|
butralin
Herbicide, plant growth regulator
HRAC K1 WSSA 3; dinitroaniline
NOMENCLATURE
Common name butralin (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); butraline ((f) F-ISO); no name (Eire, Japan)
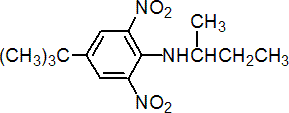
IUPAC name N-sec-butyl-4-tert-butyl-2,6-dinitroaniline
Chemical Abstracts name 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N-(1-methylpropyl)-2,6-dinitrobenzenamine
CAS RN [33629-47-9] EEC no. 251-607-4 Development codes Amchem 70-25; Amchem A-820
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³98% (without xylene). Mol. wt. 295.3 M.f. C14H21N3O4 Form Yellow-orange crystals with a slightly aromatic odour. M.p. 61 ºC; (tech., 59 °C) B.p. 134-136 ºC/0.5 mmHg V.p. 0.77 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.93 (23? °C) Henry 7.58 ´ 10-1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.063 (25 °C) Solubility In water 0.3 mg/l (25 ºC). In ethanol 73, methanol 98, hexane 300 (g/l, 25-26 °C); in dichloroethane 146, benzene 270, acetone 448 (g/100 ml, 24 °C). Stability Decomposes at 265 ºC. Hydrolytically and photochemically stable. Concentrates are stable on storage under dry conditions >3 y, but should not be stored <-5 ºC or allowed to freeze.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by S. R. McLane et al. (Proc. South. Weed Sci. Soc., 1971, 24, 58). Introduced by Amchem Products Inc. (now Bayer CropScience) and later acquired by CFPI (now Nufarm SA). Patents US 3672866 Manufacturers Nufarm SA
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by germinating seedlings, with slow translocation acropetally. Also acts as a growth regulator, suppressing the growth of shoots, branches, and suckers. Uses Pre-emergence control of annual broad-leaved weeds and grasses in cotton, soya beans, rice, barley, beans, alliums, vines, ornamentals, and orchards of fruit and nut trees; used at 1.12-3.4 kg/ha (depending on soil type). Also used to control suckers on tobacco, at 125 mg/plant. Formulation types EC. Compatibility Incompatible with strong oxidising agents. Selected products: 'Tabamex Plus' (Nufarm SA); mixtures: 'Tamex AG' (+ n-decanol) (Bayer CropScience, Nufarm SA)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Amex 820' (Nufarm SA); 'Tabamex' (Nufarm SA); 'Tamex 3' (Bayer CropScience); 'Tobago' (Nufarm SA) mixtures: 'Stifle' (+ maleic hydrazide potassium salt) (Crompton); 'Yellow Ribbon' (+ n-decanol) (SDS Biotech KK, Nufarm Ltd) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Linamex' * (+ linuron) (Nufarm SA, Zeneca)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc using an internal standard.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1170, female rats 1049 mg/kg (tech.). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 (tech.) for rabbits ³2000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to skin, moderately irritating to eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (Magnusson & Kligman and Buehler tests). Inhalation LC50 for rats >9.35 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 500 ppm (20-30 mg/kg daily). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification (Xn; R22, R63)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250, Japanese quail >>5000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >10 000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.0, rainbow trout 0.37 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.12 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.12 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) 95 mg/bee; (contact) 100 mg/bee. Other beneficial spp. Not toxic to soil microflora at usual application rate. Application at 2-10 ´ recommended rate did not significantly alter microbial population.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Extensively metabolised and excreted in urine and faeces. Metabolised in the rat by the primary metabolic processes of N-dealkylation, oxidation and nitro reduction, and by secondary processes of N-acetyl and glucuronic acid conjugation. The majority (85%) of applied butralin was excreted in the urine within 48 h. None was in the organs after 72 h. Butralin is ultimately metabolised to CO2. Soil/Environment In soil, microbial degradation occurs, with formation of the corresponding aniline, ring splitting and evolution of CO2 (P. C. Kearney et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1974, 22, 856). Moderately persistent and relatively immobile in terrestrial environments; field dissipation DT50 >3 weeks (10-72.6 d); in water <10% hydrolysed in 30 days. In terrestrial environments, the main routes of butralin dissipation appear to be dependent on microbial degradation. Strongly adsorbed and not leached; lysimeter studies show little migration of butralin beyond the top 6 cm.
|