|
boscalid
Fungicide
FRAC 7, C2; carboxamide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name boscalid (BSI, pa ISO)
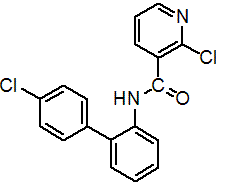
IUPAC name 2-chloro-N-(4'-chlorobiphenyl-2-yl)nicotinamide
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-(4'-chloro[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)-3-pyridinecarboxamide
Other names nicobifen (former provisional ISO name) CAS RN [188425-85-6] Development codes BAS 510 F (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 343.2 M.f. C18H12Cl2N2O Form White odourless crystals. M.p. 142.8-143.8 °C V.p. 7.2 ´ 10-4 mPa KOW logP = 2.96 Henry 5.178 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.381 (20 °C) Solubility In water 4.6 mg/l (20 °C). In n-heptane <10, methanol 40-50, acetone 160-200 (all g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis as pH 4, 5, 7 and 9; stable to aqueous photolysis.
COMMERCIALISATION
Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits succinate ubiquinone reductase, (also known as complex II), in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Mode of action Foliar fungicide. Uses For control of powdery mildew, Alternaria spp., Botrytis spp., Sclerotinia spp. and Monilia spp. on a range of fruit and vegetables. Formulation types WG; SE; SC. Selected products: 'Cantus' (BASF); 'Endura' (BASF); mixtures: 'Signum' (+ pyraclostrobin) (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Bellis' (+ pyraclostrobin) (BASF); 'Collis' (+ kresoxim-methyl) (BASF)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute dermal LD50 >2000 mg/kg; not a skin or eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) >6.7 mg/l. NOEL NOEL for rats ca. 5 mg/kg b.w. ADI 0.04 mg/kg b.w.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg b.w. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 2.7 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 5.33 mg/l Algae ErC50 (96 h) for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata 3.75 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. NOEC for Chironomus riparius 2.0 mg/l. Bees NOEC (oral) 166 µg/bee; (contact) 200 µg/bee. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Hydroxylation of the biphenyl ring, subsequent glucuronidation and sulfatation reactions. The systemically available portion of a.i. is rapidly and extensively metabolised, with rapid excretion, mainly via faeces. Plants Hydroxylation in the biphenyl and pyridine rings, and cleavage reactions in both rings, were observed. However, unchanged parent formed the major part of the residue. Soil/Environment Moderate degradation behaviour in soil; soil DT50 108 d to >1 y (lab., aerobic conditions, 20 °C); field DT50 28 d to ca. 200 d. Good degradation in natural water/sediment systems.
|