|
carbofuran
Insecticide, nematicide
IRAC 1A; carbamate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name carbofuran (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA)
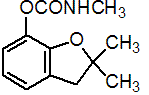
IUPAC name 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethylbenzofuran-7-yl methylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl methylcarbamate
CAS RN [1563-66-2]; (carbofuran phenol[1563-38-8]; 3-ketocarbofuran phenol [17781-16-7]) EEC no. 216-353-0 Development codes FMC 10 242; BAY 70 143 (Bayer); D 1221 Official codes OMS 864; ENT 27 164
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 221.3 M.f. C12H15NO3 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 153-154 ºC; (tech. 150-152 ºC) V.p. 0.031 mPa (20 ºC); 0.072 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 1.52 (20 ºC) S.g./density 1.18 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 320 (20 ºC), 351 (25 °C) (both in mg/l). In dichloromethane >200, isopropanol 20-50, toluene 10-20 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Unstable in alkaline media. Stable in acidic and neutral media. Decomposes >150 ºC. DT50 (22 ºC) >>1 y (pH 4), 121 d (pH 7), 31 h (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by F. L. McEwen & A. C. Davis (J. Econ. Entomol., 1965, 58, 369) and E. J. Armburst & G. C. Gyrisco (ibid., p. 940). Introduced by FMC Corp. and by Bayer AG. Patents US 3474170; US 3474171 both to FMC; DE 1493646 to Bayer Manufacturers Agrochem; Bayer CropScience; Dow AgroSciences; FMC; Hesenta; Hunan Linxiang; Jin Hung; Kuo Ching; Makhteshim-Agan; Pilarquim; Sinon; Sundat; Taiwan Tainan Giant
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic, with predominantly contact and stomach action. Uses Control of soil-dwelling and foliar-feeding insects (including wireworms, white grubs, millipedes, symphylids, frit flies, bean seed flies, root flies, flea beetles, weevils, sciarid flies, aphids, thrips, etc.) and nematodes in vegetables, ornamentals, beet, maize, sorghum, sunflowers, oilseed rape, potatoes, alfalfa, peanuts, soya beans, sugar cane, rice, cotton, coffee, cucurbits, tobacco, lavender, citrus, vines, strawberries, bananas, mushrooms, and other crops. Formulation types FS; GR; SC; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Furadan' (FMC); 'Agrofuran' (Sanonda); 'Carbodan' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Carbosect' (Barclay); 'Carbosip' (Sipcam); 'Cekufuran' (Cequisa); 'Chinufur' (Agro-Chemie); 'Curaterr' (Bayer CropScience); 'Diafuran' (Calliope); 'Furacarb' (Aimco); 'Fury' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Sesame' (Calliope); 'Terrafuran' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Vifuran' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Candor' (Pesticides India); 'Curater' (Bayer CropScience); 'Furan' (Agrochem); 'Pilarfuran' (Pilarquim); 'Reider' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Yaltox' (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Nex' * (Tripart); 'Rampart' * (Sipcam); 'Throttle' * (Quadrangle)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 20; AOAC Methods, 15th Ed., 986.10) or by i.r. spectrometry. Residues determined by glc of a derivative (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 975.40; Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, II; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6; Anal. Methods Residue Pestic., 1988, Part I, M13; R. F. Cooke, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 187; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733) or by rplc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.23). Carbofuran, and its 3-hydroxy metabolite determined in drinking water, by rplc and fluorimetry of liberated methylamine (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.06); for carbofuran phenol and 3-ketocarbofuran phenol, see also AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 992.14. Methods for determination of residues available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 77, 79 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats c. 8, dogs 15, mice 14.4 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 (24 h) for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg; mildly irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats c. 0.075 mg/l air (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 20 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 10 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.002 mg/kg b.w. [1996]. Water GV 7 mg/l (based on ADI). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I ('Furadan 4F'), II ('Furadan G') EC classification T+; R26/28| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 2.5-5 mg/kg. LC50 for Japanese quail 60-240 mg (as GR5)/kg. Tech.: LC50 0.7-8 mg/kg, depending on species. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 22-29 mg (as GR5)/l, bluegill sunfish 1.75 mg (as GR3)/l, golden orfe 107-245 mg (as GR5)/l. Tech.: 7.3-362.5 mg/l, depending on species. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 38.6 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees (except for granular formulation).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals Carbofuran is metabolised by hydrolytic and oxidative mechanisms in the rat. At 24 hours after treatment, 72% of the dose was eliminated in the urine, 2% in the faeces, and about 43% of the administered dose was hydrolysed. Over 95% of the material excreted in the urine was in the form of conjugated metabolites. The major metabolite was conjugated 3-ketocarbofuran phenol,while conjugated 3-hydroxycarbofuran was the predominant carbamate metabolite. Both metabolites were also present in the free form. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants Carbofuran is quickly metabolised into 3-hydroxycarbofuran and ketocarbofuran. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil c. 30-60 d. Most important metabolite is CO2 formed by microbiological degradation of the phenol compounds. Koc 22.
|