|
bromadiolone
Rodenticide
coumarin anticoagulant
NOMENCLATURE
Common name bromadiolone (BSI, E-ISO, (f) F-ISO); broprodifacoum (Republic of South Africa)
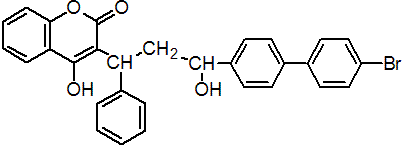
IUPAC name 3-[3-(4'-bromobiphenyl-4-yl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropyl]-4-hydroxycoumarin
Chemical Abstracts name 3-[3-(4'-bromo[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropyl]-4-hydroxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
CAS RN [28772-56-7] unstated stereochemistry Development codes LM 637 (Lipha)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Mixture of two diastereoisomers. Tech. grade bromadiolone is 97% pure. Mol. wt. 527.4 M.f. C30H23BrO4 Form Tech. is a yellowish powder. M.p. 200-210 ºC (mixture of two diastereoisomers) V.p. 0.002 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.27 Henry 5.55 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.5164 Solubility In water 19 mg/l (20 ºC). In dimethylformamide 730, ethyl acetate 25, ethanol 8.2 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Soluble in acetone; slightly soluble in chloroform; practically insoluble in diethyl ether and hexane. Stability Thermally stable below 200 ºC. F.p. 218 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
History Rodenticide reported by M. Grand (Phytiatr. Phytopharm., 1976, 25, 69). Introduced by Lipha S.A. Patents FR 96651; US 3764693; GB 1252088 Manufacturers Bell; Merck Santé; Rallis; Tecomag
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Second-generation anticoagulant rodenticide which also blocks prothrombin formation. Uses Control of rats and mice (including those resistant to warfarin) in areas containing stored products, household use, industrial buildings, and other situations. Formulation types CB; CP; RB. Selected products: 'Aldiol' (Kemio); 'Broma-D' (Trithin); 'Lafar' (Vapco); 'Maki' (LiphaTech Inc.); 'Ratoban' (Rallis); 'Super Caid' (LiphaTech S.A.S)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Endorats Premium' (Irish Drugs); 'Slaymor' (Novartis A H); 'Tomcat 2' (Antec)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 23; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 140). Details available from LiphaTech S.A.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1.125, mice 1.75, rabbits 1.00, dogs >10.0, cats >25.0 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 1.71 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 for male and female rats 0.43 mg/l. NOEL In 90 d feeding trials on rats and dogs, the only effect noted, at 8 mg/kg daily, was reduction in prothrombin rating. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia; EPA (formulation) I
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 138 mg/kg. LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks 110 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.4, bluegill sunfish 3.0 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 2.0 mg/l. Bees Not hazardous to bees when used as directed. Worms LC50 >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Leaching behaviour is inversely related to clay and organic matter content of soils. In soil column and soil layer studies, the proportion of bromadiolone remaining in the top soil layer, using aged loamy sand soil (8.8% clay, 1.05% o.m.) was 97%, with 0.1% in leachate.
|