|
bupirimate
Fungicide
FRAC 8, A2; pyrimidinol
NOMENCLATURE
Common name bupirimate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
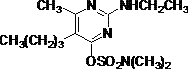
IUPAC name 5-butyl-2-ethylamino-6-methylpyrimidin-4-yl dimethylsulfamate
Chemical Abstracts name 5-butyl-2-(ethylamino)-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl dimethylsulfamate
CAS RN [41483-43-6] Development codes PP588 (ICI)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 90% pure. Mol. wt. 316.4 M.f. C13H24N4O3S Form Pale tan, waxy solid. M.p. 50-51 ºC; (tech., c. 40-45 ºC) V.p. 0.1 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.9 Henry 1.4 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.2 Solubility In water 22 mg/l (pH 5.2, 25 ºC). Soluble in most common organic solvents except paraffins. Stability Stable in dilute alkalis, but readily hydrolysed by dilute acids. Rapidly decomposed by u.v. irradiation in aqueous solution. Unstable on prolonged storage above 37 ºC. F.p. >50 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by J. R. Finney et al. (Proc. Br. Insectic. Fungic. Conf., 8th, 1975, 2, 667). Introduced by ICI Plant Protection Division (became Zeneca Agrochemicals) and first marketed in 1975. Sold to Makhteshim-Agan Industries in 2000. Patents GB 1400710 Manufacturers Makhteshim-Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits adenosine deaminase. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Absorbed by the leaves, with translocation in the xylem and translaminar action. Acts by inhibiting sporulation. Uses Control of powdery mildews of apples, pears, stone fruit, strawberries, gooseberries, currants, raspberries, vines, roses and other ornamentals, cucurbits, hops, beet, and other crops, at 150-375 g/ha. Phytotoxicity Chrysanthemums, roses, strawberries, and some varieties of apple may suffer slight injury. Formulation types EC; WP. Selected products: 'Nimrod' (Makhteshim-Agan)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Nimrod-T' (+ triforine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Oscar' (+ hexaconazole) (Makhteshim-Agan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2007) or by hplc. Identity by glc, tlc, i.r. or nmr (ibid., 1994, F, 406). Residues determined by glc of a derivative. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats, mice, rabbits, and guinea pigs >4000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 4800 mg/kg. Not irritating to eyes and skin. Moderate skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation No effect on rats exposed for 4 h to 0.035 mg respirable particles/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 100 mg/kg diet; (90 d) for rats 1000 mg/kg diet, for dogs 15 mg/kg daily. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification (Xi; R43| N; R51, R53)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail >5200, pigeons >2700 mg/kg. Oral LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >10 000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 7.3 mg/l. Bees NOEL: 0.20 mg/bee (oral); 0.050 mg/bee (contact).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, 68% of the dose is eliminated in the urine within 24 hours; 77% is eliminated in the urine and 21% in the faeces within 10 days. Soil/Environment In soil, the major degradation product is ethirimol. Soil DT50 35-90 d (non-sterile flooded or non-flooded soils, pH 5.1-7.3).
|