|
buprofezin
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 16
NOMENCLATURE
Common name buprofezin (BSI, draft E-ISO); buprofézine ((f) draft F-ISO)
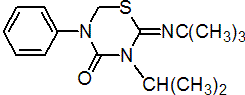
IUPAC name 2-tert-butylimino-3-isopropyl-5-phenyl-1,3,5-thiadiazinan-4-one
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)imino]tetrahydro-3-(1-methylethyl)-5-phenyl-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazin-4-one
CAS RN [69327-76-0] Development codes NNI-750 (Nihon Nohyaku)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 99.1%. Mol. wt. 305.4 M.f. C16H23N3OS Form White crystals; (tech., white or pale yellow crystalline powder). M.p. 104.5-105.5 ºC V.p. 1.25 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.3 Henry 4.24 ´ 10-1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.18 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.9 mg/l (25 ºC). In chloroform 520, benzene 370, toluene 320, acetone 240, ethanol 80, hexane 20 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable in acidic and alkaline media. Stable to heat and light.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by H. Kanno et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1981, 1, 59). Introduced by Nihon Nohyaku Co., Ltd in 1984. Manufacturers Nihon Nohyaku
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Probable chitin synthesis and prostaglandin inhibitor. Hormone disturbing effect, leading to suppression of ecdysis. Mode of action Persistent insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action; not translocated in the plant. Inhibits moulting of nymphs and larvae, leading to death. Also suppresses oviposition by adults; treated insects lay sterile eggs. Uses Insecticide with persistent larvicidal action against Homoptera, some Coleoptera and also Acarina. Effective against Cicadellidae, Deltocephalinae (leafhoppers) and Delphacidae (planthoppers) in rice, at 50-250 g/ha; Cicadellidae (lady beetle) in potatoes; Aleyrodidae (whitefly) in citrus, cotton and vegetables, at 0.025-0.075 g/ha; Coccidae, Diaspididae (scale insects) and Pseudococcidae (mealybugs) in citrus and top fruit, at 25-50 g/hl; Tarsonemidae in vegetables, at 250-500 g/ha. Suitable for IPM programmes. Phytotoxicity Slightly phytotoxic to Chinese cabbage. Formulation types DP; GR; SC; WP. Selected products: 'Applaud' (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Maestro' (Cequisa); 'Profezon' (Vapco); 'Viappla' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Accolade' (Bayer CropScience); 'Geiser' (AFRASA) mixtures: 'Fuji-One Applaud Limber' (+ furametpyr+ isoprothiolane) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Dadeci' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Karapp' * (+ lambda-cyhalothrin) (Zeneca)
ANALYSIS
Product by glc. Residues in soil and rice plants and water, by glc with ECD (M. Uchida et al., J. Pestic. Sci., 7, 397 (1982)); in crops, by glc with NPD (H. Nishizawa et al., J. AOAC International, 77, 1631 (1994)). Details from Nihon Nohyaku.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 86 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2198, female rats 2355, male and female mice >10 000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant (guinea pigs); not irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.57 mg/l air. NOEL for male rats 0.90, female rats 1.12 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg [1999]. Other Non-carcinogenic, non-mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 2.7, rainbow trout >1.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) for D. pulex 50.6 mg/l. Bees No direct effect at 2000 mg/l (WP formulation). Other beneficial spp. No effect on various predators (Euseius stipulatus 250 mg/l; Phytoseiulus persimilis 500 mg/l; Cyrtorhinus lividipennis, Microvelia atrolineata 250 mg/l; Lycosa pseudoannulata 2000 mg/l) or parasites (Aphytis lingnanensis 125 mg/l; Cales noacki, Encarsia formosa, Paracentrobia andoi 250 mg/l; Ephedrus japonicus 1000 mg/l).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Low residues were found in nearly all ruminant and poultry tissues. Extensive metabolism was observed, with a large number of minor metabolites being produced Plants Limited metabolism in most plant species; minor metabolites indicate a pathway involving hydroxylation or oxidative loss of the tert-butyl group, followed by opening of the heterocyclic ring. Soil/Environment DT50 (25 °C) 104 d (flooded conditions, silty clay loam, o.c. 3.8%, pH >6.4), 80 d (upland conditions, sandy loam, o.c. 2.4%, pH 7.0) (J. Pestic. Sci., 11, 605-610 (1986)).
|