|
carpropamid
fungicide
FRAC 16.2, I2; MBI: dehydratase
NOMENCLATURE
Common name carpropamid (BSI, pa ISO)
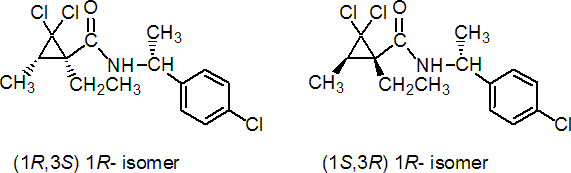
IUPAC name A mixture of (1R,3S)-2,2-dichloro-N-[(R)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide (referred to as AR enantiomer), (1S,3R)-2,2-dichloro-N-[(R)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide (referred to as BR enantiomer), (1S,3R)-2,2-dichloro-N-[(S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide, and (1R,3S)-2,2-dichloro-N-[(S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide, where the first two cited comprise at least 95% of the total
Chemical Abstracts name A mixture of [1R-[1a(R*),3b]]-2,2-dichloro-N-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide, [1S-[1a(S*),3b]]-2,2-dichloro-N-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide, [1S-[1a(R*),3b]]-2,2-dichloro-N-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide, and [1R-[1a(S*),3b]]-2,2-dichloro-N-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopropanecarboxamide
CAS RN [104030-54-8]; AR enantiomer [127641-62-7]; BR enantiomer [127640-90-8] Development codes KTU 3616 (Bayer; Nihon Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Diastereoisomeric mixture (A:B c. 1:1; RS c. 95:5); the (1R,3S,1R)- enantiomer is designated AR, the (1S,3R,1R)- enantiomer BR. Mol. wt. 334.7 M.f. C15H18Cl3NO Form Colourless crystals; (tech. is a white to yellowish powder). M.p. AR: 161.7 °C; BR: 157.6 °C V.p. AR: 2 ´ 10-3 mPa; BR: 3 ´ 10-3 mPa (both 20 °C, gas saturation method OECD 104) KOW AR: logP = 4.23, BR: logP = 4.28 (both 22 ºC) Henry AR: 4 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1, BR: 5 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (both 20 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.17 (20 °C) Solubility In water 1.7 (AR), 1.9 (BR) (both in mg/l, pH 7, 20 ºC).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered and developed jointly by Nihon Bayer Agrochem. K.K. and Bayer AG. Reported by T. Hattori et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1994, 2,517). Introduced in Korea in 1996 as a seed treatment and in 1998 as a spray. Introduced in Colombia and Japan in 1997, as a spray application and a seedling-box treatment, respectively. Patents EP 00341475 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry In Pyricularia oryzae, carpropamid inhibits melanin biosynthesis, by inhibiting the dehydration reactions from scytalone to 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene and from vermelone to 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene. Also enhances crop resistance by increasing phytoalexin production following rice blast infection. Mode of action Systemic, protective fungicide. Uses Systemic fungicide with specific action against Pyricularia oryzae; it does not provide curative properties, so protective treatment is essential. Can be used for seed treatment (300-400 g/dt), seedling box treatment (400 g/ha), seedling box drench (200-400 g/ha), and spray (75-150 g/ha). Formulation types FS; GR; SC; WS. Selected products: 'Arcado' (Bayer CropScience); 'Cleaness' (Bayer CropScience); 'Protega' (Bayer CropScience); 'Win' (Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Carrena' (+ imidacloprid) (Bayer CropScience); 'Win Admire' (+ imidacloprid) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Solazas' (Bayer CropScience); 'Zubard' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Windantotsu' (+ clothianidin) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda)
ANALYSIS
Details of methods for product and residue analysis are available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg. No eye or skin irritation (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/m3 (dust). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 400 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 200 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.03 mg/kg b.w. (Bayer proposed; Colombia, Korea); 0.014 mg/kg b.w. (Japan). Other No mutagenic effects in in vitro or in vivo tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for Japanese quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48/72 h) for carp 5.6 mg/l; LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 10 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) 410 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus >2 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (3 h) for water flea (Moina macrocopa) >20 mg/l. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg dry substrate.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration of radiolabelled carpropamid to rats, the radioactivity was readily excreted via faeces and urine. Carpropamid was metabolised oxidatively, mainly in the liver. Plants After treatment of rice plants via soil (nursery box application) or nutrient medium, carpropamid was absorbed by the roots and translocated to the shoots. The major residue in rice was carpropamid. Soil/Environment Carpropamid was metabolised oxidatively under paddy soil conditions; CO2 was the major metabolite. In field and laboratory trials, under paddy conditions, the calculated half-lives ranged from several weeks to several months, respy. Adsorption/desorption studies with the parent compound indicated that carpropamid can be classified as being of low mobility. Hydrolytically stable in sterile aqueous buffer solutions, photodegraded in natural water; degradation was significantly faster in natural water than in sterile water.
|