 h) and 1.0 mg/l (48 h). Other aquatic spp. LC50 (24 h) for Moina macrocopa 12.5-25 mg/l. Bees Moderately toxic to honeybees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 76 (WHO, 1988). Animals In rats, the carbonyl carbon is hydrolysed, and the sulfur oxidised, with N-demethylation of thiomethyl derivatives. No accumulation occurs in tissues. Rapidly excreted in the urine. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil c. 3 d.
|