|
cyhexatin
Acaricide
IRAC 12B; organotin acaricide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cyhexatin (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA); tricyclohexyltin hydroxide (JMAF)
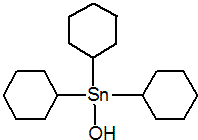
IUPAC name tricyclohexyltin hydroxide
Chemical Abstracts name tricyclohexylhydroxystannane
CAS RN [13121-70-5] EEC no. 236-049-1 Development codes Dowco 213 (Dow) Official codes ENT 27 395-X; OMS 3029
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 385.2 M.f. C18H34OSn Form Colourless crystals. V.p. Negligible (25 ºC) Solubility In water <1 mg/l (25 ºC). In chloroform 216, methanol 37, dichloromethane 34, carbon tetrachloride 28, benzene 16, toluene 10, xylene 3.6, acetone 1.3 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to 100 ºC in aqueous suspensions from slightly acid (pH 6) to alkaline conditions; degraded by u.v. light.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Acaricide reported by W. E. Allison et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1968, 61, 1254). Developed from a joint project of Dow Chemical Co. and M & T Chemicals Inc. and introduced by Dow Chemical Co. (now Dow AgroSciences, who no longer manufacture or market it). Patents US 3264177; US 3389048 Manufacturers Cerexagri; Chemia; Oxon; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation; disruptor of ATP formation. Mode of action Non-systemic acaricide with contact action. Uses Control of the motile stages of a wide range of phytophagous mites (adults and larvae) on pome fruit, stone fruit, vines, hops, nuts, bush fruit, strawberries, vegetables, tomatoes, cucurbits and ornamentals. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to deciduous fruit, vines, vegetables, and outdoor ornamentals. Slight injury (usually in the form of localised spotting) may occur on citrus fruit (particularly developing fruits and immature foliage), and glasshouse ornamentals and vegetables (seedlings and immature foliage). Formulation types SC; WP. Compatibility Should not be applied in combination with wetting agents. Selected products: 'Acarstin' (Sipcam); 'Mitacid' (Sipcam); 'Oxotin' (Oxon); 'Pennstyl' (Cerexagri); 'Sipcatin' (Sipcam)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Aracnol F' (Diachem); 'Triran' (Chemia) Discontinued products: 'Plictran' * (DowElanco)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 46; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 988.02). Residues determined by glc (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, II; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part II; E. Möllhoff, Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1977, 30, 249) or by atomic absorption spectroscopy (J. L. Love & J. E. Patterson, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1978, 61, 627).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 71, 73 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 540, rabbits 500-1000, guinea pigs 780 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Irritating to eyes. NOEL (2 y) for dogs 0.75, mice 3, rats 1 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.007 mg/kg b.w. [1994] (with azocyclotin). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R20/21/22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for chickens 650 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducklings 3189, bobwhite quail 520 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (24 h) for large-mouth bass 0.06, goldfish 0.55 mg/l. Bees Virtually non-hazardous to honeybees (dermal LD50 0.032 mg/bee) at the recommended rates of use. Other beneficial spp. Virtually non-hazardous to most predacious mites and insects at the recommended rates of use.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 15 (WHO 1980). Soil/Environment Dicyclohexyl tin hydroxide, monocyclohexyl tin hydroxide, and inorganic tin compounds are formed as metabolites. Degradation is promoted by u.v. light.
|